What Is Web3? A Complete Overview of the Next Generation Internet
Understanding Web3: The Future of Decentralized Internet
Web3 is rapidly emerging as a transformative concept that promises to reshape how we interact with digital platforms. Unlike the traditional internet, often referred to as Web2, which is dominated by centralized servers and large corporations, Web3 aims to create a more open, user-centric online environment. Built on blockchain technology and decentralized principles, it empowers users with greater control over their data and digital assets. This shift could lead to more secure transactions, transparent interactions, and new economic models like decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
The core idea behind Web3 is decentralization—distributing power away from centralized authorities such as tech giants or governments toward individual users and communities. This approach not only enhances privacy but also reduces reliance on intermediaries that often limit user agency. As a result, Web3 envisions an internet where users are both consumers and owners of their digital identities.
Historical Context: From Blockchain Beginnings to Modern Vision
The roots of Web3 trace back to the inception of blockchain technology with Bitcoin in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin introduced the concept of a peer-to-peer electronic cash system without central authority oversight. Following this breakthrough, numerous projects expanded on blockchain capabilities—Ethereum being one notable example—by enabling programmable contracts known as smart contracts.
Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, popularized the term "Web3" around 2014-2015 during discussions about creating an internet infrastructure that leverages these decentralized systems. His vision was for an online ecosystem where applications operate directly on blockchain networks rather than relying on centralized servers controlled by corporations.
Key Components That Define Web3
Several technological innovations underpin the development of Web3:
- Blockchain Technology: Serves as the foundational ledger ensuring transparency and security for all transactions.
- Decentralization: Data storage across multiple nodes prevents single points of failure or control.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements written into code facilitate automated interactions without intermediaries.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum are integral but extend beyond mere currency—they enable functionalities within decentralized applications.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): Apps built atop blockchain networks that operate without central authority influence.
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Unique digital assets representing ownership rights over art or collectibles in virtual spaces.
These components work together to create an ecosystem where trustless transactions are possible—meaning parties can interact securely without needing mutual trust beforehand.
Recent Developments Shaping Web3 Today
The landscape surrounding Web3 continues evolving at a rapid pace:
Ethereum's Transition to Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum is undergoing a major upgrade aimed at improving scalability through proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms instead of energy-intensive proof-of-work algorithms. This transition seeks to reduce transaction costs significantly while increasing network capacity—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.Growth in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Platforms like Uniswap and Aave have revolutionized financial services by offering lending, borrowing, trading—all executed via smart contracts without traditional banks or brokers involved. DeFi's explosive growth signals growing confidence in decentralized financial systems outside conventional banking frameworks.NFT Market Expansion
Non-fungible tokens have gained popularity among artists, collectors—and even brands—as they provide verifiable ownership over digital art pieces or collectibles stored securely on blockchains like Ethereum or Solana platforms such as OpenSea or Rarible.Regulatory Attention & Challenges
Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrencies and related technologies due to concerns about money laundering risks or consumer protection issues while trying not stifle innovation altogether—a delicate balance shaping policy developments globally.
Potential Risks & Challenges Facing Web3 Adoption
Despite its promising outlooks; several hurdles threaten widespread implementation:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks may hinder growth; overly restrictive policies could suppress innovation.
Scalability Issues: Current blockchain networks face congestion problems when handling large volumes—solutions like layer-two protocols aim to address this but remain under development.
Security Concerns: Smart contract vulnerabilities can be exploited if not properly audited; recent high-profile hacks underscore these risks.
Environmental Impact: Proof-of-work blockchains consume significant energy resources; transitioning towards eco-friendly consensus mechanisms remains vital for sustainability efforts.
How Stakeholders Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
For developers, investors, policymakers—and everyday users—the key lies in understanding these dynamics:
- Stay informed about technological advancements such as layer-two scaling solutions
- Advocate for balanced regulation that fosters innovation while protecting consumers
- Prioritize security measures including thorough audits before deploying smart contracts4.. Support environmentally sustainable practices within blockchain ecosystems5.. Educate oneself about managing private keys safely—the foundation for owning digital assets securely
By proactively engaging with these aspects today; stakeholders can help shape an inclusive web future rooted in decentralization principles aligned with user empowerment and transparency standards.
Exploring How Users Benefit from Moving Toward Decentralization
Web3’s promise extends beyond technological novelty—it offers tangible benefits for everyday internet users:
• Greater Data Privacy & Control – Users own their personal information rather than surrendering it wholesale to corporate entities
• Reduced Censorship – Content moderation becomes more community-driven rather than dictated solely by platform policies
• New Economic Opportunities – Participation in DeFi markets allows earning interest through lending pools; creators can monetize NFTs directly
• Enhanced Security – Distributed ledgers make tampering difficult compared with traditional databases
These advantages highlight why many see web decentralization not just as an upgrade but as a fundamental shift towards empowering individuals online.
Looking Ahead: The Future Trajectory Of Web3 Development
While still nascent compared with established web paradigms; ongoing innovations suggest robust growth potential:
– Continued improvements in scalability solutions will make dApps faster & cheaper
– Broader regulatory clarity could foster safer environments for investment & participation
– Integration across IoT devices might enable truly interconnected decentralized ecosystems
– Increased mainstream adoption driven by enterprise interest—from finance firms adopting DeFi tools—to social media platforms experimenting with NFT integrations
As stakeholders—including developers who build infrastructure,and regulators shaping policy—collaborate effectively; we may witness widespread transformation into what many envision as “the next-generation internet.”


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-15 03:28
What is Web3?
What Is Web3? A Complete Overview of the Next Generation Internet
Understanding Web3: The Future of Decentralized Internet
Web3 is rapidly emerging as a transformative concept that promises to reshape how we interact with digital platforms. Unlike the traditional internet, often referred to as Web2, which is dominated by centralized servers and large corporations, Web3 aims to create a more open, user-centric online environment. Built on blockchain technology and decentralized principles, it empowers users with greater control over their data and digital assets. This shift could lead to more secure transactions, transparent interactions, and new economic models like decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
The core idea behind Web3 is decentralization—distributing power away from centralized authorities such as tech giants or governments toward individual users and communities. This approach not only enhances privacy but also reduces reliance on intermediaries that often limit user agency. As a result, Web3 envisions an internet where users are both consumers and owners of their digital identities.
Historical Context: From Blockchain Beginnings to Modern Vision
The roots of Web3 trace back to the inception of blockchain technology with Bitcoin in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin introduced the concept of a peer-to-peer electronic cash system without central authority oversight. Following this breakthrough, numerous projects expanded on blockchain capabilities—Ethereum being one notable example—by enabling programmable contracts known as smart contracts.
Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, popularized the term "Web3" around 2014-2015 during discussions about creating an internet infrastructure that leverages these decentralized systems. His vision was for an online ecosystem where applications operate directly on blockchain networks rather than relying on centralized servers controlled by corporations.
Key Components That Define Web3
Several technological innovations underpin the development of Web3:
- Blockchain Technology: Serves as the foundational ledger ensuring transparency and security for all transactions.
- Decentralization: Data storage across multiple nodes prevents single points of failure or control.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements written into code facilitate automated interactions without intermediaries.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum are integral but extend beyond mere currency—they enable functionalities within decentralized applications.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): Apps built atop blockchain networks that operate without central authority influence.
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Unique digital assets representing ownership rights over art or collectibles in virtual spaces.
These components work together to create an ecosystem where trustless transactions are possible—meaning parties can interact securely without needing mutual trust beforehand.
Recent Developments Shaping Web3 Today
The landscape surrounding Web3 continues evolving at a rapid pace:
Ethereum's Transition to Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum is undergoing a major upgrade aimed at improving scalability through proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms instead of energy-intensive proof-of-work algorithms. This transition seeks to reduce transaction costs significantly while increasing network capacity—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.Growth in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Platforms like Uniswap and Aave have revolutionized financial services by offering lending, borrowing, trading—all executed via smart contracts without traditional banks or brokers involved. DeFi's explosive growth signals growing confidence in decentralized financial systems outside conventional banking frameworks.NFT Market Expansion
Non-fungible tokens have gained popularity among artists, collectors—and even brands—as they provide verifiable ownership over digital art pieces or collectibles stored securely on blockchains like Ethereum or Solana platforms such as OpenSea or Rarible.Regulatory Attention & Challenges
Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrencies and related technologies due to concerns about money laundering risks or consumer protection issues while trying not stifle innovation altogether—a delicate balance shaping policy developments globally.
Potential Risks & Challenges Facing Web3 Adoption
Despite its promising outlooks; several hurdles threaten widespread implementation:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks may hinder growth; overly restrictive policies could suppress innovation.
Scalability Issues: Current blockchain networks face congestion problems when handling large volumes—solutions like layer-two protocols aim to address this but remain under development.
Security Concerns: Smart contract vulnerabilities can be exploited if not properly audited; recent high-profile hacks underscore these risks.
Environmental Impact: Proof-of-work blockchains consume significant energy resources; transitioning towards eco-friendly consensus mechanisms remains vital for sustainability efforts.
How Stakeholders Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
For developers, investors, policymakers—and everyday users—the key lies in understanding these dynamics:
- Stay informed about technological advancements such as layer-two scaling solutions
- Advocate for balanced regulation that fosters innovation while protecting consumers
- Prioritize security measures including thorough audits before deploying smart contracts4.. Support environmentally sustainable practices within blockchain ecosystems5.. Educate oneself about managing private keys safely—the foundation for owning digital assets securely
By proactively engaging with these aspects today; stakeholders can help shape an inclusive web future rooted in decentralization principles aligned with user empowerment and transparency standards.
Exploring How Users Benefit from Moving Toward Decentralization
Web3’s promise extends beyond technological novelty—it offers tangible benefits for everyday internet users:
• Greater Data Privacy & Control – Users own their personal information rather than surrendering it wholesale to corporate entities
• Reduced Censorship – Content moderation becomes more community-driven rather than dictated solely by platform policies
• New Economic Opportunities – Participation in DeFi markets allows earning interest through lending pools; creators can monetize NFTs directly
• Enhanced Security – Distributed ledgers make tampering difficult compared with traditional databases
These advantages highlight why many see web decentralization not just as an upgrade but as a fundamental shift towards empowering individuals online.
Looking Ahead: The Future Trajectory Of Web3 Development
While still nascent compared with established web paradigms; ongoing innovations suggest robust growth potential:
– Continued improvements in scalability solutions will make dApps faster & cheaper
– Broader regulatory clarity could foster safer environments for investment & participation
– Integration across IoT devices might enable truly interconnected decentralized ecosystems
– Increased mainstream adoption driven by enterprise interest—from finance firms adopting DeFi tools—to social media platforms experimenting with NFT integrations
As stakeholders—including developers who build infrastructure,and regulators shaping policy—collaborate effectively; we may witness widespread transformation into what many envision as “the next-generation internet.”
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The fusion of AI and blockchain is creating a revolutionary new paradigm - moving away from centralized AI controlled by tech giants toward distributed, transparent, and democratic systems. This isn't just theoretical - it's happening now with real-world applications.
🌐 Why Decentralized AI Matters:
-
Breaks Tech Monopolies: Distributes AI models and data across networks instead of centralized control
Transparency & Trust: Blockchain records AI decision-making processes, solving the "black box problem"
Enhanced Security: Eliminates single points of failure - if one node is compromised, the network continues
Data Privacy: Uses federated learning - sensitive data stays on local devices while contributing to global models
💰 Token Economics Drive the Ecosystem:
-
Payment Layer: Users pay for AI services with native tokens
Incentive System: Rewards for providing computing power, training models, and sharing datasets
Governance Rights: Token holders vote on protocol upgrades and funding decisions
Reputation Mechanism: Staking tokens signals data quality and network participation
🔧 Real-World Applications:
-
SingularityNET & Ocean Protocol: Marketplaces for AI services and datasets
Bittensor: Decentralized network rewarding machine learning model contributions
Federated Learning: Training AI models without exposing raw data
Supply Chain Optimization: AI-driven logistics with blockchain verification
🚀 Key Benefits:
-
Democratized Access: Anyone with unused GPU can contribute and earn tokens
Lower Barriers: Transforms AI development from capital-intensive to community-driven
Verifiable AI: Blockchain immutability enables auditable AI decisions
Self-Sustaining Growth: Network effects create powerful flywheel - more participants = stronger network = higher token value
💡 Investment Opportunity: You can invest in this revolution by researching and buying native tokens of leading decentralized AI projects. Always conduct thorough due diligence on whitepapers, teams, and use cases.
Bottom Line: Decentralized AI isn't just about moving computing off central servers - it's building a new economy where AI development is transparent, inclusive, and community-owned. The convergence is already producing tangible solutions across industries.
Read the complete guide on how blockchain and AI are reshaping the future: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/decentralized-ai-combines-blockchain/?utm_source=blog
#DecentralizedAI #Blockchain #AI #Cryptocurrency #Web3


JU Blog
2025-08-16 08:46
🤖 Decentralized AI Combines Blockchain for Secure Systems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Le Genesis Ark de #JuChain lance un fonds de 100 M$ pour propulser vos projets blockchain 💥 ⚡ 1s finalité • ultra-low fees • full EVM compatible
Qui est prêt à builder l’avenir ? 🔥
#JuChain #Web3 #Blockchain



Carmelita
2025-08-15 22:13
📣 Web3 Builders, c’est votre moment !
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🛡 JuCoin101 — Learn how JuCoin protects your assets!👌
✅ Multi-layered security technology:
▪️Multi-signature cold storage technology, 99% of assets are stored offline.
▪️Real-time monitoring system with 24/7 risk warning.
▪️Distributed architecture ensures stable and reliable system.
✅ Leading risk control system:
▪️Experienced team of experts in traditional finance & digital assets.
▪️Intelligent risk control algorithm, real-time abnormal transaction detection.
▪️Comprehensive compliance process, strictly adhere to international security standards.
✅ Trusted by users:
▪️The number of users is constantly increasing, with daily activity leading the industry.
▪️There has never been a user asset security incident.
▪️Community reputation is increasingly consolidated, receiving many positive feedbacks from real users.
✅ 3 times protection fund to ensure user assets:
▪️The fund is managed independently, used for protection purposes only.
▪️Regular public audits with 100% transparency.
▪️Emergency response mechanism to quickly handle unexpected situations.
🎁 Get benefits now >>> https://bit.ly/3ZvWEto
👉 Register JuCoin now: https://bit.ly/3BVxlZ2
#JuCoin #JuCoinVietnam #Crypto #Blockchain #Web3 #Security #RiskControl #CryptoCommunity


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-08-21 07:53
🛡 JuCoin Insights | JuCoin101 — Learn how JuCoin protects your assets!👌
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
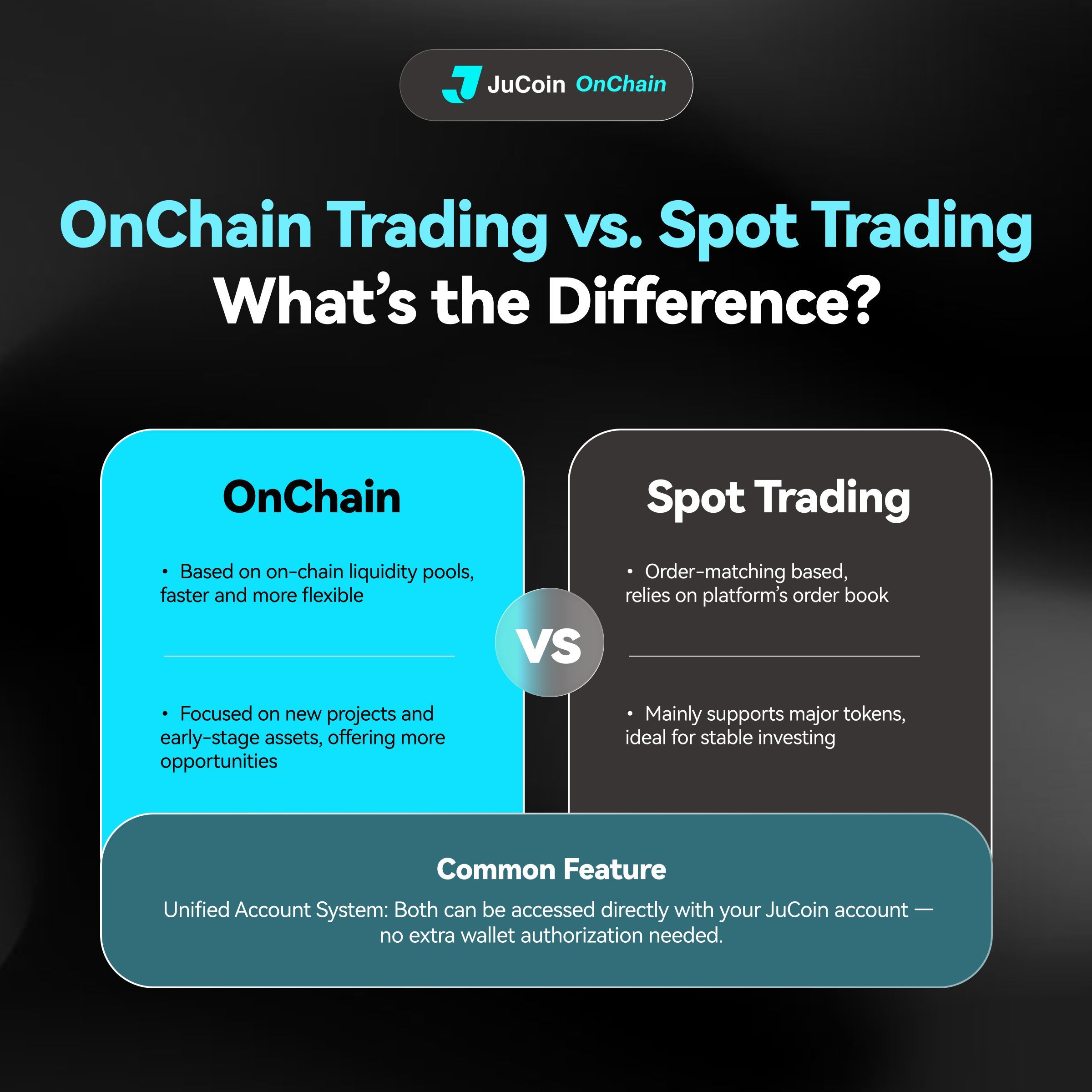
Découvrez OnChain – la façon la plus rapide de trader les nouveaux projets et actifs émergents
✅ Exécution ultra-rapide ✅ Flexibilité maximale ✅ Tradez directement avec votre compte JuCoin – pas de wallet requis
https://www.jucoin.com/en/onchain/ #JuCoin #crypto #Web3 #EarlyAccess


Carmelita
2025-08-21 15:31
Envie de profiter des opportunités en avant-première ?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Start your new week full of energy with the journey of exploring crypto, trading smart and building the future of Web3 today with #JuCoin! 🌱✨
👉 Experience and Register JuCoin now: https://bit.ly/3BVxlZ2
#JuCoin #JucoinVietnam #Crypto #Web3 #Blockchain #Trading


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-08-18 06:30
🌟 GM GM! New Week, New Opportunities with #JuCoin 🚀
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
💡 Idées → déployées en secondes 👤 Utilisateurs → onboarding sans friction 🌱 Croissance → 100M$ pour l’écosystème
Ce n’est pas un rêve, c’est #JuChain aujourd’hui 🚀
Builders, rêveurs, leaders de communautés : Le futur n’attend pas — et vous non plus.
🔗 https://www.juchain.org/en/developer-support #Web3 #crypto #BUIDL #JuChain



Carmelita
2025-08-21 14:49
JuChain Genesis Ark Program
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The blockchain space is fragmented into hundreds of isolated networks - Bitcoin's security, Ethereum's smart contracts, faster chains for low costs. This "silo problem" limits DeFi potential and user experience. Here's why cross-chain connectivity is the future:
🔗 What Is Interoperability:
-
Enables different blockchains to communicate and share data
Allows seamless asset transfers between networks
Creates a unified decentralized ecosystem like the early internet
⚙️ How It Works:
-
Cross-Chain Bridges: Lock assets on one chain, mint wrapped versions on another (like WBTC)
IBC Protocols: Direct message passing between compatible blockchains (Cosmos hub-and-spoke model)
Atomic Swaps: Peer-to-peer exchanges without centralized intermediaries
Oracles: Connect blockchains to external data and other networks
💡 Benefits of Connected Future:
-
Massive liquidity improvement and capital efficiency
Access wider range of services regardless of asset origin
Developers can leverage strengths of multiple chains
Simplified user experience - one wallet, seamless access
⚠️ Current Challenges:
-
Security vulnerabilities (billions lost in bridge exploits)
Complex technical specifications across different chains
Lack of standardized protocols
Single points of failure in cross-chain solutions
🎯 Key Impact: Without interoperability, blockchains remain "walled gardens" limiting innovation. Future solutions like native IBC and atomic swaps promise more secure connectivity, unlocking new use cases and creating the seamless Web3 experience users expect.
The race is on to solve the interoperability puzzle - whoever cracks it will unlock the true potential of a connected blockchain ecosystem.
Read the full deep-dive analysis: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/blockchain-interoperability-why-it-matters/
#Blockchain #Interoperability #CrossChain #DeFi #Web3


JU Blog
2025-08-06 10:43
🌐 Blockchain Interoperability: Breaking Down the Silos!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Ju.com announces a transformational $100 million JuChain Entrepreneurship Fund, marking the official start of its ecosystem expansion era. This fund positions JuChain not just as blockchain infrastructure, but as a complete growth platform integrating capital, technology, and real-world application scenarios.
💰 What This Means:
-
$100M dedicated fund for ecosystem projects
Transformation from exchange to ecosystem builder
Integration of blockchain, exchange, and payment systems into unified roadmap
Focus on real assets (RWA), AI, PayFi, and DeFi applications
Patient capital approach for long-term project development
🎯 Triple-Role Fund Structure:
1️⃣ Accelerator - Complete development path from concept to market: bootcamps, hackathons, MVP support, token economics design, and compliance frameworks
2️⃣ Investment Decision Center - Funding allocations prioritizing technical robustness, business viability, and on-chain/off-chain integration
3️⃣ Resource Orchestrator - Full access to Ju.com's traffic, listing pathways, payment scenarios, brand exposure, and global partner network
🌐 Key Opportunities for Builders:
-
AI Integration: Deploy intelligent trading agents and automated strategies with real liquidity and compliant payment rails
RWA Projects: Tokenize stocks, bonds, and yield rights with built-in compliance expertise
Payment & Consumption: Build seamless bridges between on-chain earnings and real-world utility
DeFi/GameFi/SocialFi: Leverage JuChain's account system for superior UX and composability
🏆 What Ju.com Brings to the Table:
-
Direct user traffic from established exchange platform
Integrated payment system (JuPay, JuCard, xBrokers)
Regulatory compliance frameworks
Global liquidity and listing support
Cross-border payment and settlement infrastructure
💡 Why Now?
-
Base layer competition shifting from performance to real business utility
Market demanding patient capital over short-term subsidy cycles
Convergence of real-world assets and crypto infrastructure
Timing aligned with AI + Crypto fusion and RWA narrative momentum
🎯 Target Ecosystem Profile:
-
Real assets and cash flows anchored on-chain with compliance
Developer-friendly infrastructure with user-invisible complexity
Self-sustaining ecosystem momentum through protocol composability
Bridge between traditional finance and crypto-native innovation
This is not just another blockchain fund announcement - it's a public declaration that JuChain's infrastructure is ready, and the ecosystem growth phase has officially begun. For Web3 builders seeking a committed partner with integrated resources, regulatory clarity, and real user pathways, this represents a new opportunity window worth serious evaluation.
Read the full strategic breakdown and ecosystem vision: 👇 https://blog.ju.com/juchain-100m-fund-ecosystem-growth/?utm_source=blog
#JuChain #Jucom #Web3 #Blockchain



JU Blog
2025-12-06 11:04
JuChain Launches $100M Entrepreneurship Fund - Ecosystem Breakout Year Begins!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
$JU Savings arrive demain ! Ne clignez pas des yeux — saisissez-le. verrouillez-le. faites-le croître. https://jucoin.online/en/accounts/register?ref=USJYGL



Carmelita
2025-09-01 22:54
Tick. Tock.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🔐 Les banques ne pourront plus couper l’accès aux clients légitimes, y compris dans les **actifs numériques**.
#CryptoPolicy #DigitalAssets #Web3




Carmelita
2025-08-07 20:18
🇺🇸 Trump signe un décret interdisant le “debanking politique”.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📍 Sheraton Hong Kong Hotel 🗓 August 27, 2025 | 10:00 – 18:00
Un rendez-vous unique pendant la Bitcoin Asia Summit Week : là où les bâtisseurs, innovateurs et passionnés de crypto s’unissent pour accélérer l’adoption Web3 en Asie. 🌐
👉 Prêt à construire le futur du blockchain avec nous ?
#Web3 #CryptoEvents



Carmelita
2025-08-26 13:17
JuCoin débarque au Snow Crash HK 2025 !
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Web3 Principles Could Reshape the Internet’s Architecture
Understanding Web3 and Its Foundations
Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how the internet operates, moving away from centralized control toward a more decentralized model. Coined by Gavin Wood in 2014, Web3 leverages blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (dApps) to empower users with greater ownership of their data and digital assets. Unlike traditional web models where data is stored on servers controlled by large corporations like Google or Facebook, Web3 distributes data across a network of computers worldwide. This decentralization aims to enhance security, transparency, and user sovereignty.
The core idea behind Web3 is to create an internet that is resilient against censorship and hacking while fostering trustless interactions through cryptography. By integrating blockchain as its backbone—an immutable ledger that records transactions transparently—Web3 ensures data integrity without relying on central authorities.
The Evolution of Internet Architecture: From Web1 to Web3
To appreciate how Web3 could reshape the internet's architecture, it’s essential to understand its historical context:
Web1 (Static Websites): The earliest version of the internet was characterized by static pages with limited interactivity. Users primarily consumed content without contributing much.
Web2 (Dynamic & Social Media): This phase introduced user-generated content through social media platforms like Facebook and YouTube. However, it also led to centralization since these platforms became gatekeepers for online activity.
Web3 (Decentralized & User-Centric): Building upon previous iterations’ limitations, Web3 aims for decentralization using blockchain technology. It shifts control from centralized entities back into users' hands while promoting transparency and security.
This progression reflects a move toward an open web where individuals have more control over their digital identities and assets rather than relying solely on corporate intermediaries.
Key Principles Driving Web3 Innovation
Several foundational principles underpin the potential transformation brought about by Web3:
Decentralization
Data isn’t stored on single servers but distributed across multiple nodes within a network. This structure makes systems more resilient against failures or attacks while reducing reliance on any single authority.
Blockchain Technology
At its core lies blockchain—a distributed ledger that records transactions securely using cryptography. Blockchain ensures data immutability; once information is added, it cannot be altered retroactively without consensus from the network participants.
Smart Contracts
These are self-executing contracts coded directly into blockchain networks that automatically enforce rules when predefined conditions are met. They eliminate intermediaries in processes such as payments or legal agreements—streamlining operations while increasing trustworthiness.
Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Built atop blockchain infrastructure, dApps operate without centralized servers or authorities. They offer services ranging from finance to gaming with increased privacy controls for users.
Recent Developments Shaping the Future of Decentralized Internet
The rapid growth of various projects highlights how close we are to mainstream adoption:
Blockchain Scalability Solutions: Projects like Polkadot, Solana, and Cosmos focus on improving transaction speeds and capacity—addressing one major barrier for widespread use.
Layer 2 Scaling Technologies: Solutions such as Polygon or Optimism process transactions off-chain before settling them onto main chains; this reduces congestion and costs.
Interoperability Protocols: Initiatives like Polkadot enable different blockchains to communicate seamlessly—creating an interconnected ecosystem rather than isolated networks.
In addition to infrastructure advancements:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms like Uniswap facilitate peer-to-peer lending via liquidity pools instead of traditional banks.
NFTs & Digital Ownership: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized art markets by certifying authenticity digitally; they’re also transforming gaming with unique in-game assets owned directly by players.
These innovations demonstrate how decentralized technologies are expanding beyond niche communities into mainstream sectors such as finance, entertainment—and potentially all facets of online interaction.
Challenges Facing Adoption: Regulatory & Environmental Concerns
Despite promising developments, several hurdles threaten widespread implementation:
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based assets creates risks for businesses trying to adopt these technologies legally—and complicates compliance efforts globally.
Security Risks
While blockchains themselves are secure due to cryptographic protocols—they’re not immune from vulnerabilities within smart contracts or exchanges which can be exploited if not properly audited before deployment.
Environmental Impact
Some proof-of-work blockchains consume significant energy resources—for example Bitcoin mining has faced criticism over carbon footprints—which raises questions about sustainability unless greener alternatives emerge (like proof-of-stake mechanisms).
Social Inequality & User Experience
Early adopters tend oftenly be tech-savvy individuals; this digital divide could widen if interfaces remain complex or inaccessible for average users who lack technical expertise—a barrier that needs addressing through better UX design.
How These Principles Could Reshape Internet Infrastructure
By embedding decentralization at every layer—from storage solutions like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) enabling distributed hosting—to identity management systems giving users control over personal credentials—the architecture becomes inherently more robust against censorship attempts or outages caused by server failures alone.
Furthermore:
Data sovereignty shifts back towards individuals rather than corporations controlling vast amounts of personal information.
Trustless interactions reduce dependency on third-party verification services—increasing efficiency across industries such as banking or supply chain management.
As interoperability improves between diverse blockchains via protocols like Polkadot’s relay chain architecture—or Layer 2 solutions facilitating faster transactions—the entire ecosystem becomes more cohesive yet resilient.
Addressing Potential Risks While Embracing Opportunities
For mass adoption beyond niche communities:
- Clearer regulations must evolve alongside technological innovation—to foster innovation while protecting consumers.
- Security audits should become standard practice before deploying smart contracts at scale.
- Sustainable consensus mechanisms need prioritizing—reducing energy consumption associated with certain cryptocurrencies will be critical for environmental sustainability.
- User experience must improve significantly so non-experts can navigate decentralized apps effortlessly—not just developers familiar with crypto wallets.
Final Thoughts: Toward a More Empowered Digital Future
The principles underlying Web3 hold transformative potential—not only redefining how we interact online but also reshaping fundamental aspects such as ownership rights over digital assets and personal identity management within cyberspace itself.. As technological advancements continue accelerating—with scalability improvements making networks faster; interoperability linking disparate chains; regulatory frameworks catching up—it’s clear that embracing these principles could lead us toward an internet built around transparency — empowering individual users rather than consolidating power among few dominant corporations..
Achieving this vision requires collaborative efforts among technologists , regulators , businesses ,and communities committed both innovation AND responsible development ensuring equitable access—and safeguarding privacy along this revolutionary journey toward decentralization.
Note: For those interested in exploring further insights into how these principles might influence future internet architectures—including detailed case studies—the works cited below provide comprehensive analyses rooted in current trends:
- "Web3: The Next Generation of the Internet" by Gavin Wood
- "The Decentralized Internet: How Blockchain Can Change Everything" by Alex Tapscott
- "Blockchain Revolution" by Don Tapscott & Alex Tapscott


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-23 01:23
How could Web3 principles reshape the Internet’s architecture?
How Web3 Principles Could Reshape the Internet’s Architecture
Understanding Web3 and Its Foundations
Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how the internet operates, moving away from centralized control toward a more decentralized model. Coined by Gavin Wood in 2014, Web3 leverages blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (dApps) to empower users with greater ownership of their data and digital assets. Unlike traditional web models where data is stored on servers controlled by large corporations like Google or Facebook, Web3 distributes data across a network of computers worldwide. This decentralization aims to enhance security, transparency, and user sovereignty.
The core idea behind Web3 is to create an internet that is resilient against censorship and hacking while fostering trustless interactions through cryptography. By integrating blockchain as its backbone—an immutable ledger that records transactions transparently—Web3 ensures data integrity without relying on central authorities.
The Evolution of Internet Architecture: From Web1 to Web3
To appreciate how Web3 could reshape the internet's architecture, it’s essential to understand its historical context:
Web1 (Static Websites): The earliest version of the internet was characterized by static pages with limited interactivity. Users primarily consumed content without contributing much.
Web2 (Dynamic & Social Media): This phase introduced user-generated content through social media platforms like Facebook and YouTube. However, it also led to centralization since these platforms became gatekeepers for online activity.
Web3 (Decentralized & User-Centric): Building upon previous iterations’ limitations, Web3 aims for decentralization using blockchain technology. It shifts control from centralized entities back into users' hands while promoting transparency and security.
This progression reflects a move toward an open web where individuals have more control over their digital identities and assets rather than relying solely on corporate intermediaries.
Key Principles Driving Web3 Innovation
Several foundational principles underpin the potential transformation brought about by Web3:
Decentralization
Data isn’t stored on single servers but distributed across multiple nodes within a network. This structure makes systems more resilient against failures or attacks while reducing reliance on any single authority.
Blockchain Technology
At its core lies blockchain—a distributed ledger that records transactions securely using cryptography. Blockchain ensures data immutability; once information is added, it cannot be altered retroactively without consensus from the network participants.
Smart Contracts
These are self-executing contracts coded directly into blockchain networks that automatically enforce rules when predefined conditions are met. They eliminate intermediaries in processes such as payments or legal agreements—streamlining operations while increasing trustworthiness.
Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Built atop blockchain infrastructure, dApps operate without centralized servers or authorities. They offer services ranging from finance to gaming with increased privacy controls for users.
Recent Developments Shaping the Future of Decentralized Internet
The rapid growth of various projects highlights how close we are to mainstream adoption:
Blockchain Scalability Solutions: Projects like Polkadot, Solana, and Cosmos focus on improving transaction speeds and capacity—addressing one major barrier for widespread use.
Layer 2 Scaling Technologies: Solutions such as Polygon or Optimism process transactions off-chain before settling them onto main chains; this reduces congestion and costs.
Interoperability Protocols: Initiatives like Polkadot enable different blockchains to communicate seamlessly—creating an interconnected ecosystem rather than isolated networks.
In addition to infrastructure advancements:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms like Uniswap facilitate peer-to-peer lending via liquidity pools instead of traditional banks.
NFTs & Digital Ownership: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized art markets by certifying authenticity digitally; they’re also transforming gaming with unique in-game assets owned directly by players.
These innovations demonstrate how decentralized technologies are expanding beyond niche communities into mainstream sectors such as finance, entertainment—and potentially all facets of online interaction.
Challenges Facing Adoption: Regulatory & Environmental Concerns
Despite promising developments, several hurdles threaten widespread implementation:
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based assets creates risks for businesses trying to adopt these technologies legally—and complicates compliance efforts globally.
Security Risks
While blockchains themselves are secure due to cryptographic protocols—they’re not immune from vulnerabilities within smart contracts or exchanges which can be exploited if not properly audited before deployment.
Environmental Impact
Some proof-of-work blockchains consume significant energy resources—for example Bitcoin mining has faced criticism over carbon footprints—which raises questions about sustainability unless greener alternatives emerge (like proof-of-stake mechanisms).
Social Inequality & User Experience
Early adopters tend oftenly be tech-savvy individuals; this digital divide could widen if interfaces remain complex or inaccessible for average users who lack technical expertise—a barrier that needs addressing through better UX design.
How These Principles Could Reshape Internet Infrastructure
By embedding decentralization at every layer—from storage solutions like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) enabling distributed hosting—to identity management systems giving users control over personal credentials—the architecture becomes inherently more robust against censorship attempts or outages caused by server failures alone.
Furthermore:
Data sovereignty shifts back towards individuals rather than corporations controlling vast amounts of personal information.
Trustless interactions reduce dependency on third-party verification services—increasing efficiency across industries such as banking or supply chain management.
As interoperability improves between diverse blockchains via protocols like Polkadot’s relay chain architecture—or Layer 2 solutions facilitating faster transactions—the entire ecosystem becomes more cohesive yet resilient.
Addressing Potential Risks While Embracing Opportunities
For mass adoption beyond niche communities:
- Clearer regulations must evolve alongside technological innovation—to foster innovation while protecting consumers.
- Security audits should become standard practice before deploying smart contracts at scale.
- Sustainable consensus mechanisms need prioritizing—reducing energy consumption associated with certain cryptocurrencies will be critical for environmental sustainability.
- User experience must improve significantly so non-experts can navigate decentralized apps effortlessly—not just developers familiar with crypto wallets.
Final Thoughts: Toward a More Empowered Digital Future
The principles underlying Web3 hold transformative potential—not only redefining how we interact online but also reshaping fundamental aspects such as ownership rights over digital assets and personal identity management within cyberspace itself.. As technological advancements continue accelerating—with scalability improvements making networks faster; interoperability linking disparate chains; regulatory frameworks catching up—it’s clear that embracing these principles could lead us toward an internet built around transparency — empowering individual users rather than consolidating power among few dominant corporations..
Achieving this vision requires collaborative efforts among technologists , regulators , businesses ,and communities committed both innovation AND responsible development ensuring equitable access—and safeguarding privacy along this revolutionary journey toward decentralization.
Note: For those interested in exploring further insights into how these principles might influence future internet architectures—including detailed case studies—the works cited below provide comprehensive analyses rooted in current trends:
- "Web3: The Next Generation of the Internet" by Gavin Wood
- "The Decentralized Internet: How Blockchain Can Change Everything" by Alex Tapscott
- "Blockchain Revolution" by Don Tapscott & Alex Tapscott
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Whether you are a user or a developer, your blockchain journey can start super fast:
👤 User: Create wallet → Bridge/Buy → Explore dApps
👨 Developer: Read whitepaper → Get test tokens → Deploy & verify
👉 Explore now: https://juchain.org
JuChain opens up a new world of decentralized applications. 🌐
#JuCoin #JuChain#Blockchain #Crypto #Web3 #DeFi #dApps #Builders #Infrastructure


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-09-05 05:31
📣 Super easy! Get started with #JuChain in just 30 seconds.🚀
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
OptimAI is pioneering a decentralized agentic AI platform powered by a Web3 data network, aiming to put personalized intelligence "on-chain" with user ownership and verifiable attribution. Here's everything you need to know about this revolutionary AI ecosystem:
🎯 What is OptimAI:
-
Decentralized reinforced data network + agentic AI ecosystem
Creates personalized AI agents that "think, plan, and act like you"
Built on OP-Stack L2 + DePIN + reinforced data layer architecture
Emphasizes privacy, attribution, and verifiability for all AI interactions
💡 Core Problems OptimAI Solves:
-
Public data is noisy, private data is hard to access for AI training
Black-box AI systems lack attribution and revenue sharing transparency
Complex agent construction has high barriers to entry
Users lack ownership and control over their AI interactions
🔧 Technical Architecture:
-
OP-Stack L2 & DePIN: EVM-compatible blockchain with decentralized compute/storage nodes
Browser Nodes: Convert web activity into anonymizable data streams (GDPR/CCPA compliant)
Reinforced Data Layer: Combines RLHF with human validation for high-quality training data
Agentic AI Platform: "Digital twin" agents created from user's own data
💰 OPI Token Utility:
-
Incentives: Rewards for running nodes, data validation, and labeling
Transactions: Settlement for models, compute, and data services
Governance: Voting rights and staking for network security
Value capture through settlement demand and network participation
📊 Current Ecosystem Metrics:
-
14k+ to 300k+ users (varying reports - check latest official figures)
100M+ data requests processed
150+ countries with active participation
Multiple node types: Lite/Core/Edge/Browser/Telegram nodes
🚀 Key Features:
-
Agent OS/Studio/Store for easy agent creation
SDK and APIs for developers
Marketplace for trading datasets, models, and compute services
Privacy-preserving computation with local processing
Cross-domain data licensing and compliance frameworks
🛣️ Roadmap Highlights:
-
Enhanced node infrastructure and settlement mechanisms
Expanded data validation coverage
Full Marketplace and GenAI platform launch
Cross-regional "user-owned AI" implementation
Integration with industry AI standards and frameworks
🌟 Unique Value Proposition: Unlike traditional AI platforms, OptimAI puts users in control of their data and AI agents while ensuring every interaction is verifiable, auditable, and revenue-sharing enabled through blockchain technology.
OptimAI represents the convergence of Web3 infrastructure with cutting-edge AI, creating a new paradigm where users truly own their digital intelligence!
Read the complete technical analysis: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/optimai-web3-data-layer-agentic/?utm_source=blog
#OptimAI #AgenticAI #Web3 #DePIN


JU Blog
2025-08-30 12:47
OptimAI Research: Web3 Data Layer & Agentic AI Systems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Web3 and How Does It Shape the Future of the Internet?
Understanding Web3 in the Context of Internet Evolution
Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with online platforms, data, and digital assets. To grasp its significance, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader history of the internet. The first generation, Web1, was characterized by static web pages where users primarily consumed content without much interaction. This era laid the groundwork for information sharing but lacked dynamic features.
The subsequent phase, Web2, introduced interactivity through social media platforms, e-commerce sites, and user-generated content. While this era empowered users to create and share content easily, it also led to increased centralization. Major corporations like Google, Facebook, and Amazon now control vast amounts of user data—raising concerns about privacy and monopolistic practices.
Web3 aims to address these issues by decentralizing control over data and digital interactions. Instead of relying on centralized servers or entities that hold user information hostage for profit or control purposes, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to distribute data across multiple nodes globally. This transition promises a more transparent internet where users have greater ownership over their digital identities.
Core Components Defining Web3
Several key technologies underpin the concept of Web3:
- Blockchain Technology: Acts as a decentralized ledger ensuring transparency and security for transactions.
- Decentralization: Data is stored across numerous nodes rather than on centralized servers—reducing reliance on single points of failure.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code facilitate trustless transactions without intermediaries.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) serve as mediums for value transfer within decentralized ecosystems.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): These applications run on blockchain networks instead of traditional servers; they include social media platforms, gaming environments, financial services (DeFi), NFTs marketplaces—and more.
Recent Innovations Accelerating Web3 Adoption
The development landscape around Web3 is rapidly evolving with several notable advancements:
Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade – Transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum aims to improve scalability while reducing energy consumption—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.
Interoperability Protocols like Polkadot & Cosmos – These projects enable different blockchains to communicate seamlessly—creating an interconnected ecosystem that enhances functionality beyond isolated networks.
NFTs Transforming Digital Ownership – Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized how creators monetize art by providing verifiable ownership rights for unique digital assets such as artwork or music files.
Growth in Decentralized Finance Platforms – DeFi protocols like Aave or Compound facilitate lending/borrowing without traditional banks—offering greater financial inclusion globally.
Regulatory Developments & Challenges – Governments worldwide are beginning to craft policies around cryptocurrencies and blockchain use cases; some embrace innovation while others impose restrictions due to concerns over fraud or money laundering.
Potential Challenges Facing Web3 Implementation
Despite its promising outlooks, several hurdles could impede widespread adoption:
Scalability remains a concern; as user numbers grow exponentially across decentralized networks—including high transaction fees during peak times—performance bottlenecks may emerge.
Security vulnerabilities persist despite blockchain's inherent robustness; smart contract bugs or malicious attacks can lead to significant losses if not properly managed.
Regulatory uncertainty creates ambiguity around compliance requirements which can deter institutional investment or mainstream acceptance.
User experience needs improvement; complex interfaces currently hinder mass adoption compared with familiar centralized apps that prioritize ease-of-use.
How Stakeholders Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
For developers, investors—and everyday users—the key lies in understanding both opportunities and risks associated with this new paradigm shift:
• Emphasize building intuitive interfaces that lower barriers for non-expert users• Prioritize security audits when deploying smart contracts• Stay informed about evolving legal frameworks affecting cryptocurrencies• Support interoperability initiatives enabling seamless cross-chain interactions• Promote education about decentralization benefits versus potential pitfalls
By proactively engaging with these aspects today—including participating in community discussions—they can help shape an inclusive ecosystem aligned with principles of transparency and fairness inherent in blockchain technology.
The Role of Trustworthiness & Expertise in Navigating Web3's Landscape
As an emerging field driven by cutting-edge innovations—from smart contracts securing automated agreements—to complex regulatory debates—it’s vital that stakeholders rely on credible sources backed by technical expertise when making decisions related to investments or development strategies within this space.
This emphasis on trustworthiness aligns closely with E-A-T principles—Expertise Authority Trust—which are crucial not only for creating reliable content but also fostering confidence among participants navigating uncharted territories like decentralized finance markets or NFT ecosystems.
Exploring How Blockchain Enables Decentralization
At its core, blockchain technology facilitates decentralization through distributed ledgers maintained collectively rather than controlled centrally by one authority entity such as a corporation or government agency. Each transaction recorded is immutable once validated via consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW). This setup ensures transparency since all participants have access rights while preventing tampering—a foundational element supporting trustless systems integral to many dApps operating within the web 3 environment.
Impacts on Privacy & Data Ownership
One significant advantage offered by Web3 involves giving individuals more control over their personal data—notably contrasting sharply against current models where large tech firms harvest user information extensively without explicit consent—or monetize it unfairly through targeted advertising strategies.
In practice:
- Users can manage their identity credentials securely using cryptographic keys,
- Selectively share specific pieces of personal info,
- Participate directly in economic activities via token-based incentives—all fostering greater privacy protections.
Future Outlook & Strategic Considerations
While promising substantial benefits—including democratizing access to financial services via DeFi platforms—the path forward requires addressing persistent challenges such as scalability issues during network congestion periods alongside developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks compatible across jurisdictions worldwide.
Stakeholders should consider investing resources into research-and-development efforts focused on improving network efficiency while advocating policies promoting innovation balanced against consumer protection standards.
By embracing collaboration among technologists regulators—and end-users—the transition toward a truly decentralized internet could redefine our digital lives profoundly over coming years.
Summary
Web3 signifies more than just technological upgrades—it embodies a philosophical shift towards empowering individuals through decentralization while fostering open access innovation rooted in blockchain's secure infrastructure.
This evolution promises enhanced privacy controls—as well as new economic models enabled through token economies—but also necessitates careful navigation around security vulnerabilities and regulatory landscapes.
As awareness grows among developers—and consumers alike—the trajectory suggests an increasingly democratized internet landscape poised at transforming how we create value online.
Note: For those interested in exploring further topics related specifically to blockchain development, cryptocurrency regulation, NFT markets, DeFi protocols, interoperability solutions, additional resources are available from leading industry organizations specializing in these areas


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 07:23
What is the concept of "Web3" in the broader internet landscape?
What Is Web3 and How Does It Shape the Future of the Internet?
Understanding Web3 in the Context of Internet Evolution
Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with online platforms, data, and digital assets. To grasp its significance, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader history of the internet. The first generation, Web1, was characterized by static web pages where users primarily consumed content without much interaction. This era laid the groundwork for information sharing but lacked dynamic features.
The subsequent phase, Web2, introduced interactivity through social media platforms, e-commerce sites, and user-generated content. While this era empowered users to create and share content easily, it also led to increased centralization. Major corporations like Google, Facebook, and Amazon now control vast amounts of user data—raising concerns about privacy and monopolistic practices.
Web3 aims to address these issues by decentralizing control over data and digital interactions. Instead of relying on centralized servers or entities that hold user information hostage for profit or control purposes, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to distribute data across multiple nodes globally. This transition promises a more transparent internet where users have greater ownership over their digital identities.
Core Components Defining Web3
Several key technologies underpin the concept of Web3:
- Blockchain Technology: Acts as a decentralized ledger ensuring transparency and security for transactions.
- Decentralization: Data is stored across numerous nodes rather than on centralized servers—reducing reliance on single points of failure.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code facilitate trustless transactions without intermediaries.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) serve as mediums for value transfer within decentralized ecosystems.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): These applications run on blockchain networks instead of traditional servers; they include social media platforms, gaming environments, financial services (DeFi), NFTs marketplaces—and more.
Recent Innovations Accelerating Web3 Adoption
The development landscape around Web3 is rapidly evolving with several notable advancements:
Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade – Transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum aims to improve scalability while reducing energy consumption—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.
Interoperability Protocols like Polkadot & Cosmos – These projects enable different blockchains to communicate seamlessly—creating an interconnected ecosystem that enhances functionality beyond isolated networks.
NFTs Transforming Digital Ownership – Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized how creators monetize art by providing verifiable ownership rights for unique digital assets such as artwork or music files.
Growth in Decentralized Finance Platforms – DeFi protocols like Aave or Compound facilitate lending/borrowing without traditional banks—offering greater financial inclusion globally.
Regulatory Developments & Challenges – Governments worldwide are beginning to craft policies around cryptocurrencies and blockchain use cases; some embrace innovation while others impose restrictions due to concerns over fraud or money laundering.
Potential Challenges Facing Web3 Implementation
Despite its promising outlooks, several hurdles could impede widespread adoption:
Scalability remains a concern; as user numbers grow exponentially across decentralized networks—including high transaction fees during peak times—performance bottlenecks may emerge.
Security vulnerabilities persist despite blockchain's inherent robustness; smart contract bugs or malicious attacks can lead to significant losses if not properly managed.
Regulatory uncertainty creates ambiguity around compliance requirements which can deter institutional investment or mainstream acceptance.
User experience needs improvement; complex interfaces currently hinder mass adoption compared with familiar centralized apps that prioritize ease-of-use.
How Stakeholders Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
For developers, investors—and everyday users—the key lies in understanding both opportunities and risks associated with this new paradigm shift:
• Emphasize building intuitive interfaces that lower barriers for non-expert users• Prioritize security audits when deploying smart contracts• Stay informed about evolving legal frameworks affecting cryptocurrencies• Support interoperability initiatives enabling seamless cross-chain interactions• Promote education about decentralization benefits versus potential pitfalls
By proactively engaging with these aspects today—including participating in community discussions—they can help shape an inclusive ecosystem aligned with principles of transparency and fairness inherent in blockchain technology.
The Role of Trustworthiness & Expertise in Navigating Web3's Landscape
As an emerging field driven by cutting-edge innovations—from smart contracts securing automated agreements—to complex regulatory debates—it’s vital that stakeholders rely on credible sources backed by technical expertise when making decisions related to investments or development strategies within this space.
This emphasis on trustworthiness aligns closely with E-A-T principles—Expertise Authority Trust—which are crucial not only for creating reliable content but also fostering confidence among participants navigating uncharted territories like decentralized finance markets or NFT ecosystems.
Exploring How Blockchain Enables Decentralization
At its core, blockchain technology facilitates decentralization through distributed ledgers maintained collectively rather than controlled centrally by one authority entity such as a corporation or government agency. Each transaction recorded is immutable once validated via consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW). This setup ensures transparency since all participants have access rights while preventing tampering—a foundational element supporting trustless systems integral to many dApps operating within the web 3 environment.
Impacts on Privacy & Data Ownership
One significant advantage offered by Web3 involves giving individuals more control over their personal data—notably contrasting sharply against current models where large tech firms harvest user information extensively without explicit consent—or monetize it unfairly through targeted advertising strategies.
In practice:
- Users can manage their identity credentials securely using cryptographic keys,
- Selectively share specific pieces of personal info,
- Participate directly in economic activities via token-based incentives—all fostering greater privacy protections.
Future Outlook & Strategic Considerations
While promising substantial benefits—including democratizing access to financial services via DeFi platforms—the path forward requires addressing persistent challenges such as scalability issues during network congestion periods alongside developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks compatible across jurisdictions worldwide.
Stakeholders should consider investing resources into research-and-development efforts focused on improving network efficiency while advocating policies promoting innovation balanced against consumer protection standards.
By embracing collaboration among technologists regulators—and end-users—the transition toward a truly decentralized internet could redefine our digital lives profoundly over coming years.
Summary
Web3 signifies more than just technological upgrades—it embodies a philosophical shift towards empowering individuals through decentralization while fostering open access innovation rooted in blockchain's secure infrastructure.
This evolution promises enhanced privacy controls—as well as new economic models enabled through token economies—but also necessitates careful navigation around security vulnerabilities and regulatory landscapes.
As awareness grows among developers—and consumers alike—the trajectory suggests an increasingly democratized internet landscape poised at transforming how we create value online.
Note: For those interested in exploring further topics related specifically to blockchain development, cryptocurrency regulation, NFT markets, DeFi protocols, interoperability solutions, additional resources are available from leading industry organizations specializing in these areas
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Web3: Unlocking the Future of the Internet
Understanding Web3 and Its Potential
Web3 is often described as the next evolution of the internet, promising a more decentralized, transparent, and user-centric digital landscape. Coined by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to fundamentally change how data is stored, shared, and controlled online. Unlike its predecessors—Web1 (static content) and Web2 (interactive platforms)—Web3 aims to empower users with ownership over their digital identities and assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
This shift is driven by advancements in blockchain technology that enable secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate processes and enforce agreements automatically once predefined conditions are met. As a result, Web3 has the potential to redefine online interactions across sectors such as finance, social media, gaming, art, and real estate.
The Evolution from Web1 to Web3
The internet's journey began with static web pages where users primarily consumed content without much interaction. This era was characterized by limited user engagement but offered broad accessibility. The advent of Web2 introduced dynamic content through social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter alongside e-commerce giants such as Amazon. While this era fostered unprecedented connectivity and innovation—enabling sharing of information at scale—it also concentrated power within large corporations that control vast amounts of user data.
Recognizing these issues has fueled interest in decentralization principles underpinning Web3. By distributing data across multiple nodes rather than central servers—and utilizing blockchain for transparency—Web3 seeks to address privacy concerns while giving users more control over their personal information.
Key Technologies Powering Web3
Blockchain Technology: At its core lies distributed ledger technology that ensures security through cryptography while maintaining transparency via public transaction records. Once data enters a blockchain network—such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—it becomes immutable; it cannot be altered or erased later.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing code snippets embedded within blockchains that facilitate automatic transactions based on predetermined rules without human intervention. They reduce reliance on intermediaries like banks or legal entities for executing agreements securely.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Built atop blockchain networks, dApps operate without centralized servers—they run on peer-to-peer networks ensuring resilience against censorship or shutdowns.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms recreate traditional financial services such as lending or trading using smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum; they aim to democratize access to financial tools globally.
NFTs & Digital Assets: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized ownership rights for digital art collectibles but also extend into domains like virtual real estate or gaming assets—all secured via blockchain’s transparency features.
Opportunities Presented by Web3
Enhanced User Control & Privacy
One significant advantage of Web3 is empowering individuals with ownership over their personal data through decentralized identity solutions (DIDs). Users can decide what information they share—and with whom—reducing risks associated with centralized databases prone to breaches. This shift fosters greater trust between users and service providers because transactions are transparent yet privacy-preserving when designed correctly.
Financial Inclusion & Innovation
DeFi applications eliminate barriers posed by traditional banking systems—especially in underserved regions—by providing accessible financial services via smartphones connected directly to blockchain networks. This democratization could lead toward broader economic participation worldwide while fostering innovative business models built around token economies or microtransactions.
Content Ownership & Monetization Opportunities
NFTs enable creators—from artists to musicians—to monetize their work directly without intermediaries like galleries or record labels. Blockchain’s provenance tracking assures buyers about authenticity while enabling new revenue streams through royalties embedded into smart contracts—a game-changer for creative industries adapting to digital transformation trends.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite its promise, several hurdles remain before full-scale adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications—which can create legal ambiguities affecting innovation timelines.Scalability Issues: Current blockchain infrastructure faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs; solutions like layer-2 scaling protocols are under development but not yet universally adopted.Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities have led to notable exploits causing significant financial losses; rigorous auditing practices are essential.Digital Divide Concerns
While decentralization offers empowerment opportunities globally—including in developing nations—the technological complexity might widen existing inequalities if access remains limited due to infrastructure gaps or lack of technical literacy among certain populations.Environmental Impact Considerations
Some consensus mechanisms used in popular blockchains consume substantial energy—for example proof-of-work systems—which raises sustainability questions amid growing environmental awareness.Moving Toward Mainstream Adoption
To realize the full potential of Web3:
- Infrastructure must become more scalable—with faster transaction speeds at lower costs.
- Clearer regulatory frameworks should be established globally—to foster innovation while protecting consumers.
- Education initiatives need expansion—to bridge knowledge gaps among general users unfamiliar with complex technologies involved.
- Sustainable consensus mechanisms should be prioritized—to minimize environmental footprints associated with network maintenance efforts.
How Businesses Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
Organizations aiming for future-proof strategies should consider integrating decentralized principles into their operations gradually:
- Explore partnerships within the crypto ecosystem—for example, adopting NFT-based loyalty programs.
- Invest in employee training focused on understanding blockchain fundamentals.
- Develop pilot projects leveraging smart contracts for supply chain management or payments processing.
- Stay informed about evolving regulations impacting digital assets.
The Role of Regulation in Shaping Wepb’s Future
Regulatory clarity will play a pivotal role in determining how quickly mainstream adoption occurs—and whether innovations flourish sustainably within legal boundaries. Governments worldwide are balancing fostering innovation against consumer protection concerns; some have embraced cryptocurrencies openly whereas others impose restrictions due diligence measures which could influence market growth trajectories.
Final Thoughts
Web3 holds transformative potential across multiple sectors—from redefining ownership rights through NFTs to creating inclusive financial ecosystems via DeFi platforms—all built upon robust security features inherent in blockchain technology. However—as it stands—the path forward requires addressing scalability challenges、regulatory uncertainties、security vulnerabilities、and social equity considerations。 By proactively tackling these issues—with collaboration among technologists、 policymakers、and communities—the vision of an open、transparent,and user-controlled internet can become reality.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 09:40
What potential does Web3 have for the future of the internet?
Web3: Unlocking the Future of the Internet
Understanding Web3 and Its Potential
Web3 is often described as the next evolution of the internet, promising a more decentralized, transparent, and user-centric digital landscape. Coined by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to fundamentally change how data is stored, shared, and controlled online. Unlike its predecessors—Web1 (static content) and Web2 (interactive platforms)—Web3 aims to empower users with ownership over their digital identities and assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
This shift is driven by advancements in blockchain technology that enable secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate processes and enforce agreements automatically once predefined conditions are met. As a result, Web3 has the potential to redefine online interactions across sectors such as finance, social media, gaming, art, and real estate.
The Evolution from Web1 to Web3
The internet's journey began with static web pages where users primarily consumed content without much interaction. This era was characterized by limited user engagement but offered broad accessibility. The advent of Web2 introduced dynamic content through social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter alongside e-commerce giants such as Amazon. While this era fostered unprecedented connectivity and innovation—enabling sharing of information at scale—it also concentrated power within large corporations that control vast amounts of user data.
Recognizing these issues has fueled interest in decentralization principles underpinning Web3. By distributing data across multiple nodes rather than central servers—and utilizing blockchain for transparency—Web3 seeks to address privacy concerns while giving users more control over their personal information.
Key Technologies Powering Web3
Blockchain Technology: At its core lies distributed ledger technology that ensures security through cryptography while maintaining transparency via public transaction records. Once data enters a blockchain network—such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—it becomes immutable; it cannot be altered or erased later.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing code snippets embedded within blockchains that facilitate automatic transactions based on predetermined rules without human intervention. They reduce reliance on intermediaries like banks or legal entities for executing agreements securely.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Built atop blockchain networks, dApps operate without centralized servers—they run on peer-to-peer networks ensuring resilience against censorship or shutdowns.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms recreate traditional financial services such as lending or trading using smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum; they aim to democratize access to financial tools globally.
NFTs & Digital Assets: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized ownership rights for digital art collectibles but also extend into domains like virtual real estate or gaming assets—all secured via blockchain’s transparency features.
Opportunities Presented by Web3
Enhanced User Control & Privacy
One significant advantage of Web3 is empowering individuals with ownership over their personal data through decentralized identity solutions (DIDs). Users can decide what information they share—and with whom—reducing risks associated with centralized databases prone to breaches. This shift fosters greater trust between users and service providers because transactions are transparent yet privacy-preserving when designed correctly.
Financial Inclusion & Innovation
DeFi applications eliminate barriers posed by traditional banking systems—especially in underserved regions—by providing accessible financial services via smartphones connected directly to blockchain networks. This democratization could lead toward broader economic participation worldwide while fostering innovative business models built around token economies or microtransactions.
Content Ownership & Monetization Opportunities
NFTs enable creators—from artists to musicians—to monetize their work directly without intermediaries like galleries or record labels. Blockchain’s provenance tracking assures buyers about authenticity while enabling new revenue streams through royalties embedded into smart contracts—a game-changer for creative industries adapting to digital transformation trends.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite its promise, several hurdles remain before full-scale adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications—which can create legal ambiguities affecting innovation timelines.Scalability Issues: Current blockchain infrastructure faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs; solutions like layer-2 scaling protocols are under development but not yet universally adopted.Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities have led to notable exploits causing significant financial losses; rigorous auditing practices are essential.Digital Divide Concerns
While decentralization offers empowerment opportunities globally—including in developing nations—the technological complexity might widen existing inequalities if access remains limited due to infrastructure gaps or lack of technical literacy among certain populations.Environmental Impact Considerations
Some consensus mechanisms used in popular blockchains consume substantial energy—for example proof-of-work systems—which raises sustainability questions amid growing environmental awareness.Moving Toward Mainstream Adoption
To realize the full potential of Web3:
- Infrastructure must become more scalable—with faster transaction speeds at lower costs.
- Clearer regulatory frameworks should be established globally—to foster innovation while protecting consumers.
- Education initiatives need expansion—to bridge knowledge gaps among general users unfamiliar with complex technologies involved.
- Sustainable consensus mechanisms should be prioritized—to minimize environmental footprints associated with network maintenance efforts.
How Businesses Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
Organizations aiming for future-proof strategies should consider integrating decentralized principles into their operations gradually:
- Explore partnerships within the crypto ecosystem—for example, adopting NFT-based loyalty programs.
- Invest in employee training focused on understanding blockchain fundamentals.
- Develop pilot projects leveraging smart contracts for supply chain management or payments processing.
- Stay informed about evolving regulations impacting digital assets.
The Role of Regulation in Shaping Wepb’s Future
Regulatory clarity will play a pivotal role in determining how quickly mainstream adoption occurs—and whether innovations flourish sustainably within legal boundaries. Governments worldwide are balancing fostering innovation against consumer protection concerns; some have embraced cryptocurrencies openly whereas others impose restrictions due diligence measures which could influence market growth trajectories.
Final Thoughts
Web3 holds transformative potential across multiple sectors—from redefining ownership rights through NFTs to creating inclusive financial ecosystems via DeFi platforms—all built upon robust security features inherent in blockchain technology. However—as it stands—the path forward requires addressing scalability challenges、regulatory uncertainties、security vulnerabilities、and social equity considerations。 By proactively tackling these issues—with collaboration among technologists、 policymakers、and communities—the vision of an open、transparent,and user-controlled internet can become reality.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Decentralized Identity (DID) and Why Is It Important?
Understanding Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized Identity, commonly known as DID, is transforming how individuals manage their digital identities. Unlike traditional systems where personal data is stored and controlled by centralized authorities such as governments or corporations, DID empowers users with full control over their identity information. This shift aims to enhance privacy, security, and user autonomy in the digital landscape.
At its core, DID leverages blockchain technology to create a secure and tamper-proof framework for managing identities. Individuals generate cryptographic keys that serve as their digital credentials. These keys enable them to authenticate themselves across various platforms without relying on third-party providers. The system also utilizes decentralized storage solutions—such as blockchain networks—to store identity data securely while maintaining user sovereignty.
Key Components of Decentralized Identity
Decentralized identity systems are built around several essential elements:
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Users have complete ownership of their identity data without dependence on external authorities.
- Decentralized Storage: Instead of centralized servers, identity information resides on distributed ledgers or peer-to-peer networks.
- Cryptographic Keys: Unique cryptographic pairs (public/private keys) facilitate secure authentication and verification processes.
This architecture ensures that users can selectively share verified parts of their identities—like age or citizenship—without exposing unnecessary personal details.
Historical Context and Development
The concept of decentralized identity has been evolving over the past decade. Its roots trace back to early efforts by organizations like the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which began exploring standards for digital identities around 2015. By 2017, W3C published the first specifications for DIDs—a significant milestone that laid the groundwork for interoperability across different platforms.
Blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in this evolution by providing an immutable ledger where all transactions related to identity creation or updates are recorded transparently yet securely. This foundation supports trustless verification mechanisms vital for decentralized ecosystems like Web3.
DID’s Role in Blockchain Ecosystems
Blockchain's inherent features—such as decentralization, transparency, and security—make it an ideal backbone for DID solutions. These attributes allow individuals to maintain control over their identities without relying on central authorities prone to breaches or misuse of data.
In addition to providing a secure infrastructure, blockchain enables functionalities like:
- Immutable Record-Keeping: Ensures all changes or updates are permanently logged.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Guarantee agreement among network nodes about the current state of an individual's identity data.
Furthermore, integration with smart contracts enhances automation capabilities—for example, automatically verifying credentials when certain conditions are met within decentralized applications (dApps).
Why Decentralized Identity Matters Today
The significance of DID extends beyond technical innovation; it addresses pressing concerns related to privacy rights and data security in our increasingly digital world.
Enhanced Privacy & Security
Traditional online services often require users to surrender large amounts of personal information stored centrally—a tempting target for hackers. In contrast, DID allows users granular control over what they share at any given moment through selective disclosure techniques. Cryptographic protections further safeguard against unauthorized access or impersonation attempts.
User Autonomy & Data Portability
With self-sovereign identities, individuals can seamlessly carry their verified credentials across multiple platforms without repeated registration processes. This portability reduces friction while empowering users with greater agency over their online presence.
Compliance & Regulatory Challenges
As governments worldwide implement stricter data protection laws such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California—and future regulations emerge—the adoption of decentralized IDs could facilitate compliance by minimizing unnecessary data collection while ensuring verifiable proof-of-identity mechanisms remain intact.
Recent Advances in Decentralized Identity Technology
Over recent years, several projects have advanced practical implementations that bring DID closer to mainstream adoption:
W3C Standards Development
The World Wide Web Consortium continues refining standards; its latest version from 2020 provides comprehensive guidelines ensuring interoperability between different implementations globally.
Industry Adoption
- Uport: An early pioneer offering portable digital identities built atop Ethereum-based infrastructure.
- Microsoft ION: A scalable solution integrated into Azure Active Directory designed specifically for enterprise use cases.
- Polkadot’s DIM: A modular approach allowing developers flexibility within multi-chain environments focused on secure ID management.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite promising progress—and growing interest from both private sector entities and governments—the path toward widespread deployment faces hurdles:
Scalability Concerns
Blockchain networks still grapple with transaction throughput limitations which could hinder large-scale use cases involving millions of identities simultaneously.
Regulatory Uncertainty
As regulatory frameworks evolve differently across jurisdictions regarding privacy rights and biometric verification methods—which may conflict with decentralization principles—it becomes challenging for organizations seeking compliance without compromising user sovereignty.
Looking Ahead: Opportunities & Considerations
The future trajectory suggests continued innovation driven by technological advances such as layer-two scaling solutions (e.g., rollups), zero-knowledge proofs enhancing privacy guarantees—and increasing collaboration among industry stakeholders aiming at standardization efforts led by bodies like W3C will be crucial.
For individuals interested in adopting decentralized IDs today—or organizations considering integration—the key lies in understanding both benefits: enhanced control over personal data; improved security; seamless cross-platform experiences—and challenges: scalability issues; regulatory compliance complexities.
By embracing these emerging technologies thoughtfully—with attention toward ethical considerations—they can significantly reshape how we verify our identities online while safeguarding fundamental rights.
Key Milestones Timeline
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2015 | W3C begins exploring standards for decentralized identifiers |
| 2017 | First official DID specifications published |
| 2020 | Release of W3C's v1.0 DID standard |
Further Resources For Deeper Understanding
To explore more about this transformative technology:
- W3C Decentralized Identifiers Specification
- Uport's Approach To Self-Sovereign Identities
- Microsoft ION Documentation
By staying informed about ongoing developments—from technical standards through real-world implementations—you can better appreciate how decentralized identity is poised not only to redefine online authentication but also empower individual sovereignty amid rapid technological change


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 13:52
What is decentralized identity (DID), and why is it significant?
What Is Decentralized Identity (DID) and Why Is It Important?
Understanding Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized Identity, commonly known as DID, is transforming how individuals manage their digital identities. Unlike traditional systems where personal data is stored and controlled by centralized authorities such as governments or corporations, DID empowers users with full control over their identity information. This shift aims to enhance privacy, security, and user autonomy in the digital landscape.
At its core, DID leverages blockchain technology to create a secure and tamper-proof framework for managing identities. Individuals generate cryptographic keys that serve as their digital credentials. These keys enable them to authenticate themselves across various platforms without relying on third-party providers. The system also utilizes decentralized storage solutions—such as blockchain networks—to store identity data securely while maintaining user sovereignty.
Key Components of Decentralized Identity
Decentralized identity systems are built around several essential elements:
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Users have complete ownership of their identity data without dependence on external authorities.
- Decentralized Storage: Instead of centralized servers, identity information resides on distributed ledgers or peer-to-peer networks.
- Cryptographic Keys: Unique cryptographic pairs (public/private keys) facilitate secure authentication and verification processes.
This architecture ensures that users can selectively share verified parts of their identities—like age or citizenship—without exposing unnecessary personal details.
Historical Context and Development
The concept of decentralized identity has been evolving over the past decade. Its roots trace back to early efforts by organizations like the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which began exploring standards for digital identities around 2015. By 2017, W3C published the first specifications for DIDs—a significant milestone that laid the groundwork for interoperability across different platforms.
Blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in this evolution by providing an immutable ledger where all transactions related to identity creation or updates are recorded transparently yet securely. This foundation supports trustless verification mechanisms vital for decentralized ecosystems like Web3.
DID’s Role in Blockchain Ecosystems
Blockchain's inherent features—such as decentralization, transparency, and security—make it an ideal backbone for DID solutions. These attributes allow individuals to maintain control over their identities without relying on central authorities prone to breaches or misuse of data.
In addition to providing a secure infrastructure, blockchain enables functionalities like:
- Immutable Record-Keeping: Ensures all changes or updates are permanently logged.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Guarantee agreement among network nodes about the current state of an individual's identity data.
Furthermore, integration with smart contracts enhances automation capabilities—for example, automatically verifying credentials when certain conditions are met within decentralized applications (dApps).
Why Decentralized Identity Matters Today
The significance of DID extends beyond technical innovation; it addresses pressing concerns related to privacy rights and data security in our increasingly digital world.
Enhanced Privacy & Security
Traditional online services often require users to surrender large amounts of personal information stored centrally—a tempting target for hackers. In contrast, DID allows users granular control over what they share at any given moment through selective disclosure techniques. Cryptographic protections further safeguard against unauthorized access or impersonation attempts.
User Autonomy & Data Portability
With self-sovereign identities, individuals can seamlessly carry their verified credentials across multiple platforms without repeated registration processes. This portability reduces friction while empowering users with greater agency over their online presence.
Compliance & Regulatory Challenges
As governments worldwide implement stricter data protection laws such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California—and future regulations emerge—the adoption of decentralized IDs could facilitate compliance by minimizing unnecessary data collection while ensuring verifiable proof-of-identity mechanisms remain intact.
Recent Advances in Decentralized Identity Technology
Over recent years, several projects have advanced practical implementations that bring DID closer to mainstream adoption:
W3C Standards Development
The World Wide Web Consortium continues refining standards; its latest version from 2020 provides comprehensive guidelines ensuring interoperability between different implementations globally.
Industry Adoption
- Uport: An early pioneer offering portable digital identities built atop Ethereum-based infrastructure.
- Microsoft ION: A scalable solution integrated into Azure Active Directory designed specifically for enterprise use cases.
- Polkadot’s DIM: A modular approach allowing developers flexibility within multi-chain environments focused on secure ID management.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite promising progress—and growing interest from both private sector entities and governments—the path toward widespread deployment faces hurdles:
Scalability Concerns
Blockchain networks still grapple with transaction throughput limitations which could hinder large-scale use cases involving millions of identities simultaneously.
Regulatory Uncertainty
As regulatory frameworks evolve differently across jurisdictions regarding privacy rights and biometric verification methods—which may conflict with decentralization principles—it becomes challenging for organizations seeking compliance without compromising user sovereignty.
Looking Ahead: Opportunities & Considerations
The future trajectory suggests continued innovation driven by technological advances such as layer-two scaling solutions (e.g., rollups), zero-knowledge proofs enhancing privacy guarantees—and increasing collaboration among industry stakeholders aiming at standardization efforts led by bodies like W3C will be crucial.
For individuals interested in adopting decentralized IDs today—or organizations considering integration—the key lies in understanding both benefits: enhanced control over personal data; improved security; seamless cross-platform experiences—and challenges: scalability issues; regulatory compliance complexities.
By embracing these emerging technologies thoughtfully—with attention toward ethical considerations—they can significantly reshape how we verify our identities online while safeguarding fundamental rights.
Key Milestones Timeline
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2015 | W3C begins exploring standards for decentralized identifiers |
| 2017 | First official DID specifications published |
| 2020 | Release of W3C's v1.0 DID standard |
Further Resources For Deeper Understanding
To explore more about this transformative technology:
- W3C Decentralized Identifiers Specification
- Uport's Approach To Self-Sovereign Identities
- Microsoft ION Documentation
By staying informed about ongoing developments—from technical standards through real-world implementations—you can better appreciate how decentralized identity is poised not only to redefine online authentication but also empower individual sovereignty amid rapid technological change
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Web3 Could Reshape the Architecture of the Internet
The internet as we know it today is largely built on centralized servers controlled by a handful of major corporations. This structure has served us well for decades but also raises significant concerns about data privacy, security, censorship, and control. Enter Web3 — an innovative paradigm shift that promises to fundamentally change how the internet operates by leveraging blockchain technology and decentralized networks. Understanding how Web3 could reshape internet architecture involves exploring its core principles, recent advancements, and potential challenges.
The Current State of Internet Architecture
Today’s internet relies heavily on centralized data storage. Major tech giants like Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Microsoft manage vast amounts of user data across their servers. While this model offers convenience and efficiency, it also creates vulnerabilities: data breaches are common; users have limited control over their information; censorship can be easily enforced; and monopolistic practices can stifle competition.
This centralization has prompted calls for a more resilient system—one where power is distributed rather than concentrated in a few entities. That’s where Web3 comes into play.
Core Principles of Web3: Decentralization & Blockchain Technology
At its foundation, Web3 aims to decentralize digital infrastructure using blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system that records transactions securely across multiple nodes without a single controlling authority. Unlike traditional databases stored in one location or controlled by one entity, blockchains are immutable and transparent because every participant maintains a copy of the ledger.
Decentralization ensures no single point of failure or control within the network. This makes systems more resistant to attacks or censorship attempts while empowering users with greater ownership over their digital assets and identities.
Smart contracts are another critical component—they’re self-executing agreements written into code that automatically enforce rules without intermediaries. These enable trustless transactions across various applications like finance (DeFi), gaming (NFTs), or identity management—all integral parts of the emerging Web3 ecosystem.
How Blockchain Enhances Privacy & Security
Blockchain's transparency allows users to verify transactions independently while maintaining privacy through cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs. This combination enhances security compared to traditional systems vulnerable to hacking or insider threats.
Moreover, distributed ledger technology (DLT) creates immutable records—once data is recorded on the blockchain it cannot be altered retroactively—adding an extra layer against fraud or tampering.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum serve as native assets within these networks for transferring value securely without relying on banks or third-party payment processors—a fundamental shift from conventional financial systems toward decentralized finance (DeFi).
Interoperability: Connecting Different Blockchain Networks
For widespread adoption beyond niche communities, interoperability between various blockchains becomes essential. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos aim to facilitate seamless communication among diverse networks through standardized protocols:
- Polkadot enables different blockchains (“parachains”) to interoperate within a shared ecosystem.
- Cosmos provides tools for creating independent yet interconnected blockchains called “zones.”
Interoperability ensures that users aren’t locked into isolated platforms but can transfer assets seamlessly across multiple chains—crucial for building an integrated decentralized web infrastructure.
Recent Developments Driving Adoption
Several technological advances signal progress toward realizing Web3’s vision:
Ethereum 2.0: Transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum 2.0 reduces energy consumption significantly while improving scalability—a key factor in handling increased user demand.
NFTs & DeFi: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized ownership rights over digital art and collectibles; DeFi platforms offer decentralized lending/borrowing services that challenge traditional banking models.
Interoperable Blockchains: Projects like Polkadot enable cross-chain communication which broadens possibilities for developers creating interconnected applications.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments worldwide are beginning to recognize digital assets’ importance with guidelines from agencies such as the SEC shaping future legal landscapes around cryptocurrencies and tokens.
These developments demonstrate growing maturity within the ecosystem but also highlight ongoing challenges related to regulation compliance—and how they might influence future growth trajectories.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite promising advancements, several hurdles remain before fully realizing a decentralized web:
Scalability Issues: As user numbers grow exponentially on blockchain networks like Ethereum or Bitcoin—their transaction speeds slow down with higher fees due mainly due to capacity limits.
Security Risks: While blockchain offers enhanced security features overall—including resistance against certain types of attacks—it isn’t immune from vulnerabilities such as smart contract bugs or social engineering scams targeting users.
Environmental Concerns: Proof-of-work consensus mechanisms consume large amounts of energy—as seen with Bitcoin—which raises sustainability questions prompting shifts toward greener alternatives like proof-of-stake.
User Experience & Adoption Barriers: For mainstream acceptance, interfaces must become more intuitive; complex onboarding processes currently hinder mass adoption outside tech-savvy communities.
5.. Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks may deter businesses from fully embracing decentralization due to fears over compliance risks.
The Future Impact: Toward a More Resilient Digital Ecosystem
Web3 holds transformative potential—not just technologically but socially too—by redistributing power back into individual hands rather than centralized institutions alone.. It could lead towards an internet where individuals own their identities directly via cryptographic keys instead of relying on third-party providers who often hold sensitive personal information..
Furthermore,
- Data sovereignty would become standard practice,
- Censorship-resistant platforms could flourish,
- New economic models enabled by token economies might emerge,and
- Cross-platform interoperability would foster innovation at unprecedented levels.
However—and this is crucial—the path forward depends heavily upon addressing current limitations around scalability,safety,and regulation while fostering broader user-friendly experiences.
Final Thoughts
Web3 represents more than just technological evolution—it signifies a paradigm shift towards decentralizing our digital lives fundamentally altering how we interact online today.. Its success hinges upon collaborative efforts among developers,policymakers,and end-users alike—to build secure,inclusive,and scalable infrastructures capable of supporting tomorrow’s internet landscape.. As these technologies mature,it will be fascinating—and vital—to observe how they reshape our online world in ways both predictableand unforeseen.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 03:32
How could Web3 reshape the architecture of the Internet?
How Web3 Could Reshape the Architecture of the Internet
The internet as we know it today is largely built on centralized servers controlled by a handful of major corporations. This structure has served us well for decades but also raises significant concerns about data privacy, security, censorship, and control. Enter Web3 — an innovative paradigm shift that promises to fundamentally change how the internet operates by leveraging blockchain technology and decentralized networks. Understanding how Web3 could reshape internet architecture involves exploring its core principles, recent advancements, and potential challenges.
The Current State of Internet Architecture
Today’s internet relies heavily on centralized data storage. Major tech giants like Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Microsoft manage vast amounts of user data across their servers. While this model offers convenience and efficiency, it also creates vulnerabilities: data breaches are common; users have limited control over their information; censorship can be easily enforced; and monopolistic practices can stifle competition.
This centralization has prompted calls for a more resilient system—one where power is distributed rather than concentrated in a few entities. That’s where Web3 comes into play.
Core Principles of Web3: Decentralization & Blockchain Technology
At its foundation, Web3 aims to decentralize digital infrastructure using blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system that records transactions securely across multiple nodes without a single controlling authority. Unlike traditional databases stored in one location or controlled by one entity, blockchains are immutable and transparent because every participant maintains a copy of the ledger.
Decentralization ensures no single point of failure or control within the network. This makes systems more resistant to attacks or censorship attempts while empowering users with greater ownership over their digital assets and identities.
Smart contracts are another critical component—they’re self-executing agreements written into code that automatically enforce rules without intermediaries. These enable trustless transactions across various applications like finance (DeFi), gaming (NFTs), or identity management—all integral parts of the emerging Web3 ecosystem.
How Blockchain Enhances Privacy & Security
Blockchain's transparency allows users to verify transactions independently while maintaining privacy through cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs. This combination enhances security compared to traditional systems vulnerable to hacking or insider threats.
Moreover, distributed ledger technology (DLT) creates immutable records—once data is recorded on the blockchain it cannot be altered retroactively—adding an extra layer against fraud or tampering.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum serve as native assets within these networks for transferring value securely without relying on banks or third-party payment processors—a fundamental shift from conventional financial systems toward decentralized finance (DeFi).
Interoperability: Connecting Different Blockchain Networks
For widespread adoption beyond niche communities, interoperability between various blockchains becomes essential. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos aim to facilitate seamless communication among diverse networks through standardized protocols:
- Polkadot enables different blockchains (“parachains”) to interoperate within a shared ecosystem.
- Cosmos provides tools for creating independent yet interconnected blockchains called “zones.”
Interoperability ensures that users aren’t locked into isolated platforms but can transfer assets seamlessly across multiple chains—crucial for building an integrated decentralized web infrastructure.
Recent Developments Driving Adoption
Several technological advances signal progress toward realizing Web3’s vision:
Ethereum 2.0: Transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum 2.0 reduces energy consumption significantly while improving scalability—a key factor in handling increased user demand.
NFTs & DeFi: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized ownership rights over digital art and collectibles; DeFi platforms offer decentralized lending/borrowing services that challenge traditional banking models.
Interoperable Blockchains: Projects like Polkadot enable cross-chain communication which broadens possibilities for developers creating interconnected applications.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments worldwide are beginning to recognize digital assets’ importance with guidelines from agencies such as the SEC shaping future legal landscapes around cryptocurrencies and tokens.
These developments demonstrate growing maturity within the ecosystem but also highlight ongoing challenges related to regulation compliance—and how they might influence future growth trajectories.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite promising advancements, several hurdles remain before fully realizing a decentralized web:
Scalability Issues: As user numbers grow exponentially on blockchain networks like Ethereum or Bitcoin—their transaction speeds slow down with higher fees due mainly due to capacity limits.
Security Risks: While blockchain offers enhanced security features overall—including resistance against certain types of attacks—it isn’t immune from vulnerabilities such as smart contract bugs or social engineering scams targeting users.
Environmental Concerns: Proof-of-work consensus mechanisms consume large amounts of energy—as seen with Bitcoin—which raises sustainability questions prompting shifts toward greener alternatives like proof-of-stake.
User Experience & Adoption Barriers: For mainstream acceptance, interfaces must become more intuitive; complex onboarding processes currently hinder mass adoption outside tech-savvy communities.
5.. Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks may deter businesses from fully embracing decentralization due to fears over compliance risks.
The Future Impact: Toward a More Resilient Digital Ecosystem
Web3 holds transformative potential—not just technologically but socially too—by redistributing power back into individual hands rather than centralized institutions alone.. It could lead towards an internet where individuals own their identities directly via cryptographic keys instead of relying on third-party providers who often hold sensitive personal information..
Furthermore,
- Data sovereignty would become standard practice,
- Censorship-resistant platforms could flourish,
- New economic models enabled by token economies might emerge,and
- Cross-platform interoperability would foster innovation at unprecedented levels.
However—and this is crucial—the path forward depends heavily upon addressing current limitations around scalability,safety,and regulation while fostering broader user-friendly experiences.
Final Thoughts
Web3 represents more than just technological evolution—it signifies a paradigm shift towards decentralizing our digital lives fundamentally altering how we interact online today.. Its success hinges upon collaborative efforts among developers,policymakers,and end-users alike—to build secure,inclusive,and scalable infrastructures capable of supporting tomorrow’s internet landscape.. As these technologies mature,it will be fascinating—and vital—to observe how they reshape our online world in ways both predictableand unforeseen.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
❤️ We have upgraded the mechanism to optimize the long-term growth experience for futures traders. Hashrate Mechanism 1.0 is now terminated. Get ready for this upgrade!
🔍 Learn more: https://support.jucoin.blog/hc/en-001/articles/50229552477337
#JuCoin #Futures #Hashrate #JuCoinVietnam #Web3 #CEX #Blockchain #Crypto #DeFi 🚀


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-08-29 11:37
🚨 JuCoin Futures Subsidy Hashrate Mechanism 2.0 Officially Launched!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.