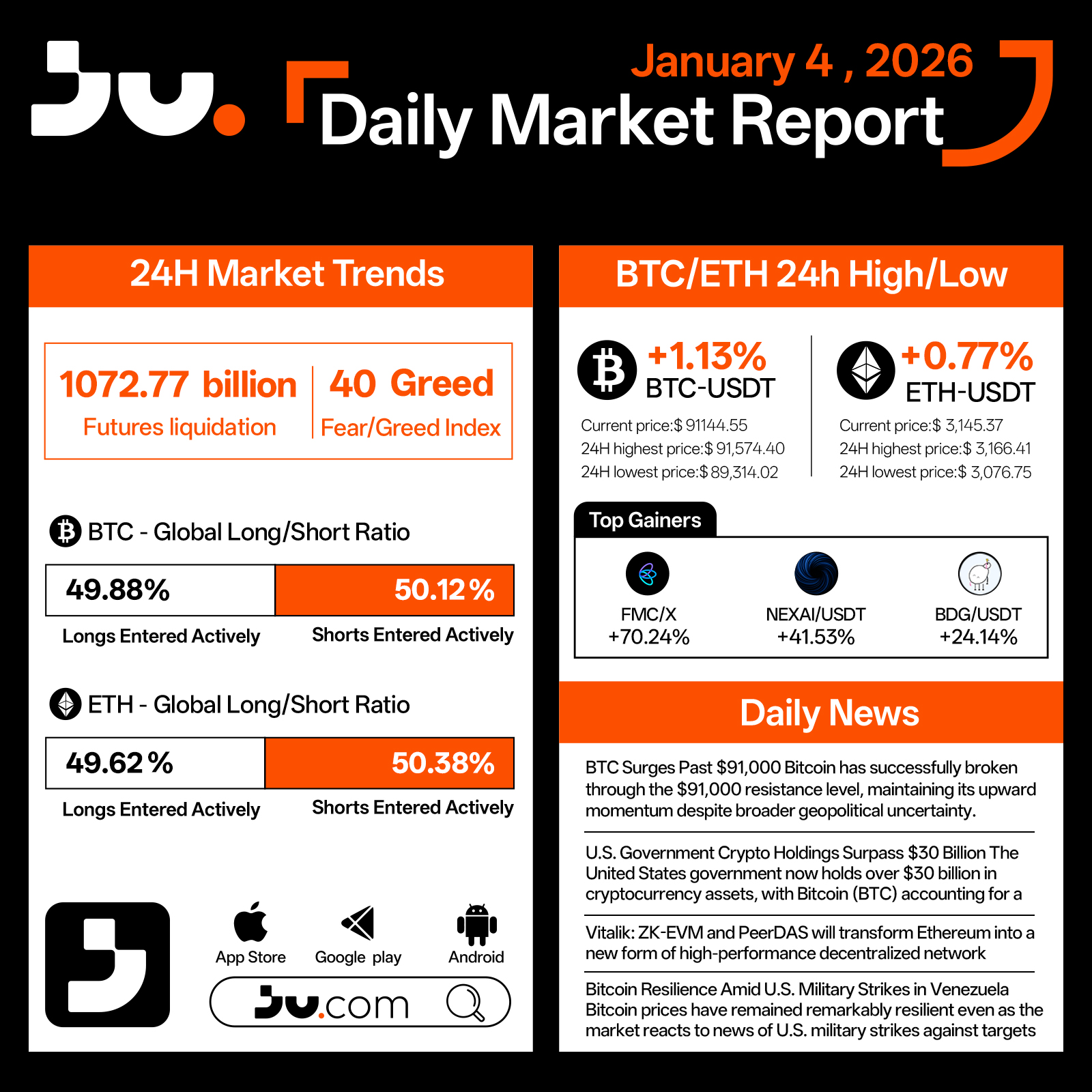
On January 4, the crypto market carried forward its early-year momentum, with Bitcoin decisively breaking through a key resistance level and lifting overall sentiment. Over the past 24 hours, market activity expanded notably, with total turnover and liquidations reaching $107.27 billion, while the Fear & Greed Index climbed to 40, signaling a clear rebound in risk appetite compared with year-end conditions.
Bitcoin rose 1.13% to $91,144.55, posting an intraday high of $91,574.40 and a low of $89,314.02. The successful break above the $91,000 level and subsequent consolidation suggest sustained bullish momentum. Ethereum followed with a 0.77% gain to $3,145.37, trading within a $3,166.41–$3,076.75 range and maintaining a steady correlation with BTC’s upward move. Positioning remained balanced, with BTC longs at 49.88% and ETH longs at 49.62%, indicating that the advance has been driven more by spot demand and trend-following capital than by excessive leverage.
Structural opportunities remained active across smaller-cap assets. FMC/X surged 70.24%, while NEXAI/USDT and PIPPIN/USDT advanced 41.53% and 24.14%, respectively. These moves reflect selective capital rotation as traders respond to Bitcoin’s breakout without broad-based risk expansion.
Macro and fundamental signals added depth to the move. The U.S. government disclosed that its cryptocurrency holdings now exceed $30 billion, with Bitcoin accounting for 97% of the total, reinforcing BTC’s status as the dominant digital reserve asset. On the Ethereum front, Vitalik Buterin stated that ZK-EVM and PeerDAS will transform Ethereum into a new form of high-performance decentralized network, strengthening long-term scalability and data availability narratives. Despite heightened geopolitical headlines, including reports of U.S. military strikes in Venezuela, Bitcoin prices remained resilient, underscoring its growing role as an asset capable of withstanding external shocks.
Overall, the opening days of 2026 show a market regaining directional clarity. Bitcoin’s breakout provides a clear technical anchor, while Ethereum’s roadmap supports medium-term confidence. With liquidity and sentiment improving in tandem, the crypto market appears to be entering the early phase of a new structural advance.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain


JU Blog
2026-01-09 04:40
Bitcoin Breaks Above $91K as Risk Appetite Rebounds Amid Geopolitical Noise - Jan 4, 2026
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
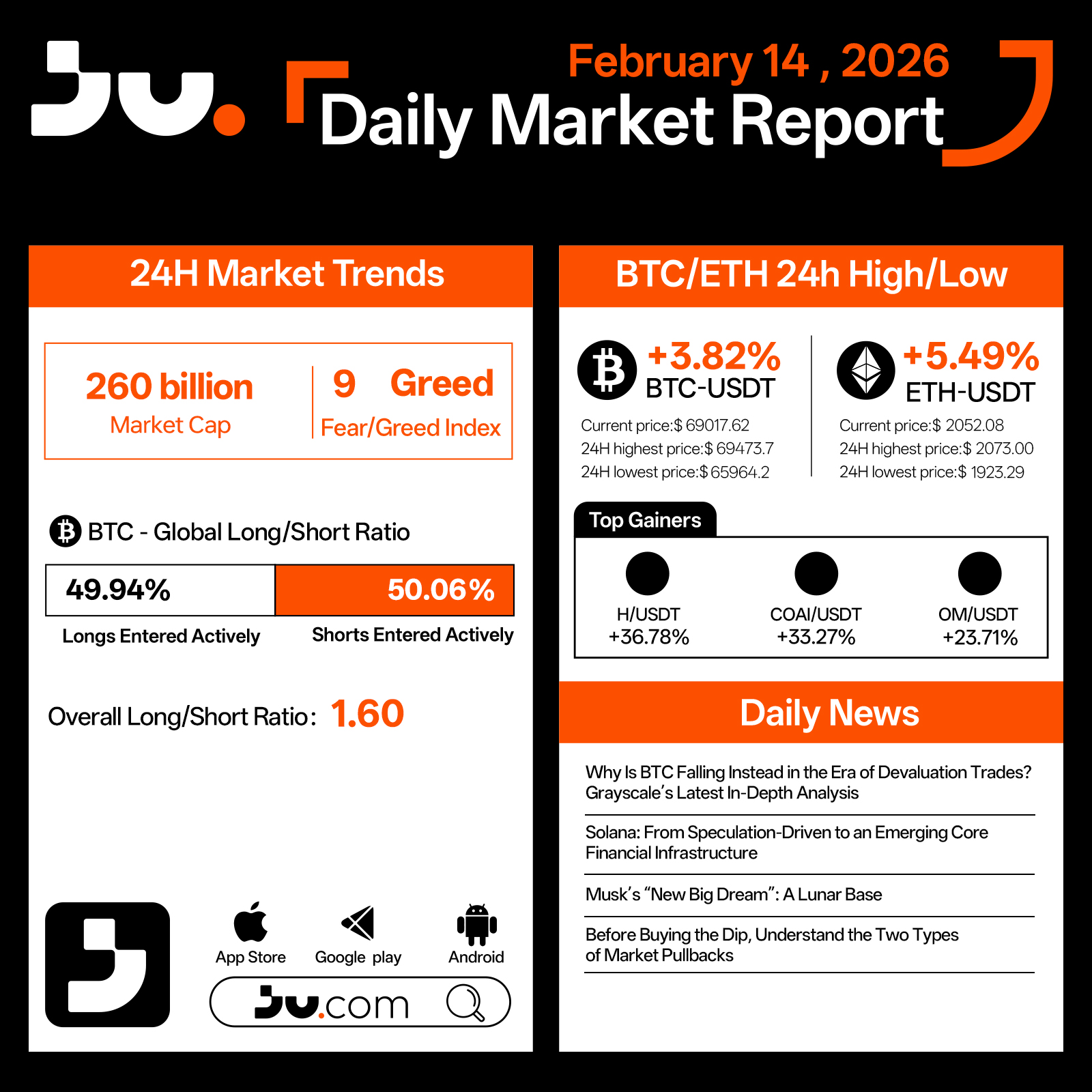
On February 14, the crypto market staged a notable rebound following consecutive sessions of decline, with total market capitalization rising to $260 billion. Although the Fear & Greed Index remains at 9, firmly within extreme fear territory, price action suggests that immediate selling pressure has eased, allowing for short-term recovery momentum.
Bitcoin gained 3.82% to $69,017.62, trading between $65,964.2 and $69,473.7 during the session. Long positions account for 49.94%, while shorts stand at 50.06%, with the aggregate long–short ratio declining to 1.60, reflecting a contraction in leveraged exposure. The rebound appears driven by short covering and tactical dip buying rather than a confirmed structural reversal.
Ethereum outperformed, rising 5.49% to $2,052.08, after dipping to $1,923.29 intraday. As a higher-beta asset, ETH demonstrated stronger recovery elasticity, highlighting renewed risk appetite at lower price levels, though broader market structure remains in a rebuilding phase.
Among leading gainers, H, COAI, and OM posted significant advances, largely attributable to oversold bounces and speculative positioning rather than a broad-based improvement in fundamentals.
Narrative focus centered on Grayscale’s analysis of why Bitcoin has not fully aligned with the “devaluation trade” thesis, emphasizing that macro liquidity dynamics continue to influence crypto pricing. Discussions around Solana’s transition from speculation-driven momentum to a potential core financial infrastructure further underscore evolving sector narratives. Analysts also cautioned investors to distinguish between different types of market pullbacks before engaging in dip-buying strategies.
Overall, February 14 reflects a technical rebound rather than a confirmed trend reversal. While short-term sentiment has improved marginally, extreme fear readings indicate that confidence remains fragile. In the absence of clearer liquidity or policy catalysts, volatility and consolidation are likely to persist in the near term.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #JU #Jucom


JU Blog
2026-02-14 06:12
Technical Rebound Emerges Amid Persistent Extreme Fear - Daily Market Report | February 14, 2026
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
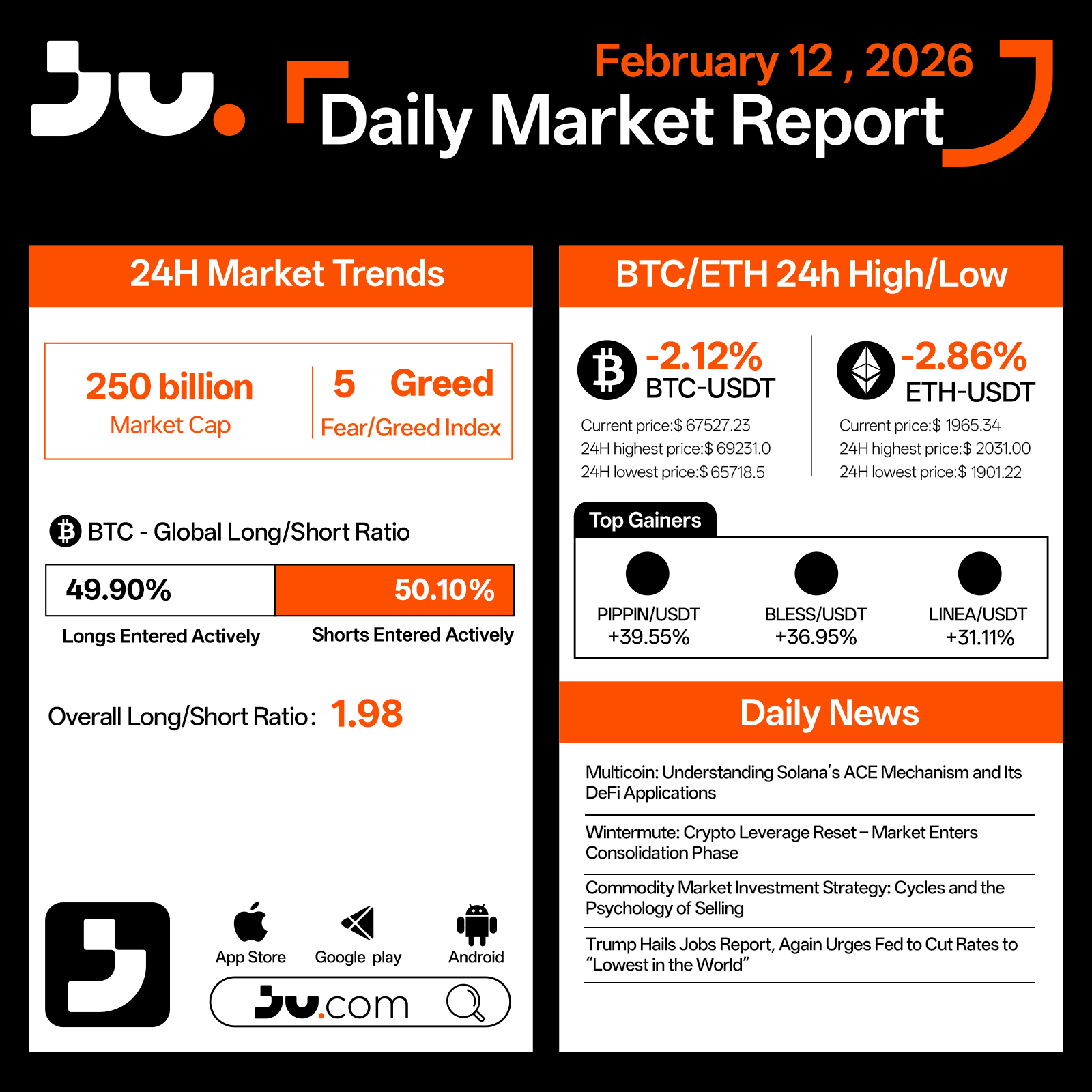
On February 12, the crypto market extended its decline, with total market capitalization falling to $250 billion. The Fear & Greed Index plunged to 5, marking one of the lowest readings of the current cycle and signaling extreme market anxiety. Liquidity remains tight, and post-leverage liquidation dynamics continue to shape price action.
Bitcoin dropped 2.12% to $67,527.23, trading between $65,718.5 and $69,231.0 during the session. Long positions account for 49.90%, while shorts stand at 50.10%, with an aggregate long–short ratio of 1.98, indicating near-balanced positioning despite continued downward pressure. The breakdown below key psychological levels has reinforced cautious sentiment, and volatility remains elevated.
Ethereum declined 2.86% to $1,965.34, with an intraday low of $1,901.22. As a higher-beta asset, ETH continues to exhibit greater downside sensitivity compared to BTC, reflecting ongoing risk reduction across the broader market.
Among top performers, PIPPIN, BLESS, and LINEA recorded strong gains, largely driven by tactical flows and sector rotation rather than a broad-based recovery in sentiment.
From a narrative perspective, Multicoin’s analysis of Solana’s ACE mechanism and its DeFi applications highlights continued innovation within high-performance blockchain ecosystems. Wintermute suggests that following a broad leverage reset, the market may enter a consolidation phase. Discussions surrounding commodity cycles and selling psychology further underscore prevailing macro uncertainty. Meanwhile, renewed political pressure for aggressive rate cuts adds another layer of complexity to risk asset pricing.
Overall, February 12 reflects a market in extreme fear territory. While such readings can historically coincide with late-stage capitulation, the absence of a clear liquidity or policy pivot suggests that consolidation at lower levels may persist before a more sustainable recovery emerges.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #technical analysis #JU #Jucom


JU Blog
2026-02-12 04:28
Extreme Fear Deepens as Market Tests Lower Boundaries - Daily Market Report | February 12, 2026
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bitcoin bags are getting blown out today, as the price of BTC falls to nearly $80,000 and marks a new seven-month low.
- The continued downward pressure on its price has pushed Bitcoin into a so-called death cross—when the average price of an asset over the short term falls below the average price over the long term. It’s a technical pattern that typically signals extended bearish momentum. For traders who study charts, it confirms what permabulls don’t want to hear: It’s over—at least for now.
- It’s happening as the crypto market as a whole shrinks to $2.91 trillion, shedding nearly $60 billion in the past 24 hours alone. Almost every single coin in the top 100 by market cap is bleeding red.
- The Fear and Greed Index, which measures market sentiment on a scale from 0 to 100, has cratered to 14 points—just four points above the year's low of 10 back in February. When this index drops below 20, it signals "extreme fear," and right now, traders are absolutely terrified.
- But it's not just crypto drama driving the market selloff. The macro picture is turning nasty. Just weeks ago, markets were pricing in a 97% chance the Federal Reserve would cut interest rates in December. Now? Those odds have collapsed to somewhere between 22% and 43%, depending on which metric you check.
- Fed officials are openly divided, with many signaling they'd prefer to keep rates unchanged through year-end. For risk assets like crypto that thrive on easy money, this is poison.
- On Myriad, a prediction market developed by Decrypt’s parent company Dastan, traders are now overwhelmingly convinced that Bitcoin will not mark a new all-time high this year, placing odds at almost 90% that BTC will not top the $126K mark that it hit on October 6.
- The bearish vibes are so strong, Myriad traders also currently place 40% odds that Bitcoin falls as low as $69K. So how low will it go? Here’s what the charts say.
- Bitcoin opened today at $86,691 and immediately sold off, hitting an intraday low of $80,620 before bouncing slightly to its current price at $85,187. That's a 1.61% drop on the day after being almost 5% down over the last 24 hours. More importantly, for traders, it further confirms the death cross pattern that's been progressively forming since its all-time high in early October. The death cross pattern was first confirmed on Wednesday as Bitcoin slid to around $88,000—now it’s fallen deeper.
- Here's what's happening on the charts: Exponential Moving Averages, or EMAs, help traders identify trend direction by tracking the average price of an asset over the short, medium, and long term. When the short-term 50-day EMA falls below the longer-term 200-day EMA, it means bears are in control and the longer-term bull market structure has been broken.
- For Bitcoin, the 50-day EMA has now decisively crossed below the 200-day EMA. In short, this tells traders market momentum has shifted from bullish to bearish. The gap between both EMAs increases the more the price of BTC trades below those targets—and the bigger the gap, the stronger the trend.
- The price of Bitcoin is now trading well below both EMAs, which creates a situation where each bounce attempt faces immediate resistance, increasing the gap between the two EMAs, making the bearish trend even stronger. Bulls trying to push higher will need to first reclaim the 50-day EMA, then tackle the 200-day—a double wall of resistance that's historically tough to crack in one go.
- As for other technical indicators, the Average Directional Index, or ADX, sits at 41, which is considered "strong." ADX measures trend strength regardless of direction, with readings above 25 indicating a clear trend is in place. At 41, this tells us we’re not seeing just a minor correction, but a potentially extended move lower.
- The Relative Strength Index, or RSI, has plunged to 23.18, placing Bitcoin deep in oversold territory. RSI measures momentum on a scale from 0 to 100, with readings below 30 signaling oversold conditions where assets are potentially undervalued. However, "oversold" doesn't mean the selling has to stop—in strong downtrends, RSI can remain in oversold territory for extended periods as prices continue grinding lower. But, yes, this also provides hopium for momentum traders as it signals that the worst of it may be over. (The worst being an accelerated crash, not necessarily a steady drop.)
- The Squeeze Momentum Indicator is flashing "bearish impulse," meaning selling pressure is intensifying rather than easing. Meanwhile, the Volume Profile Visible Range (VPVP) shows the price of Bitcoin trading "below" key volume nodes, suggesting there's not much buying interest at current levels.
- So, everything is bearish, clearly. But where's the next support? How low can the price of BTC go? The chart reveals several key horizontal levels to watch.
- The immediate danger zone is $80,697, which briefly held today but looked shaky. If that breaks, the next major support sits at $74,555, followed by $65,727, and potentially all the way down to $53,059 if panic really sets in during a crypto winter. Those price levels have previous consolidation zones where significant trading volume accumulated, making them natural landing spots for oversold bounces.
- For resistances, traders will watch for BTC’s price breaking past $90,000 again and look at $100,000 as the major psychological target.
- Ethereum opened at $2,830.7 and dropped as low as $2,621 intraday before stabilizing around $2,798—a 1.16% loss on the day. While not as dramatic as Bitcoin's selloff, ETH's technical picture is equally concerning.
- Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum hasn't fully confirmed its death cross yet—the 50-day EMA is still technically above the 200-day, giving it a "long" signal on an indicator that is obviously hours away from changing to bearish. The gap is razor-thin and closing fast. More importantly, ETH’s price is trading well below both EMAs, rendering that technical distinction somewhat meaningless. The bearish momentum is clearly established.
- A good way to see the natural support zones is using the Fibonacci retracements: a set of natural clusters that appear during a trend, showing supports and resistances in a specific timeframe—not because of price, but because of natural proportions.
- Right now, ETH is testing the 0.618 Fibonacci level at approximately $2,755. If this level breaks, the next Fibonacci support doesn't appear until $2,180, which would represent a massive 22% drop from current prices, and would resolve a price market on Myriad betting on ETH’s moon or doom.
- The ADX for Ethereum is even stronger than Bitcoin's at 46, indicating the downtrend is rock-solid. Meanwhile, RSI sits at 28.46—not quite as oversold as Bitcoin but definitely in stressed territory. The Squeeze Momentum Indicator shows "bearish impulse" here too, confirming sellers are in control.
- XRP is showing relative strength compared to its larger peers, down just 0.50% to close at $1.98 after opening at $1.99 and hitting an intraday low of $1.81796. Don't let that modest percentage fool you though—the technical damage is real.
- Like Bitcoin, the Ripple-linked XRP has confirmed a full death cross with its 50-day EMA now below the 200-day. The price of XRP is trading beneath both EMAs, and with an ADX of 32, the downtrend has enough strength to continue. While 32 isn't as extreme as Bitcoin's 41 or Ethereum's 46, it's still well above the 25 threshold that confirms a trend is in place rather than just random chop.
- The RSI at 32.86 shows XRP is approaching oversold territory but hasn't quite reached the extreme stress levels of Bitcoin and Ethereum. This could mean two things: either XRP has more downside before finding equilibrium, or it's showing genuine relative strength that could make it a safer harbor if the broader market continues tanking.
- XRP had such a crazy year that its price action shows only two major horizontal support levels that should concern XRP holders—and that would be very painful for hodlers, considering the movement from the all-time high to those targets.
- The next major support zone sits at $1.589, which represents a potential 20% drop from current levels. If that breaks, there's very little support until $0.66, a catastrophic 67% plunge from current prices and almost 80% from all-time high zone that would take XRP back to early 2024 levels.
The Squeeze Momentum Indicator is showing "bearish impulse," and like the other coins, the volume profile indicates XRP’s price is trading below key volume levels, meaning there's not much buying interest stepping in to defend current prices.
#Bitcoin #BitcoinDeathCross #Jucom #cryptocurrency #blockchain $BTC/USDT $JU/USDT $ETH/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-22 13:17
😱 Bitcoin in a Death Cross: How Low Will We Go?📛📛
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
While discussions are growing that Bitcoin-focused company Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) could be removed from MSCI indices, the company’s chairman, Michael Saylor, maintained that the operating model is robust and that this possibility will not affect the company’s roadmap.
- MSCI has proposed removing “digital asset treasury companies” whose portfolios consist largely of cryptocurrencies from its indexes. While it noted that such companies “may exhibit characteristics similar to mutual funds,” it stated that these structures are not suitable for the indexes. The final decision will be announced on January 15th.
- In his latest post, Saylor explained that Strategy is an operating company. He pointed out that, in addition to its Bitcoin reserves, it also has a $500 million enterprise software division that has been serving corporations and public institutions for over 20 years.
- Saylor stated, “We understand that index providers periodically review their methodologies, but Strategy is not an ETF, it is not a closed-end fund, and it is certainly not a passive proxy for Bitcoin. We produce, operate, and grow just like any other business.” He added that inclusion or removal from the index would not change the company's strategy, operations, or long-term belief in BTC.
- JPMorgan issued a note this week warning that Strategy's removal from the index could lead to billions of dollars in passive outflows. Analysts estimate that a potential removal from MSCI could lead to a $2.8 billion outflow from passive funds. Overall, approximately $9 billion of Strategy's market capitalization is estimated to be tied to passive, index-tracking ETFs and mutual funds.
The sharp decline in Bitcoin's price is also putting pressure on Strategy shares, which have lost nearly 40% of their value this year.
#Bitcoin #MicroStrategy #MichaelSaylor #Jucom #cryptocurrency $BTC/USDT $JU/USDT $ETH/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-22 13:06
📛 Bitcoin Bull MicroStrategy May Be Removed from US Indexes – Michael Saylor Answers.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The price of Cardano (ADA) was down on Friday after the blockchain suffered an unexpected chain split, which was caused by a malformed delegation transaction that triggered a software flaw. That created problems for Cardano users, and prompted a public apology from the user who claimed that they caused it.
- Intersect, the Cardano ecosystem’s governance organization, said in an incident report that the divergence began when the malformed transaction passed validation on newer node versions, but nodes running older software rejected it.
- “This exploited a bug in an underlying software library that was not trapped by validation code,” Intersect wrote. “The execution of this transaction caused a divergence in the blockchain, effectively splitting the network into two distinct chains: one containing the ‘poisoned’ transaction and a ‘healthy’ chain without it.”
- Earlier that day, Cardano co-founder Charles Hoskinson posted on X that it was a “premeditated attack from a disgruntled [stake pool operator]” who was “actively looking at ways to harm the brand and reputation of [Cardano developer Input/Output Global].”
- According to Hoskinson, all Cardano users were impacted. The price of Cardano’s token ADA was down more than 6% recently, following the incident.
- According to the incident report, the mismatch caused operators to build blocks on different branches of the chain until patched node software was deployed. Developers and service providers coordinated an emergency response, and operators were urged to upgrade to rejoin the main chain.
- Intersect said the wallet responsible for the malformed transaction has been identified, while Hoskinson said it will take weeks to clean up the mess.
- “Forensic analysis suggests links to a participant from the Incentivized Testnet (ITN) era,” Intersect wrote. “As this incident constitutes a potential cyberattack on a digital network, relevant authorities, including the Federal Bureau of Investigation, are being engaged to investigate.”
- Hours after the incident, an X user posting under the name Homer J. said they were responsible for submitting the transaction that triggered the split.
- “Sorry Cardano folks, it was me who endangered the network with my careless action yesterday evening,” they wrote, describing the attempt as a personal challenge to reproduce the “bad transaction” and said he relied on AI-generated instructions while blocking traffic on their server.
- “I've felt awful as soon as I realized the scale of what I've caused. I know there's nothing I can do to make up for all the pain and stress I've caused over the past X hours,” they added. “Difficult to quantify the negligence on my behalf. I am sorry, I truly am. I didn't have evil intentions.”
- Homer wrote that he did not sell or short ADA, did not coordinate with anyone else, and did not act for financial gain. “I'm ashamed of my carelessness and take full responsibility for it and whatever consequences will follow,” he said.
- According to Intersect, no user funds were lost, and most retail wallets were unaffected because they were running node components that handled the malformed transaction safely.
- Hoskinson, the outspoken co-founder of Cardano, claimed in a video message that the network “didn’t go down,” though users did encounter issues before the problem was fixed.
“It is important to note that the network did not stall. Block production continued on both chains throughout the incident, and at least some identical transactions appeared on both chains,” Intersect wrote. “However, to ensure the integrity of the ledger, exchanges and third-party providers largely paused deposits and withdrawals as a precautionary measure.”
#Cardano #CardanoNetwork #Jucom #cryptocurrency #blockchain $ADA/USDT $JU/USDT $BTC/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-22 13:03
📛 Cardano Network Disrupted by 'Poisoned' Transaction Attack.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Total Number of Transactions on the Bitcoin Network?
Understanding the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network is essential for grasping how active and widely used this pioneering cryptocurrency truly is. This metric offers insights into user engagement, network health, and overall adoption trends. In this article, we will explore what influences transaction volume, recent developments in 2023, and what these figures mean for investors and users alike.
How Does Transaction Volume Reflect Network Activity?
The total number of Bitcoin transactions indicates how frequently users are transferring funds or engaging with blockchain-based applications. On average, as of 2023, around 250,000 to 300,000 transactions occur daily. These fluctuations are driven by various factors such as market sentiment—bullish periods tend to see increased activity—as well as regulatory environments that can either encourage or restrict usage.
High transaction volumes suggest a vibrant ecosystem where users actively buy, sell, or transfer Bitcoin. Conversely, dips may signal reduced interest or external pressures like stricter regulations. Monitoring these numbers helps stakeholders gauge whether Bitcoin remains a popular medium for peer-to-peer payments or speculative trading.
Factors Influencing Transaction Counts
Several key elements impact how many transactions are recorded on the blockchain:
- Market Conditions: Bull markets often lead to increased trading activity as investors seek opportunities.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter laws can temporarily suppress transaction volumes; conversely, favorable policies may boost activity.
- Network Congestion: When many users transact simultaneously—such as during major price swings—transaction fees rise due to limited block space.
- Technological Developments: Improvements like SegWit (Segregated Witness) have optimized transaction processing times and costs over time.
These factors collectively shape daily transaction counts and influence user behavior across different periods.
Recent Trends in 2023: Fluctuations in Transaction Numbers
In April 2023, the Bitcoin network experienced a notable surge in transaction volume driven by heightened market speculation amid potential regulatory shifts in major economies. This increase was partly fueled by traders reacting to news about possible government interventions that could impact cryptocurrency markets globally.
However, May saw an uptick in average transaction fees—about a 20% rise compared to previous months—which reflects higher network congestion. Elevated fees can discourage smaller transactions from occurring frequently because they become less cost-effective for everyday use cases like micro-payments or casual transfers.
These recent trends highlight how external events directly influence not only how much activity occurs but also its economic viability for typical users.
Blockchain Size and Its Impact on Transactions
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain itself provides context about overall network activity; it stood at approximately 400 GB in early 2023—a significant increase from previous years due to continuous addition of new blocks containing transactional data.
A larger blockchain signifies more historical data stored across nodes worldwide but also raises concerns regarding scalability:
- Larger blockchains require more storage capacity.
- Synchronization times increase for new nodes joining the network.
- Higher data loads can contribute to slower confirmation times during peak periods unless scaling solutions are implemented effectively.
Efforts such as Lightning Network aim to address these scalability challenges by enabling faster off-chain transactions while maintaining security through underlying blockchain settlement layers.
The Role of Miners and Validation Processes
Miners play a crucial role in maintaining accurate records by validating transactions through complex computational puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work (PoW). They compete within seconds to add new blocks containing pending transactions onto the chain; successful miners receive rewards plus associated fees paid by transacting parties.
This validation process ensures integrity but is energy-intensive: estimates suggest that mining consumes substantial electricity globally. As demand increases with higher transaction volumes during active periods like April-May 2023’s surge,
the environmental footprint becomes more prominent concern among regulators and advocates alike.
Key Points About Mining:
- Miners validate hundreds of thousands of daily transactions
- Validation ensures decentralization & security
- Rising demand impacts energy consumption
Regulatory Environment's Effect on Transaction Volumes
Government policies significantly influence user participation levels on the Bitcoin network. In early 2023,
several countries introduced stricter regulations targeting crypto exchanges,which temporarily dampened trading activities reflected through decreased transaction counts initially observed after policy announcements.
However,
some jurisdictions adopted clearer frameworks encouraging institutional involvement,potentially stabilizing or increasing future transactional activity once compliance mechanisms were established.
Summary:
Regulatory uncertainty remains one of the most unpredictable factors affecting total bitcoin transactions; ongoing legislative developments will continue shaping usage patterns moving forward.
Future Outlook: Scalability Solutions & Adoption Trends
As interest grows among retail investors and institutions alike,
scalability solutions such as Taproot upgrades,Lightning Network implementations,and sidechains aim to facilitate faster processing at lower costs.
These technological advancements could help sustain higher throughput levels necessary for mainstream adoption while reducing congestion-related fee hikes seen earlier this year.
Moreover,
wider acceptance from merchants accepting bitcoin payments directly enhances real-world utility beyond speculative trading,
potentially leading toward sustained growth in total number of daily transactions over coming years.
By continuously monitoring metrics like total bitcoin transaction count alongside technological improvements and regulatory changes,
stakeholders—from individual users to large-scale investors—can better understand market dynamics
and make informed decisions aligned with evolving industry conditions.
References
- CoinDesk — General information on Bitcoin networks
- Blockchain.com Charts — Historical data analysis
- Blockchain Size Data — Blockchain growth insights
- Transaction Fees & Congestion — Impact analysis
- Bitcoin Mining Process — Technical validation overview
- Regulatory Impact Reports — Policy effects assessment
Understanding how many people transact using Bitcoin provides valuable insight into its current state—and future potential—as both an investment asset and a decentralized payment system amidst an ever-changing global landscape


Lo
2025-05-06 07:37
What is the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network?
What Is the Total Number of Transactions on the Bitcoin Network?
Understanding the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network is essential for grasping how active and widely used this pioneering cryptocurrency truly is. This metric offers insights into user engagement, network health, and overall adoption trends. In this article, we will explore what influences transaction volume, recent developments in 2023, and what these figures mean for investors and users alike.
How Does Transaction Volume Reflect Network Activity?
The total number of Bitcoin transactions indicates how frequently users are transferring funds or engaging with blockchain-based applications. On average, as of 2023, around 250,000 to 300,000 transactions occur daily. These fluctuations are driven by various factors such as market sentiment—bullish periods tend to see increased activity—as well as regulatory environments that can either encourage or restrict usage.
High transaction volumes suggest a vibrant ecosystem where users actively buy, sell, or transfer Bitcoin. Conversely, dips may signal reduced interest or external pressures like stricter regulations. Monitoring these numbers helps stakeholders gauge whether Bitcoin remains a popular medium for peer-to-peer payments or speculative trading.
Factors Influencing Transaction Counts
Several key elements impact how many transactions are recorded on the blockchain:
- Market Conditions: Bull markets often lead to increased trading activity as investors seek opportunities.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter laws can temporarily suppress transaction volumes; conversely, favorable policies may boost activity.
- Network Congestion: When many users transact simultaneously—such as during major price swings—transaction fees rise due to limited block space.
- Technological Developments: Improvements like SegWit (Segregated Witness) have optimized transaction processing times and costs over time.
These factors collectively shape daily transaction counts and influence user behavior across different periods.
Recent Trends in 2023: Fluctuations in Transaction Numbers
In April 2023, the Bitcoin network experienced a notable surge in transaction volume driven by heightened market speculation amid potential regulatory shifts in major economies. This increase was partly fueled by traders reacting to news about possible government interventions that could impact cryptocurrency markets globally.
However, May saw an uptick in average transaction fees—about a 20% rise compared to previous months—which reflects higher network congestion. Elevated fees can discourage smaller transactions from occurring frequently because they become less cost-effective for everyday use cases like micro-payments or casual transfers.
These recent trends highlight how external events directly influence not only how much activity occurs but also its economic viability for typical users.
Blockchain Size and Its Impact on Transactions
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain itself provides context about overall network activity; it stood at approximately 400 GB in early 2023—a significant increase from previous years due to continuous addition of new blocks containing transactional data.
A larger blockchain signifies more historical data stored across nodes worldwide but also raises concerns regarding scalability:
- Larger blockchains require more storage capacity.
- Synchronization times increase for new nodes joining the network.
- Higher data loads can contribute to slower confirmation times during peak periods unless scaling solutions are implemented effectively.
Efforts such as Lightning Network aim to address these scalability challenges by enabling faster off-chain transactions while maintaining security through underlying blockchain settlement layers.
The Role of Miners and Validation Processes
Miners play a crucial role in maintaining accurate records by validating transactions through complex computational puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work (PoW). They compete within seconds to add new blocks containing pending transactions onto the chain; successful miners receive rewards plus associated fees paid by transacting parties.
This validation process ensures integrity but is energy-intensive: estimates suggest that mining consumes substantial electricity globally. As demand increases with higher transaction volumes during active periods like April-May 2023’s surge,
the environmental footprint becomes more prominent concern among regulators and advocates alike.
Key Points About Mining:
- Miners validate hundreds of thousands of daily transactions
- Validation ensures decentralization & security
- Rising demand impacts energy consumption
Regulatory Environment's Effect on Transaction Volumes
Government policies significantly influence user participation levels on the Bitcoin network. In early 2023,
several countries introduced stricter regulations targeting crypto exchanges,which temporarily dampened trading activities reflected through decreased transaction counts initially observed after policy announcements.
However,
some jurisdictions adopted clearer frameworks encouraging institutional involvement,potentially stabilizing or increasing future transactional activity once compliance mechanisms were established.
Summary:
Regulatory uncertainty remains one of the most unpredictable factors affecting total bitcoin transactions; ongoing legislative developments will continue shaping usage patterns moving forward.
Future Outlook: Scalability Solutions & Adoption Trends
As interest grows among retail investors and institutions alike,
scalability solutions such as Taproot upgrades,Lightning Network implementations,and sidechains aim to facilitate faster processing at lower costs.
These technological advancements could help sustain higher throughput levels necessary for mainstream adoption while reducing congestion-related fee hikes seen earlier this year.
Moreover,
wider acceptance from merchants accepting bitcoin payments directly enhances real-world utility beyond speculative trading,
potentially leading toward sustained growth in total number of daily transactions over coming years.
By continuously monitoring metrics like total bitcoin transaction count alongside technological improvements and regulatory changes,
stakeholders—from individual users to large-scale investors—can better understand market dynamics
and make informed decisions aligned with evolving industry conditions.
References
- CoinDesk — General information on Bitcoin networks
- Blockchain.com Charts — Historical data analysis
- Blockchain Size Data — Blockchain growth insights
- Transaction Fees & Congestion — Impact analysis
- Bitcoin Mining Process — Technical validation overview
- Regulatory Impact Reports — Policy effects assessment
Understanding how many people transact using Bitcoin provides valuable insight into its current state—and future potential—as both an investment asset and a decentralized payment system amidst an ever-changing global landscape
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The Ethereum co-founder has repeatedly spoken this year about treating privacy as a basic necessity for digital systems.
- Following a recent data breach involving major US banks, where client information from institutions including JPMorgan, Citi, and Morgan Stanley may have been exposed after a cyberattack on mortgage technology vendor SitusAMC, Buterin responded by describing privacy as a form of “hygiene.”
- Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin said end-to-end encrypted messaging is essential for protecting digital privacy, identifying permissionless account creation and metadata privacy as the next major priorities for the sector.
He pointed to Session and SimpleX as two projects working on these areas and disclosed that he has donated 128 ETH to each of them.
Major ETH Donations
- In a post on X this week, Buterin said both applications are attempting to strengthen decentralization and enhance user protections without relying on phone numbers, while also addressing challenges such as multi-device support and resistance to Sybil or denial-of-service attacks.
- Buterin said the donation addresses are publicly available on the projects’ websites and added that, although the platforms are not yet perfect, they represent active efforts to advance privacy-preserving communication.
- He also called for more developers to help tackle the technical problems that still remain, and added that these issues “need more eyes on them.”
- It is important to note that while Signal has emerged as a widely used encrypted messaging app, it faced renewed scrutiny following a March incident in which senior US national security officials accidentally included a reporter in a Signal group discussing strikes on Houthi targets in Yemen.
- Days later, a Pentagon-wide advisory warned against using the app for any non-public information, citing a vulnerability tied to its linked-devices feature.
- The memo said Russian hacking groups were targeting the users of the app through phishing tactics. Signal later attributed the issue to user-targeted attacks rather than problems with its encryption, and that the company had already implemented safeguards and warnings.
Buterin’s Privacy Push
- In an essay published in April, he argued that “privacy is an important guarantor of decentralization” and outlined a path for Ethereum to support stealth addresses, selective disclosure, and application-level zero-knowledge tools to help reduce unnecessary data exposure.
- More recently, he warned that X’s new geo-inference system, which assigns country labels to user accounts, poses privacy risks.
He said such systems can still reveal sensitive location information and may endanger vulnerable users, even when only broad regions are disclosed.
#Ethereum #VitalikButerin #Jucom #cryptocurrency #EncryptedMessages $ETH/USDT $JU/USDT $BTC/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-28 05:01
🔥Ethereum Co-Founder Vitalik Buterin Launches 256 ETH to Boost Next-Generation Encrypted Messaging!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Wallet Address Clustering?
Wallet address clustering is a crucial technique in the blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem that involves grouping multiple wallet addresses based on shared transaction behaviors or characteristics. This process helps analysts, security professionals, and regulators better understand how digital assets move across the network, identify potential illicit activities, and improve privacy measures for users.
Understanding Wallet Addresses in Cryptocurrency
In the world of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, each user interacts with the blockchain through wallet addresses—unique alphanumeric strings that serve as digital bank accounts. These addresses are generated cryptographically to ensure pseudonymity; they do not directly reveal personal identities. However, despite this pseudonymity, all transactions linked to these addresses are publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger.
As transaction volumes grow exponentially over time, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain complete anonymity for individual users. Every transaction leaves a trail that can potentially be traced back to specific entities or behaviors if analyzed correctly. This is where wallet address clustering comes into play—it aims to analyze patterns across multiple addresses to infer relationships or groupings.
How Does Wallet Address Clustering Work?
Wallet address clustering employs various algorithms and analytical techniques designed to detect similarities among different addresses based on their activity patterns. These methods include:
- Transaction Pattern Analysis: Examining transfer amounts, timing between transactions, and frequency.
- Behavioral Signatures: Identifying common usage habits such as recurring transfers or specific asset types.
- Graph-Based Clustering: Creating visual maps of interconnected addresses based on shared inputs or outputs within transactions.
Popular algorithms used in this context include k-means clustering (which partitions data into predefined groups), hierarchical clustering (which builds nested clusters), and density-based methods like DBSCAN (which identifies clusters of varying shapes). Each has its strengths depending on dataset complexity and analysis goals.
Why Is Wallet Address Clustering Important?
The significance of wallet address clustering extends across several key areas:
Enhancing Privacy
While cryptocurrencies are often touted for their privacy features, true anonymity remains elusive due to transparent transaction records. By grouping related addresses together through clustering techniques, third parties find it more challenging to link individual transactions back to specific users—especially when combined with other privacy-preserving tools like mixers or privacy coins.
Security Monitoring
Clustering enables security teams and law enforcement agencies to detect suspicious activities such as money laundering schemes or fraud rings by spotting unusual patterns—like rapid transfers between clustered groups or large volume spikes—that deviate from typical user behavior.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions operating within regulatory frameworks use wallet address analysis for anti-money laundering (AML) efforts and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures. While full anonymization isn't always possible with effective clustering tools, these techniques help create a more compliant environment by providing insights into transactional relationships without exposing sensitive details unnecessarily.
Recent Advances in Wallet Address Clustering
Over recent years, significant progress has been made in refining clustering methodologies:
- Improved Algorithms: Researchers have developed sophisticated models capable of handling vast datasets efficiently while uncovering complex behavioral patterns.
- Integration Into Blockchain Analytics Platforms: Major analytics providers now incorporate advanced clustering features into their tools—enabling users ranging from law enforcement agencies to financial firms—to gain deeper insights.
- Privacy-Centric Cryptocurrencies: Some projects have integrated cluster-aware features directly into their protocols—for example, enhancing user privacy while still allowing legitimate analysis under certain conditions—which reflects ongoing innovation balancing transparency with confidentiality.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, wallet address clustering raises important concerns:
Regulatory Dilemmas: As authorities seek greater oversight over illicit activities like money laundering or terrorist financing via blockchain analysis tools—including those employing clustering—they face challenges balancing user privacy rights against compliance needs.
Potential for Misuse: If improperly implemented—or used without proper safeguards—clustering could inadvertently obscure legitimate transactions involving businesses or individuals who rely on enhanced privacy measures.
Ethical Debates: The debate continues around whether such analytical techniques should be solely used for security purposes—or if they risk infringing upon personal freedoms by enabling pervasive surveillance without adequate oversight.
Timeline of Key Developments
Understanding how wallet address clustering has evolved provides context about its current state:
- 2020: Academic research focused on evaluating different algorithms' effectiveness at preserving user privacy while enabling meaningful analysis.
- 2021: Major blockchain analytics platforms began integrating advanced cluster detection features amid rising demand from compliance-focused clients.
- 2022: The rise of privacy-centric cryptocurrencies prompted developers to embed cluster-aware mechanisms directly within protocols themselves.
- 2023: Regulatory discussions intensified regarding how best practices can balance effective AML/KYC processes with respecting individual rights—a debate ongoing today.
By grasping what wallet address clustering entails—and recognizing both its capabilities and limitations—you can better appreciate its role within broader efforts toward secure yet private cryptocurrency usage. Whether you're an investor seeking insight into transaction behaviors—or a regulator aiming at compliance—the evolving landscape underscores the importance of understanding this powerful analytical tool in today's digital economy.
Keywords: cryptocurrency wallets | blockchain analysis | transaction pattern recognition | crypto privacy | AML compliance | crypto security | decentralized finance


Lo
2025-05-15 03:19
What is wallet address clustering?
What is Wallet Address Clustering?
Wallet address clustering is a crucial technique in the blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem that involves grouping multiple wallet addresses based on shared transaction behaviors or characteristics. This process helps analysts, security professionals, and regulators better understand how digital assets move across the network, identify potential illicit activities, and improve privacy measures for users.
Understanding Wallet Addresses in Cryptocurrency
In the world of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, each user interacts with the blockchain through wallet addresses—unique alphanumeric strings that serve as digital bank accounts. These addresses are generated cryptographically to ensure pseudonymity; they do not directly reveal personal identities. However, despite this pseudonymity, all transactions linked to these addresses are publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger.
As transaction volumes grow exponentially over time, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain complete anonymity for individual users. Every transaction leaves a trail that can potentially be traced back to specific entities or behaviors if analyzed correctly. This is where wallet address clustering comes into play—it aims to analyze patterns across multiple addresses to infer relationships or groupings.
How Does Wallet Address Clustering Work?
Wallet address clustering employs various algorithms and analytical techniques designed to detect similarities among different addresses based on their activity patterns. These methods include:
- Transaction Pattern Analysis: Examining transfer amounts, timing between transactions, and frequency.
- Behavioral Signatures: Identifying common usage habits such as recurring transfers or specific asset types.
- Graph-Based Clustering: Creating visual maps of interconnected addresses based on shared inputs or outputs within transactions.
Popular algorithms used in this context include k-means clustering (which partitions data into predefined groups), hierarchical clustering (which builds nested clusters), and density-based methods like DBSCAN (which identifies clusters of varying shapes). Each has its strengths depending on dataset complexity and analysis goals.
Why Is Wallet Address Clustering Important?
The significance of wallet address clustering extends across several key areas:
Enhancing Privacy
While cryptocurrencies are often touted for their privacy features, true anonymity remains elusive due to transparent transaction records. By grouping related addresses together through clustering techniques, third parties find it more challenging to link individual transactions back to specific users—especially when combined with other privacy-preserving tools like mixers or privacy coins.
Security Monitoring
Clustering enables security teams and law enforcement agencies to detect suspicious activities such as money laundering schemes or fraud rings by spotting unusual patterns—like rapid transfers between clustered groups or large volume spikes—that deviate from typical user behavior.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions operating within regulatory frameworks use wallet address analysis for anti-money laundering (AML) efforts and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures. While full anonymization isn't always possible with effective clustering tools, these techniques help create a more compliant environment by providing insights into transactional relationships without exposing sensitive details unnecessarily.
Recent Advances in Wallet Address Clustering
Over recent years, significant progress has been made in refining clustering methodologies:
- Improved Algorithms: Researchers have developed sophisticated models capable of handling vast datasets efficiently while uncovering complex behavioral patterns.
- Integration Into Blockchain Analytics Platforms: Major analytics providers now incorporate advanced clustering features into their tools—enabling users ranging from law enforcement agencies to financial firms—to gain deeper insights.
- Privacy-Centric Cryptocurrencies: Some projects have integrated cluster-aware features directly into their protocols—for example, enhancing user privacy while still allowing legitimate analysis under certain conditions—which reflects ongoing innovation balancing transparency with confidentiality.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, wallet address clustering raises important concerns:
Regulatory Dilemmas: As authorities seek greater oversight over illicit activities like money laundering or terrorist financing via blockchain analysis tools—including those employing clustering—they face challenges balancing user privacy rights against compliance needs.
Potential for Misuse: If improperly implemented—or used without proper safeguards—clustering could inadvertently obscure legitimate transactions involving businesses or individuals who rely on enhanced privacy measures.
Ethical Debates: The debate continues around whether such analytical techniques should be solely used for security purposes—or if they risk infringing upon personal freedoms by enabling pervasive surveillance without adequate oversight.
Timeline of Key Developments
Understanding how wallet address clustering has evolved provides context about its current state:
- 2020: Academic research focused on evaluating different algorithms' effectiveness at preserving user privacy while enabling meaningful analysis.
- 2021: Major blockchain analytics platforms began integrating advanced cluster detection features amid rising demand from compliance-focused clients.
- 2022: The rise of privacy-centric cryptocurrencies prompted developers to embed cluster-aware mechanisms directly within protocols themselves.
- 2023: Regulatory discussions intensified regarding how best practices can balance effective AML/KYC processes with respecting individual rights—a debate ongoing today.
By grasping what wallet address clustering entails—and recognizing both its capabilities and limitations—you can better appreciate its role within broader efforts toward secure yet private cryptocurrency usage. Whether you're an investor seeking insight into transaction behaviors—or a regulator aiming at compliance—the evolving landscape underscores the importance of understanding this powerful analytical tool in today's digital economy.
Keywords: cryptocurrency wallets | blockchain analysis | transaction pattern recognition | crypto privacy | AML compliance | crypto security | decentralized finance
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Google released Gemini 3 Pro in a public preview today, calling it the company's most capable AI model to date.
- The system handles text, images, audio, and video simultaneously while processing up to 1 million tokens of context—roughly equivalent to 700,000 words, or about 10 full-length novels.
- The preview model is available for free for anyone to try here.
- Google said the model outperformed its predecessor, Gemini 2.5 Pro, across nearly every benchmark the company tested.
- On Humanity's Last Exam, an academic reasoning test, Gemini 3 Pro scored 37.5% compared to 2.5 Pro's 21.6%. On ARC-AGI-2, a visual reasoning puzzle benchmark, the gap widened further: 31.1% versus 4.9%.
- Of course, the real challenge at this point in the AI race isn’t technical so much as it is gaining commercial market share.
- Google, which once seemed indomitable in the search space, has given up an enormous amount of ground to OpenAI, which claims some 800 million weekly users ChatGPT versus Gemini, which reportedly has around 650 million monthly users. Google has not said how many weekly numbers it has, but that would be far fewer than its monthly count.
Still, the technical achievements of Gemini 3 are impressive.
Introducing Gemini 3 — our most intelligent model that helps you bring any idea to life.
Gemini 3 is our next step on the path toward AGI and has: 🧠 State-of-the-art reasoning 🖼️ Deep multimodal understanding 💻 Powerful vibe coding so you can go from prompt to app in one shot… pic.twitter.com/zG8r95pGcS
— Google (@Google) November 18, 2025
- Gemini 3 Pro uses what Google calls a sparse mixture-of-experts architecture. Instead of activating all 1 trillion-plus parameters for every query, the system routes each input to specialized subnetworks.
- Only a fraction of the model—the expert at that specific task—runs at any given time, cutting computational costs while maintaining performance.
- Unlike GPT and Claude, which are large, dense models (a jack of all trades), Google’s approach acts like a large organization would operate.
- A company with 1,000 employees doesn't call everyone to every meeting; specific teams handle specific problems. Gemini 3 Pro works the same way, directing questions to the right expert networks.
- Google trained the model on web documents, code repositories, images, audio files, and video—plus synthetic data generated by other AI systems.
- The company filtered the training data for quality and safety, removing pornographic content, violent material, and anything violating child safety laws. Training happened on Google's Tensor Processing Units using JAX and ML Pathways software.
- A quick test of the model showed that it was very capable. In our usual coding test asking to generate a stealth game, this was the first model that generated a 3D game instead of a 2D experience. Other runs provided 2D versions, but all were functional and fast.
- This approach follows the style of ChatGPT or Perplexity which encourage further interactions by sharing follow-up questions and suggestions, but Google’s implementation is a lot cleaner and more helpful.
- While generating code, the interface provides tips to help in subsequent prompts, so the user can guide the model into generating better code, fixing bugs, and improving the app’s logic, UI, etc. It also gives users the option to deploy their code and code Gemini-powered apps.
Overall, this model seems to be especially focused on coding tasks. Creativity is not its strong point, but it can be easy to guide with a good system prompt and examples, as it has a very large token context window.
- An archived version of Gemini 3’s model card—a document that provides essential information about the model's design, intended use, performance, and limitations—published by Google DeepMind shows that Gemini 3 Pro can generate up to 64,000 tokens of output and maintains a knowledge cutoff of January 2025.
- Google acknowledged the model may hallucinate and occasionally experiences slowness or timeouts. An official model card is not currently available.
- As mentioned, Google AI Studio is currently offering everyone free access to Gemini 3 Pro. Vertex AI and the Gemini API also support the model. Gemini 3 Pro is not yet available through the Gemini app, however—not even for paying Gemini Pro subscribers.
- The November release positions Google against Anthropic's Claude Sonnet 4.5, Grok 4.1 and even OpenAI's GPT-5.1. Benchmark scores suggest Gemini 3 Pro leads in reasoning and multimodal tasks, though real-world performance varies by use case.
Google distributed Gemini 3 Pro through its cloud platforms subject to existing terms of service. The company's generative AI prohibited use policy applies, blocking use in dangerous activities, security compromises, sexually explicit content, violence, hate speech, and misinformation. #Google#AIModel#Gemini3#Jucom #cryptocurrency $BTC/USDT $ETH/USDT $JU/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-19 11:02
📣 Google Releases Its Most Powerful AI Model, Gemini 3 — Here's What You Need to Know.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
A UK operation against Russian sanctions evasion has resulted in 128 arrests and the seizure of $32.6 million in cryptocurrency and cash.
The UK's National Crime Agency (NCA) has revealed that a UK-led operation to crack down on Russian sanctions evasion has resulted in the arrest of 128 people and the seizure of $32.6 million in cryptocurrency and cash.🚨🚨🚨
The operation, dubbed "Operation Destabilize," was first announced in 2024. As of December last year, it had resulted in 84 arrests and the seizure of $25.5 million.💡💡💡
However, the latest NCA data shows that the operation has also resulted in the arrest of a further 45 people suspected of money laundering and the seizure of more than $6.6 million in cash.⭐️⭐️⭐️
#InternationalNews #cryptocurrency #blockchain #Jucom #finance $BTC/USDT $ETH/USDT $JU/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-22 04:50
⭐️⭐️⭐️#InternationalNews
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Blockchain Interoperability? A Complete Overview
Understanding Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and transfer assets seamlessly. Unlike traditional financial systems where institutions can easily exchange information through standardized protocols, blockchain ecosystems are often isolated due to differing architectures and protocols. Interoperability aims to bridge these gaps, creating a more interconnected decentralized environment. This capability is essential for enabling cross-chain transactions, expanding the utility of digital assets, and fostering innovation across various blockchain platforms.
Why Is Interoperability Important in Blockchain Technology?
As blockchain technology matures, its applications have diversified into areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), supply chain management, and more. These use cases often require interaction between multiple blockchains—for example, transferring an NFT from one platform to another or executing a DeFi trade across different networks. Without interoperability, users face fragmentation; they must navigate multiple interfaces or convert assets manually through exchanges.
Interoperability enhances user experience by allowing smooth asset transfers and data sharing without intermediaries or complex procedures. It also promotes scalability by enabling specialized blockchains optimized for specific tasks while still maintaining connectivity with broader ecosystems.
Types of Blockchain Interoperability
There are primarily two types of interoperability based on how blockchains connect:
Homogeneous Interoperability: This involves different chains that share similar consensus mechanisms and protocols—think of it as connecting similar "languages." For example, two Ethereum-compatible chains can communicate more straightforwardly because they follow compatible standards.
Heterogeneous Interoperability: This connects fundamentally different blockchains with distinct architectures—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—requiring more complex solutions like cross-chain bridges or protocol adapters.
Technologies Enabling Cross-Chain Communication
Several innovative technologies facilitate interoperability:
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps: These enable the direct exchange of assets between two separate blockchains without intermediaries. They rely on smart contracts that ensure both parties fulfill their obligations simultaneously.
Sidechains: Smaller chains linked to a main chain via pegging mechanisms allow assets to move back and forth securely while leveraging the main chain’s security features.
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Lightning Network (Bitcoin) or Optimism (Ethereum) improve scalability and enable faster cross-chain interactions by processing transactions off the main chain before settling them on-chain.
Interoperability Protocols:
- Cosmos IBC: The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol allows independent zones within Cosmos’ ecosystem—and beyond—to transfer data securely.
- Polkadot Relay Chain: Acts as a central hub connecting various parachains (independent but connected chains), facilitating asset transfers across diverse networks.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Interoperability
Despite promising advancements, several hurdles remain:
Scalability Concerns: Ensuring rapid transaction speeds without compromising security is challenging when connecting multiple networks with varying capacities.
Security Risks: Cross-chain bridges are vulnerable points; exploits could lead to significant losses if not properly secured against attacks such as double-spending or 51% attacks.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Different jurisdictions impose varying rules on cryptocurrencies which complicate compliance efforts during cross-border transactions involving multiple legal frameworks.
Recent Developments in Cross-Chain Compatibility
The landscape has seen notable progress recently:
Cosmos launched its IBC protocol in 2020, enabling seamless communication among Cosmos-based chains—a significant step toward an interconnected ecosystem.
Polkadot’s Relay Chain has been operational since 2020; it facilitates asset transfers between parachains within its network while exploring connections outside its ecosystem.
Binance Smart Chain has integrated several interoperability solutions including atomic swaps and sidechain integrations with Ethereum-compatible projects.
Solana is actively exploring partnerships aimed at bridging its high-performance network with Ethereum through technological collaborations designed for cross-platform compatibility.
Potential Risks & Future Outlook
While these developments mark substantial progress toward interconnectedness in blockchain space, potential risks could impact adoption:
Security vulnerabilities remain a concern if bridges aren’t implemented correctly—they could be exploited leading to loss of funds or data breaches.
Regulatory challenges may arise as authorities develop frameworks around cross-border digital asset movements; inconsistent policies might hinder seamless integration globally.
Market sentiment can also be affected by technological failures or delays in deploying robust interoperability solutions—affecting investor confidence and asset prices alike.
Looking ahead,
the push towards universal compatibility continues driven by demand from users seeking streamlined experiences across platforms. As technical standards mature alongside regulatory clarity,
blockchain interoperability promises not only enhanced functionality but also increased mainstream adoption of decentralized technologies.
Understanding how diverse networks connect will be vital for developers aiming at building scalable dApps,
investors seeking diversified portfolios,
and regulators working towards balanced oversight that fosters innovation without compromising security.
By addressing current challenges head-on through collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders,
the vision of an fully interoperable blockchain universe becomes increasingly attainable—one where digital assets flow freely regardless of underlying architecture.
This comprehensive overview underscores why blockchain interoperability is fundamental for advancing decentralized technology's potential—and why ongoing innovations will shape the future landscape significantly


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 03:34
What is interoperability between blockchains?
What Is Blockchain Interoperability? A Complete Overview
Understanding Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and transfer assets seamlessly. Unlike traditional financial systems where institutions can easily exchange information through standardized protocols, blockchain ecosystems are often isolated due to differing architectures and protocols. Interoperability aims to bridge these gaps, creating a more interconnected decentralized environment. This capability is essential for enabling cross-chain transactions, expanding the utility of digital assets, and fostering innovation across various blockchain platforms.
Why Is Interoperability Important in Blockchain Technology?
As blockchain technology matures, its applications have diversified into areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), supply chain management, and more. These use cases often require interaction between multiple blockchains—for example, transferring an NFT from one platform to another or executing a DeFi trade across different networks. Without interoperability, users face fragmentation; they must navigate multiple interfaces or convert assets manually through exchanges.
Interoperability enhances user experience by allowing smooth asset transfers and data sharing without intermediaries or complex procedures. It also promotes scalability by enabling specialized blockchains optimized for specific tasks while still maintaining connectivity with broader ecosystems.
Types of Blockchain Interoperability
There are primarily two types of interoperability based on how blockchains connect:
Homogeneous Interoperability: This involves different chains that share similar consensus mechanisms and protocols—think of it as connecting similar "languages." For example, two Ethereum-compatible chains can communicate more straightforwardly because they follow compatible standards.
Heterogeneous Interoperability: This connects fundamentally different blockchains with distinct architectures—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—requiring more complex solutions like cross-chain bridges or protocol adapters.
Technologies Enabling Cross-Chain Communication
Several innovative technologies facilitate interoperability:
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps: These enable the direct exchange of assets between two separate blockchains without intermediaries. They rely on smart contracts that ensure both parties fulfill their obligations simultaneously.
Sidechains: Smaller chains linked to a main chain via pegging mechanisms allow assets to move back and forth securely while leveraging the main chain’s security features.
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Lightning Network (Bitcoin) or Optimism (Ethereum) improve scalability and enable faster cross-chain interactions by processing transactions off the main chain before settling them on-chain.
Interoperability Protocols:
- Cosmos IBC: The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol allows independent zones within Cosmos’ ecosystem—and beyond—to transfer data securely.
- Polkadot Relay Chain: Acts as a central hub connecting various parachains (independent but connected chains), facilitating asset transfers across diverse networks.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Interoperability
Despite promising advancements, several hurdles remain:
Scalability Concerns: Ensuring rapid transaction speeds without compromising security is challenging when connecting multiple networks with varying capacities.
Security Risks: Cross-chain bridges are vulnerable points; exploits could lead to significant losses if not properly secured against attacks such as double-spending or 51% attacks.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Different jurisdictions impose varying rules on cryptocurrencies which complicate compliance efforts during cross-border transactions involving multiple legal frameworks.
Recent Developments in Cross-Chain Compatibility
The landscape has seen notable progress recently:
Cosmos launched its IBC protocol in 2020, enabling seamless communication among Cosmos-based chains—a significant step toward an interconnected ecosystem.
Polkadot’s Relay Chain has been operational since 2020; it facilitates asset transfers between parachains within its network while exploring connections outside its ecosystem.
Binance Smart Chain has integrated several interoperability solutions including atomic swaps and sidechain integrations with Ethereum-compatible projects.
Solana is actively exploring partnerships aimed at bridging its high-performance network with Ethereum through technological collaborations designed for cross-platform compatibility.
Potential Risks & Future Outlook
While these developments mark substantial progress toward interconnectedness in blockchain space, potential risks could impact adoption:
Security vulnerabilities remain a concern if bridges aren’t implemented correctly—they could be exploited leading to loss of funds or data breaches.
Regulatory challenges may arise as authorities develop frameworks around cross-border digital asset movements; inconsistent policies might hinder seamless integration globally.
Market sentiment can also be affected by technological failures or delays in deploying robust interoperability solutions—affecting investor confidence and asset prices alike.
Looking ahead,
the push towards universal compatibility continues driven by demand from users seeking streamlined experiences across platforms. As technical standards mature alongside regulatory clarity,
blockchain interoperability promises not only enhanced functionality but also increased mainstream adoption of decentralized technologies.
Understanding how diverse networks connect will be vital for developers aiming at building scalable dApps,
investors seeking diversified portfolios,
and regulators working towards balanced oversight that fosters innovation without compromising security.
By addressing current challenges head-on through collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders,
the vision of an fully interoperable blockchain universe becomes increasingly attainable—one where digital assets flow freely regardless of underlying architecture.
This comprehensive overview underscores why blockchain interoperability is fundamental for advancing decentralized technology's potential—and why ongoing innovations will shape the future landscape significantly
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
It’s been just over a month since Bitcoin hit an All-Time-High of $126,272.76 on October 6 , but things have gone from bad to worse since then. Now, that peak seems like a distant memory.
- Bitcoin fell more than 9% in the week ending November 14 , and was trading below $92,000 on Monday. The sharp decline — partly due to whales selling — has pushed BTC below several key technical levels.
- Last week, Bitcoin entered a “bear market,” meaning it fell 20% or more from its recent peak. Over the weekend, BTC also appeared in a “death cross” technical pattern — when the 50-day moving Medium crossed below the 200-day Medium . Not only that, Bitcoin officially wiped out all of its gains for 2025 .
- All these signals indicate that negative sentiment is surrounding Bitcoin. But does that mean “crypto winter” is coming?
- “ I don’t think we’re in a crypto winter. I think we’re seeing Bitcoin mature ,” Louis LaValle, CEO of Frontier Investments, told MarketWatch.
- He argues that this is not a typical recession model where people give up, prices crash 70–80%, liquidation disappears, and interest evaporates. Instead, Bitcoin is going through a market structure shift , not a traditional bear cycle.
Beware of margin call risk
- Kevin Kelly — portfolio manager at Amplify ETFs — said that in the past, Bitcoin has often fallen in price without institutional involvement.
- But this bear cycle is quite different because BTC is now a “mature asset,” with more liquidation and more institutional acceptance, such as JP Morgan reportedly accepting Bitcoin as collateral .
- Data from CryptoQuant shows that investors who are selling BTC are still profitable , meaning there are no signs of capitulation or margin calls. However, retail investors are not buying the Dip , while whales are buying at low prices.
- CryptoQuant's Julio Moreno said that the amount of BTC held in US ETFs has dropped sharply from 441,000 BTC on October 10 to just 271,000 BTC, reflecting weak demand from the US. At the same time, the " Medium order" in the spot market also shows that retail has not returned.
Technical perspective
- While on-chain data hasn't shown anything too serious, weak demand hasn't been enough to stop the sell-off.
- Analyst Luke Lango said the recent death cross is a worrying sign. He noted that over the past 13 years, every time Bitcoin broke the 50-week moving Medium during a bull run, the market crashed in the following 1-2 years.
- BTC is now down about 27% from its recent peak — still within “normal range,” as the Medium Bitcoin bear market decline is about 30.8% (based on data going back to 2014). In 2022, there have been two declines of more than 45%.
- Kelly said that tightening global liquidation , the Fed's delay in cutting interest rates, and the TGA's withdrawal of liquidation from the system have made BTC much more vulnerable.
- He assessed the current situation as a combination of weak liquidation , continuous sell-offs, and declining sentiment , rather than a single shock.
“The Zone of Extreme Fear”
- The market has entered “extreme fear territory” after Bitcoin failed to hold the psychological $100,000 mark, according to Kelly.
- But investors have not lost interest. After the hot growth period since the January 2023 Dip , a “digestion wave” is normal.
- History also shows that when the market falls into “extreme fear zones,” it is a good opportunity to cash in — especially for long-term investors who Medium over time.
Macro still favors Bitcoin
- Frank Holmes — co-founder of HIVE Digital Technologies — says the macro backdrop is becoming more positive for both Bitcoin and gold.
- “ Excessive government spending and constant money printing create long-term support for scarce and decentralized assets ,” he observed.
Holmes also emphasized that even if new user growth slows in the short term, structural trends such as rising debt, monetary expansion, and geopolitical Shard still favor Bitcoin in the long term.
#Bitcoin #CryptoMarket #Jucom #cryptocurrency #blockchain $BTC/USDT $ETH/USDT $JU/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-19 11:27
💢 Bitcoin Just Wiped Out All Its 2025 Gains. What Would a “Crypto Winter” Look Like?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Daily Market Report - Nov 28, 2025
Crypto markets strengthened further on November 28, with sentiment showing noticeable improvement. Total futures liquidations over the past 24 hours dropped to $116.12 billion, while the Fear & Greed Index rose to 20, marking the most optimistic reading of the week. Bitcoin (BTC) climbed 3.33% to $91,154.98, trading between a high of $91,931.70 and a low of $90,449.99. Ethereum (ETH) followed with a 2.69% gain, settling at $3,012.76, with intraday volatility ranging from $3,071.24 down to $2,986.30.
BTC’s global long–short ratio remained slightly bearish with 48.95% longs and 51.05% shorts, while ETH maintained a mild long bias at 50.20% longs versus 49.80% shorts, showing a cautiously optimistic market posture. Among the day’s top performers, BDG/USDT surged 198%, ZYPHORA/USDT rose 87.66%, and NEXAI/USDT advanced 58.38%, highlighting strong speculative flows within specific high-momentum sectors.
Several major developments shaped today’s narrative. The Bitwise DOGE spot ETF officially launched, recording a $365,000 net inflow in its first day of trading. South Korea’s Upbit suffered a significant security breach involving approximately 54 billion KRW in Solana-based assets, prompting an immediate suspension of deposits and withdrawals. Cathie Wood suggested that liquidity conditions in the crypto sector may shift in the coming weeks, potentially marking the beginning of a new capital cycle. Russian lawmakers proposed an amnesty policy for crypto miners, signaling a shift toward more structured regulatory oversight. Meanwhile, institutional analysts projected that the US dollar could weaken again in 2026, driven by expectations of a Federal Reserve rate cut.
With BTC and ETH extending their upward momentum and speculative activity gaining strength, market sentiment has clearly improved. As the month draws to a close, traders will closely monitor ETF flows, regulatory developments, and security risks to gauge whether this recovery can sustain into early December.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #Bitcoin #ETH
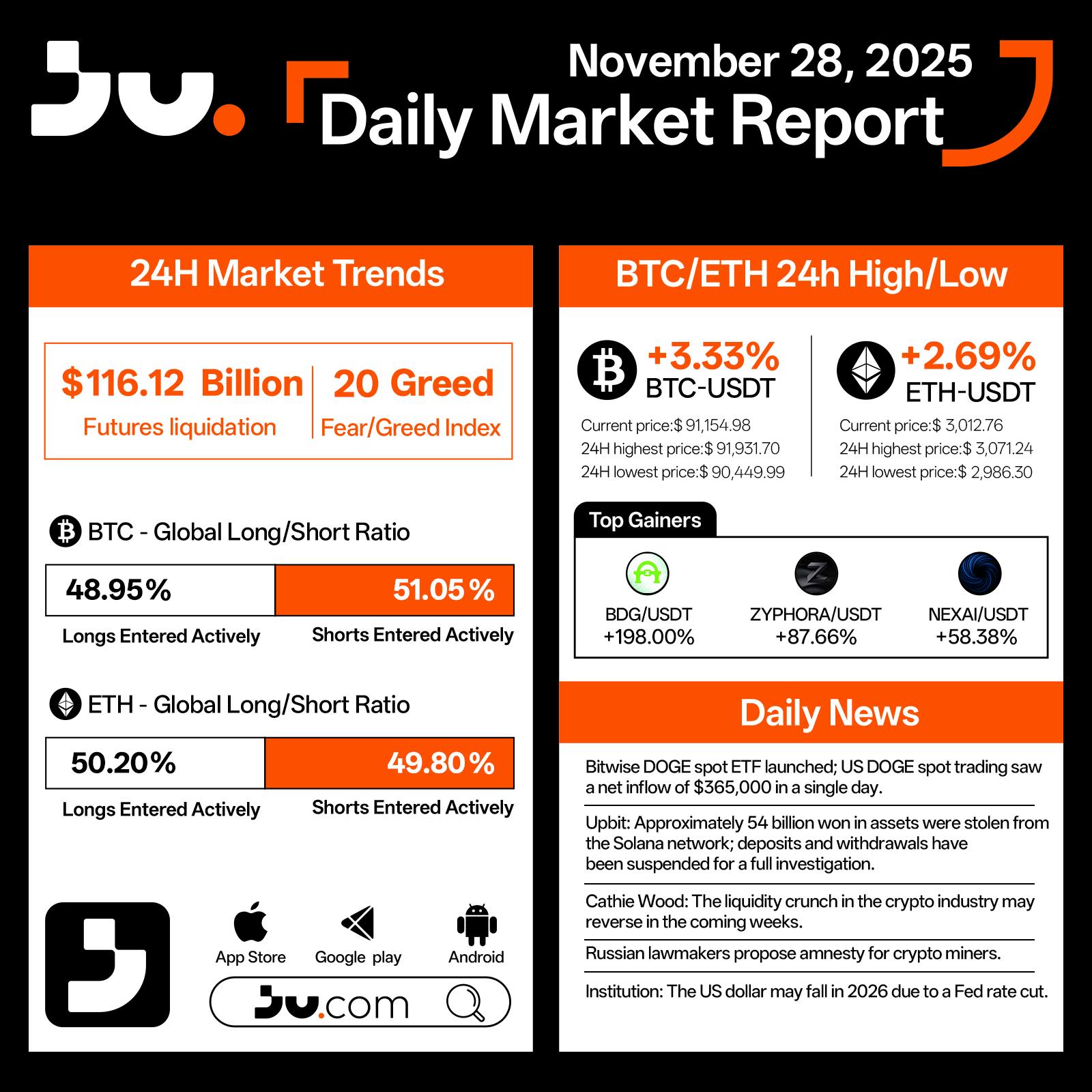


JU Blog
2025-11-28 04:48
BTC and ETH Extend Rally as Market Sentiment Improves - November 28, 2025
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Blockchain Analytics Tools?
Blockchain analytics tools are software platforms designed to analyze and interpret data from blockchain networks. These tools help users track transactions, monitor network activity, assess market trends, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. As blockchain technology becomes more widespread, the need for transparent and reliable analytics has grown exponentially. Whether you're an investor, regulator, or developer, understanding how these tools work is essential for navigating the complex landscape of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi).
These platforms leverage advanced algorithms to sift through vast amounts of on-chain data—such as transaction histories, wallet addresses, token movements—and present insights in a user-friendly manner. They also incorporate features like risk assessment and compliance checks to help institutions meet legal requirements while maintaining transparency.
Leading Blockchain Analytics Platforms
Several key players dominate the blockchain analytics space today. Each offers unique features tailored to different needs within the ecosystem:
Chainalysis
Chainalysis stands out as one of the most comprehensive solutions available for blockchain analysis. It provides real-time transaction monitoring that helps identify suspicious activities such as money laundering or fraud attempts. Its detailed reports on cryptocurrency flows assist law enforcement agencies and financial institutions in tracking illicit transactions across multiple blockchains.
In 2023, Chainalysis introduced "CryptoSlate," a feature that delivers deeper insights into market performance trends—making it easier for users to understand broader industry shifts alongside individual transaction data.
Elliptic
Elliptic specializes in anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance solutions tailored for financial institutions operating within crypto markets. Its platform offers advanced risk scoring models based on transaction patterns and wallet behaviors.
Recent updates in 2024 expanded Elliptic’s coverage to include more cryptocurrencies beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum—covering emerging tokens used in DeFi applications—and broadened its client base among banks and exchanges seeking regulatory adherence.
Glassnode
Unlike traditional analytics focusing solely on transactional data, Glassnode emphasizes on-chain metrics that gauge network health and market sentiment. Metrics like Network Value to Transactions (NVT) ratio or Market Value to Realized Value (MVRV) provide insights into whether a cryptocurrency is overbought or undervalued.
In 2025, Glassnode launched new analytical ratios such as "NVT Ratio" which helps traders assess whether current prices reflect underlying network activity—a vital tool during periods of high volatility when quick decision-making is crucial.
CryptoSlate
CryptoSlate acts as an aggregator platform pulling data from various sources—including other analytics tools—to offer comprehensive reports about crypto markets globally. It combines real-time price feeds with news updates relevant to ongoing developments within blockchain ecosystems.
The platform's recent expansion in 2024 included enhanced NFT tracking features—allowing users not only to monitor token sales but also analyze buying patterns across digital art marketplaces—a reflection of NFT market maturation.
Nansen
Nansen focuses heavily on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Its strength lies in providing granular insights into user behavior—such as large wallet movements or protocol-specific risk factors—which are invaluable for investors looking at yield farming strategies or NFT investments.
In 2025, Nansen partnered with major DeFi projects aiming at improving its risk assessment capabilities further—helping users avoid scams while optimizing their investment strategies based on behavioral signals observed across protocols.
Recent Trends Shaping Blockchain Analytics Tools
The development of these platforms has been influenced by several recent industry trends:
Regulatory Environment: Governments worldwide have increased scrutiny over crypto activities since 2023. Tools like Chainalysis have played pivotal roles by helping exchanges comply with AML/KYC regulations through detailed transaction monitoring.
Market Volatility: The unpredictable swings seen recently make real-time analysis more critical than ever; platforms like Glassnode provide timely metrics that inform trading decisions during turbulent periods.
Growth of DeFi: Decentralized finance continues expanding rapidly; Nansen’s focus on DeFi protocols allows investors to navigate this complex sector effectively.
NFT Market Expansion: The surge in digital collectibles has prompted analytic providers like CryptoSlate to develop specialized modules tracking NFT sales volumes & buyer behaviors.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Analytics Solutions
Despite their advantages, these tools face several hurdles:
Regulatory Risks: As authorities impose stricter rules around privacy & transparency standards—for example GDPR-like regulations—they may limit what data can be collected & analyzed legally.
Data Privacy Concerns: Large-scale collection raises questions about user privacy rights; balancing transparency with confidentiality remains a delicate issue.
Market Fluctuations Impact Accuracy: Rapid price swings can distort metrics temporarily; analytic models must adapt quickly without producing misleading signals.
Intense Competition & Innovation Pressure: With many startups entering this space regularly—from niche providers focusing solely on NFTs or specific chains—the landscape demands continuous innovation.
Why Blockchain Analytics Matter Today
Understanding how these tools function is crucial not just for traders but also regulators seeking transparency within increasingly complex networks. They enable detection of illicit activities such as frauds or money laundering while supporting compliance efforts globally—a vital aspect considering evolving legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies worldwide.
Moreover, they empower investors by providing actionable insights derived from deep analysis rather than speculation alone — especially important amid volatile markets where timing can significantly impact profitability.
Future Outlook: Evolving Capabilities & Industry Needs
As blockchain technology matures further—with innovations like layer-two scaling solutions—the role of analytics will become even more significant. Future developments may include enhanced AI-driven predictive models capable of forecasting market movements before they happen or improved cross-chain analysis enabling seamless tracking across multiple networks simultaneously.
Furthermore:
- Increased integration between different analytical platforms could foster richer datasets.*
- Privacy-preserving techniques might emerge allowing detailed analysis without compromising user confidentiality.*
- Regulatory frameworks will likely shape product offerings further—as companies adapt their services accordingly.*
Staying informed about these advancements ensures stakeholders remain equipped with cutting-edge tools necessary for navigating this dynamic environment effectively.
Keywords: blockchain analytics tools , cryptocurrency monitoring software , DeFi analysis platforms , NFT trend trackers , AML/KYC solutions , real-time transaction monitoring


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 08:49
What tools exist for blockchain analytics?
What Are Blockchain Analytics Tools?
Blockchain analytics tools are software platforms designed to analyze and interpret data from blockchain networks. These tools help users track transactions, monitor network activity, assess market trends, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. As blockchain technology becomes more widespread, the need for transparent and reliable analytics has grown exponentially. Whether you're an investor, regulator, or developer, understanding how these tools work is essential for navigating the complex landscape of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi).
These platforms leverage advanced algorithms to sift through vast amounts of on-chain data—such as transaction histories, wallet addresses, token movements—and present insights in a user-friendly manner. They also incorporate features like risk assessment and compliance checks to help institutions meet legal requirements while maintaining transparency.
Leading Blockchain Analytics Platforms
Several key players dominate the blockchain analytics space today. Each offers unique features tailored to different needs within the ecosystem:
Chainalysis
Chainalysis stands out as one of the most comprehensive solutions available for blockchain analysis. It provides real-time transaction monitoring that helps identify suspicious activities such as money laundering or fraud attempts. Its detailed reports on cryptocurrency flows assist law enforcement agencies and financial institutions in tracking illicit transactions across multiple blockchains.
In 2023, Chainalysis introduced "CryptoSlate," a feature that delivers deeper insights into market performance trends—making it easier for users to understand broader industry shifts alongside individual transaction data.
Elliptic
Elliptic specializes in anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance solutions tailored for financial institutions operating within crypto markets. Its platform offers advanced risk scoring models based on transaction patterns and wallet behaviors.
Recent updates in 2024 expanded Elliptic’s coverage to include more cryptocurrencies beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum—covering emerging tokens used in DeFi applications—and broadened its client base among banks and exchanges seeking regulatory adherence.
Glassnode
Unlike traditional analytics focusing solely on transactional data, Glassnode emphasizes on-chain metrics that gauge network health and market sentiment. Metrics like Network Value to Transactions (NVT) ratio or Market Value to Realized Value (MVRV) provide insights into whether a cryptocurrency is overbought or undervalued.
In 2025, Glassnode launched new analytical ratios such as "NVT Ratio" which helps traders assess whether current prices reflect underlying network activity—a vital tool during periods of high volatility when quick decision-making is crucial.
CryptoSlate
CryptoSlate acts as an aggregator platform pulling data from various sources—including other analytics tools—to offer comprehensive reports about crypto markets globally. It combines real-time price feeds with news updates relevant to ongoing developments within blockchain ecosystems.
The platform's recent expansion in 2024 included enhanced NFT tracking features—allowing users not only to monitor token sales but also analyze buying patterns across digital art marketplaces—a reflection of NFT market maturation.
Nansen
Nansen focuses heavily on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Its strength lies in providing granular insights into user behavior—such as large wallet movements or protocol-specific risk factors—which are invaluable for investors looking at yield farming strategies or NFT investments.
In 2025, Nansen partnered with major DeFi projects aiming at improving its risk assessment capabilities further—helping users avoid scams while optimizing their investment strategies based on behavioral signals observed across protocols.
Recent Trends Shaping Blockchain Analytics Tools
The development of these platforms has been influenced by several recent industry trends:
Regulatory Environment: Governments worldwide have increased scrutiny over crypto activities since 2023. Tools like Chainalysis have played pivotal roles by helping exchanges comply with AML/KYC regulations through detailed transaction monitoring.
Market Volatility: The unpredictable swings seen recently make real-time analysis more critical than ever; platforms like Glassnode provide timely metrics that inform trading decisions during turbulent periods.
Growth of DeFi: Decentralized finance continues expanding rapidly; Nansen’s focus on DeFi protocols allows investors to navigate this complex sector effectively.
NFT Market Expansion: The surge in digital collectibles has prompted analytic providers like CryptoSlate to develop specialized modules tracking NFT sales volumes & buyer behaviors.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Analytics Solutions
Despite their advantages, these tools face several hurdles:
Regulatory Risks: As authorities impose stricter rules around privacy & transparency standards—for example GDPR-like regulations—they may limit what data can be collected & analyzed legally.
Data Privacy Concerns: Large-scale collection raises questions about user privacy rights; balancing transparency with confidentiality remains a delicate issue.
Market Fluctuations Impact Accuracy: Rapid price swings can distort metrics temporarily; analytic models must adapt quickly without producing misleading signals.
Intense Competition & Innovation Pressure: With many startups entering this space regularly—from niche providers focusing solely on NFTs or specific chains—the landscape demands continuous innovation.
Why Blockchain Analytics Matter Today
Understanding how these tools function is crucial not just for traders but also regulators seeking transparency within increasingly complex networks. They enable detection of illicit activities such as frauds or money laundering while supporting compliance efforts globally—a vital aspect considering evolving legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies worldwide.
Moreover, they empower investors by providing actionable insights derived from deep analysis rather than speculation alone — especially important amid volatile markets where timing can significantly impact profitability.
Future Outlook: Evolving Capabilities & Industry Needs
As blockchain technology matures further—with innovations like layer-two scaling solutions—the role of analytics will become even more significant. Future developments may include enhanced AI-driven predictive models capable of forecasting market movements before they happen or improved cross-chain analysis enabling seamless tracking across multiple networks simultaneously.
Furthermore:
- Increased integration between different analytical platforms could foster richer datasets.*
- Privacy-preserving techniques might emerge allowing detailed analysis without compromising user confidentiality.*
- Regulatory frameworks will likely shape product offerings further—as companies adapt their services accordingly.*
Staying informed about these advancements ensures stakeholders remain equipped with cutting-edge tools necessary for navigating this dynamic environment effectively.
Keywords: blockchain analytics tools , cryptocurrency monitoring software , DeFi analysis platforms , NFT trend trackers , AML/KYC solutions , real-time transaction monitoring
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
- The crypto market is showing its first meaningful recovery after a harsh November sell-off, and several metrics now resemble the same conditions seen around Thanksgiving in both 2022 and 2023.
- Bitcoin has reclaimed the $91,000 level, ETH is back above $3,000, and the wider market has returned to a cautious green. This bounce comes as traders enter a long US holiday weekend that has historically set the tone for December.
Market Indicators Turn Positive After Weeks of Fear
- Fear and Greed Index data shows sentiment improving from 11 last week to 22 today, although it remains in “Extreme Fear.”
- This shift aligns with a steady rise in average crypto RSI, which climbed from 38.5 seven days ago to 58.3 today. The reading signals growing strength after deep oversold conditions earlier in the month.
- Momentum also flipped. The normalized MACD across major assets has turned positive for the first time since early November.
- About 82% of tracked cryptocurrencies now show positive trend momentum. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana appear in the bullish zone of CoinMarketCap’s MACD heatmap.
- Price action supports this shift. Bitcoin is up 6% on the week. Ethereum has gained nearly 8%. Solana climbed almost 8% in the same period.
- The market cap has grown to $3.21 trillion, rising 1.1% over the last 24 hours.
A Familiar Post-Thanksgiving Setup Has Emerged
- The current recovery mirrors a structure seen twice before. In both 2022 and 2023, the market entered Thanksgiving after a sharp drawdown and then stabilized into December.
- In 2022, Bitcoin fell to near $16,000 following the FTX collapse. By Thanksgiving, selling pressure had exhausted, and the market traded sideways into Christmas.
- It was a deep bear consolidation phase rather than a rally.
- In 2023, Bitcoin entered Thanksgiving at $37,000 after a steep September-October correction. Strong ETF expectations and improving liquidity conditions pushed BTC to $43,600 by Christmas. It was a classic early-bull December rally.
- This year, the pattern again repeats one familiar element: the November crash came early, and by Thanksgiving, selling momentum had eased.
- Bitcoin’s 90-day Taker CVD has shifted from persistent sell dominance to neutral, signalling that aggressive sellers have stepped back. Funding rates and leverage data support the same interpretation.
BREAKING: The S&P 500 closes the day +0.7% higher, adding +$2.5 trillion of market cap since last week’s low. Happy Thanksgiving to all! pic.twitter.com/tsjKylr5UV
Liquidity Damage Still Shapes the Current Cycle
- BitMine chairman Tom Lee described the market as “limping” after the October 10 liquidation shock.
- He said market makers were forced to shrink their balance sheets, weakening market depth across exchanges. That fragility persisted through November.
- However, Lee also argued that Bitcoin tends to make its biggest moves in short bursts when liquidity recovers. He expects a strong December rally if the Federal Reserve signals a softer stance.
- On-chain data aligns with this view. Nexo collateral figures show users still prefer borrowing against Bitcoin rather than selling it.
- BTC makes up more than 53% of all collateral on the platform. This behavior suppresses immediate sell pressure, helping stabilize spot markets. But it also adds hidden leverage that could amplify future volatility.
'@Nexo users aren’t selling their Bitcoin, they’re borrowing against it. BTC now accounts for 54.3% of all collateral on the platform, holding a steady 53–57% range for months. It confirms Bitcoin is the dominant asset users leverage when they need liquidity. pic.twitter.com/bhmL9UdUvO
We May Be Entering a Two-Year Holiday Pattern
Three factors now look similar to the post-Thanksgiving conditions of 2022 and 2023:
- Seller exhaustion: Taker CVD shifting to neutral signals the end of forced selling for now.
- Momentum recovery: MACD and RSI metrics have reversed sharply after bottoming earlier in November.
- Liquidity stabilization: Market makers are still wounded, but volatility has cooled, and ETF outflows have slowed.
If this pattern continues, December could produce one of two outcomes based on the last two years:
- A sideways consolidation like 2022 if liquidity remains thin.
- A short, sharp rally like 2023 if macro conditions turn supportive.
The deciding factor will likely be the Federal Reserve’s tone in early December and the behavior of Bitcoin ETF flows. Thin liquidity means even moderate inflows could move prices quickly.
#Bitcoin Testing 90k if it holds its the first step to a Santa Rally pic.twitter.com/QhHQNfDQPk
December May Deliver a Large Move in Either Direction
- The market has entered a transition phase rather than a clear trend. Sentiment is still extremely fearful, but price and momentum indicators show recovery.
- Bitcoin’s position above $91,000 suggests buyers are willing to defend key levels, yet order-book depth remains weak.
- With selling pressure fading and technical momentum rising, the environment now resembles the same post-Thanksgiving setups that marked the last two end-of-year cycles.
Bitcoin dominance looks weak here. ETH/BTC is holding above the 0.03-0.032 support zone. It seems like we could see ETH outperformance in December. pic.twitter.com/IRQS05mETi
- If the pattern holds, December will not be flat. It will likely bring a decisive move as liquidity conditions shift.
- The direction, however, will depend less on crypto narratives and more on macro signals and ETF demand in the coming weeks.
- The post Crypto Market Hints at a Two-Year Post-Thanksgiving Pattern Returning appeared first on BeInCrypto.
Average Crypto RSI On Thanksgiving 2025. Source: CoinMarketCapAverage Crypto MACD On Thanksgiving 2025. Source: CoinMarketCapBitcoin Performance Between Thanksgiving and Christmas (2021–2024) #CryptoMarket #Thanksgiving #Jucom #cryptocurrency #blockchain $BTC/USDT $JU/USDT $ETH/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-28 05:10
‼️ Crypto Market Hints at a Two-Year Post-Thanksgiving Pattern Returning!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Amundi, Europe’s largest asset manager, has introduced its first tokenized share class for a euro money market fund.
- The fund is now offered in a hybrid structure, allowing investors to choose between the traditional version and the new blockchain-based one. The first transaction was recorded on the Ethereum network on Nov. 4.
- The rollout was developed in collaboration with CACEIS, a European asset-servicing group that provided the tokenization infrastructure, investor wallets, and the digital order system used to process subscriptions and redemptions.
- According to the companies, tokenizing the fund streamlines order processing, widens access to new investor channels, and enables 24/7 trading.
- Amundi said the fund holds short-term, high-quality euro-denominated debt, primarily comprising money-market instruments and overnight repurchase agreements with European sovereigns.
According to the company’s website, it manages about 2.3 trillion euros ($2.6 trillion) in assets and serves more than 100 million retail clients. Amundi is based in Paris, France.
BlackRock and Franklin Templeton drive growth in tokenized funds
- Tokenized money market funds investing in US Treasurys have expanded rapidly in 2025. RWA.xyz data shows BlackRock’s onchain money market product currently holds $2.3 billion in tokenized assets, while Franklin Templeton’s money market fund has more than $826 million in assets.
- Both funds have been expanding across multiple blockchains. On Nov. 12, Franklin Templeton announced that its tokenization platform joined the Canton Network, enabling its money market fund to operate within a permissioned ecosystem built for financial institutions.
- BlackRock has also expanded its tokenized fund beyond Ethereum, adding support for Aptos, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Optimism and Polygon.
- A Bank for International Settlements bulletin released on Wednesday noted that tokenized money market funds had climbed to $9 billion in value by the end of October, up from about $770 million at the end of 2023.
However, the report warned that the growing adoption of tokenized Treasury portfolios as collateral could expose the financial system to new operational and liquidity vulnerabilities.
#Amundi #BlackRock #TokenizedShare #Jucom #cryptocurrency $BTC/USDT $ETH/USDT $JU/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-28 04:56
📣 Amundi brings euro money market fund onchain with first tokenized share.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The U.S. Department of Justice on Tuesday charged the founder of a Chicago-based crypto ATM company with taking in at least $10 million in criminal proceeds, and moving the money into digital wallets to conceal its origins.
- The indictment, unsealed in the Northern District of Illinois, accused Firas Isa of running the operation through Virtual Assets LLC, a company that did business as Crypto Dispensers and operated cash-to-cryptocurrency ATMs across the United States.
- According to the filing, victims and criminals sent the funds to Isa, his company, or a co-conspirator. While Bitcoin ATMs are supposed to institute know-your-customer (KYC) policies to curb money laundering through the machines, prosecutors said Isa converted the illicit funds the Crypto Dispensers ATMs received into cryptocurrency before transferring it to other wallets.
- “The indictment alleges that Isa knew the money was derived from fraud,” the DOJ wrote.
- The DOJ did not say in the indictment which cryptocurrencies or wallet providers were allegedly used by Isa in the scheme. Isa did not immediately respond to a request for comment by Decrypt.
- Isa and Virtual Assets LLC were each charged with one count of money-laundering conspiracy, a charge that carries a maximum sentence of 20 years in federal prison. Both entered not-guilty pleas. A status hearing was set for January 30, 2026, before U.S. District Judge Elaine Bucklo.
- The charge arrived at a time when federal prosecutors are adjusting how they police the crypto market. In April, the Justice Department said it would dissolve its National Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team and stop bringing criminal cases against exchanges, mixing services, or cold-wallet holders for the actions of their users.
- Last week, the DOJ, FBI, and U.S. Secret Service announced a new Scam Center Strike Force aimed at combating crypto scams that originated in China.
- Prosecutors noted that the indictment against Isa and Virtual Assets is an allegation, and they are presumed innocent unless the government proves guilt beyond a reasonable doubt.
If Isa or Virtual Assets LLC were convicted, they would be required to forfeit any property involved in the alleged money-laundering offense, including a personal money judgment, and the government could seek substitute assets if the original property could not be recovered.
#Bitcoin #BitcoinATM #Jucom #cryptocurrency #blockchain $BTC/USDT $ETH/USDT $JU/USDT


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-11-19 11:12
📛 Bitcoin ATM Company Founder Charged in Alleged $10 Million Money Laundering Scheme!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
When hype took over 🚀, Bob sold his car 🚗, took out a loan 💳, and went all-in on a trending coin 💰. Then the market crashed 📉 -99%, and Bob was left with nothing but a banana peel 🍌.
This short is your reminder: don’t just ape in 🦍. Don’t go all-in ⚠️. Do your research 📚, protect your capital 💵, and avoid becoming the next Bob.
Not financial advice. Always DYOR 🔍.


Ju.com Media
2025-08-08 14:19
Bob Aped-In… And Lost EVERYTHING 🍌💥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
$JU/USDT just hit new ATH: $22
Road to $50
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #JU

Mrconfamm
2025-08-30 17:54
$JU Touch new ATH
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.