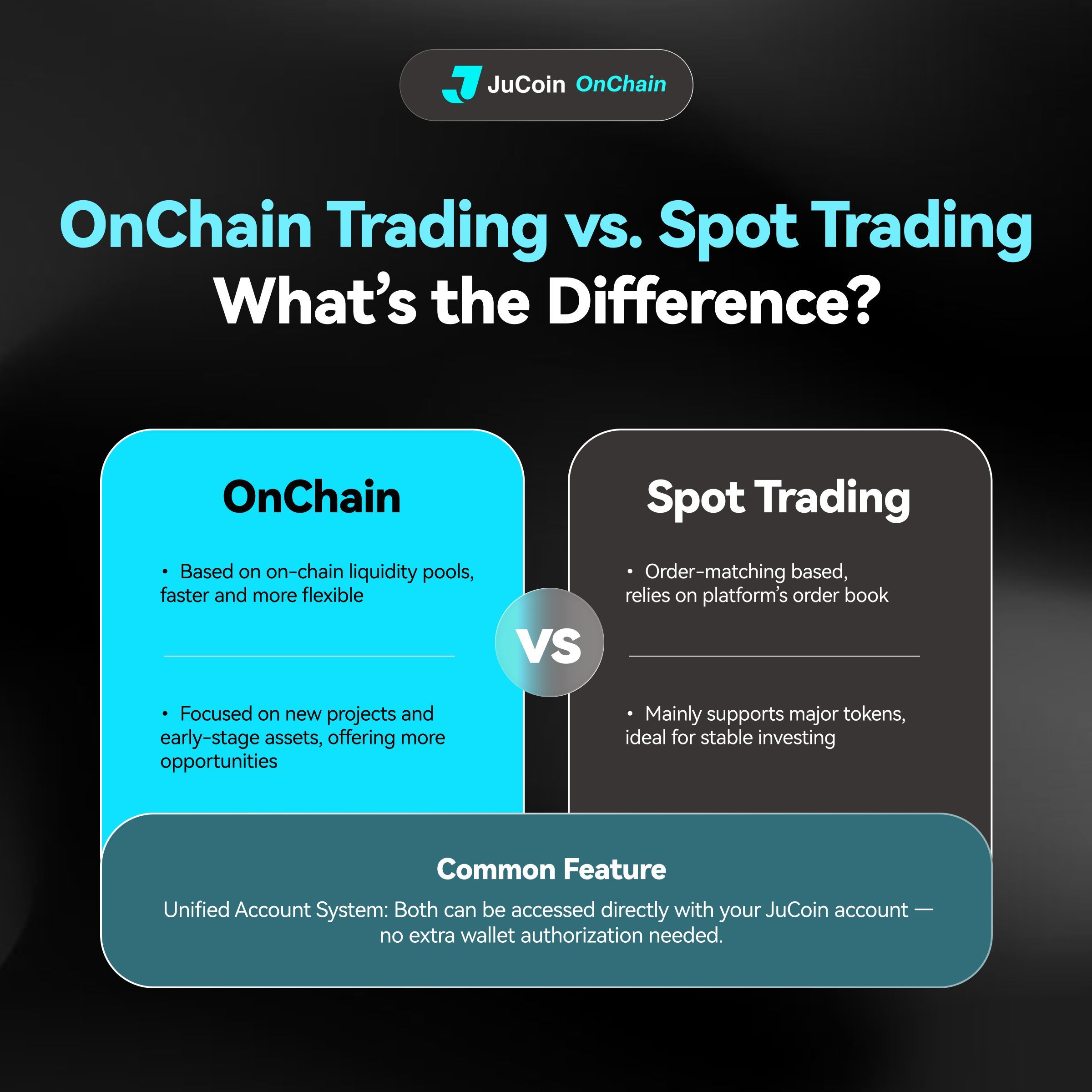
Découvrez OnChain – la façon la plus rapide de trader les nouveaux projets et actifs émergents
✅ Exécution ultra-rapide ✅ Flexibilité maximale ✅ Tradez directement avec votre compte JuCoin – pas de wallet requis
https://www.jucoin.com/en/onchain/ #JuCoin #crypto #Web3 #EarlyAccess


Carmelita
2025-08-21 15:31
Envie de profiter des opportunités en avant-première ?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Gagne $100 en $YZY – 5 gagnants à se partager le lot
✅ Commente ton UID ✅ Remplis le formulaire 👉 https://gleam.io/lOPaN/join-to-win-100-worth-of-yzy
⏰ 48h pour participer ⚡ Ne rate pas ta chance ! #YZY #crypto #Giveaway #Airdrop



Carmelita
2025-08-21 14:43
🎁 Giveaway Alert! 💙
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Chaque hausse = victoire signée par la communauté 💎🙌
💬 Team hodl ou team FOMO ? #JuCoin #crypto #ATH #Bullish



Carmelita
2025-08-19 13:36
🔥 $JU frappe un nouvel ATH : 19$ !
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
💡 Idées → déployées en secondes 👤 Utilisateurs → onboarding sans friction 🌱 Croissance → 100M$ pour l’écosystème
Ce n’est pas un rêve, c’est #JuChain aujourd’hui 🚀
Builders, rêveurs, leaders de communautés : Le futur n’attend pas — et vous non plus.
🔗 https://www.juchain.org/en/developer-support #Web3 #crypto #BUIDL #JuChain



Carmelita
2025-08-21 14:49
JuChain Genesis Ark Program
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Future Challenges for Global Crypto Adoption
As the world increasingly integrates digital currencies into everyday life, understanding the hurdles that could impede widespread crypto adoption becomes essential. While blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies have made significant strides, several persistent challenges threaten to slow or even halt their mainstream acceptance. This article explores these obstacles in detail, providing insights into regulatory, security, market, infrastructural, educational, environmental, and scalability issues that lie ahead.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Its Impact on Cryptocurrency Growth
One of the most significant barriers to global crypto adoption is the lack of clear and consistent regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. Countries vary widely in how they approach digital assets—some embrace cryptocurrencies with open arms; others impose strict bans or ambiguous rules. This patchwork creates a landscape fraught with legal ambiguity for investors and businesses alike.
Recent developments highlight this ongoing uncertainty. For instance, in April 2025, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued a statement clarifying its stance on digital asset regulation—a move met with mixed reactions from industry stakeholders. Such regulatory ambiguity can deter institutional investors who seek clarity before committing substantial capital to crypto markets.
The absence of comprehensive regulations can lead to legal risks for companies operating within this space—potentially resulting in fines or shutdowns—and discourage mainstream financial institutions from integrating cryptocurrencies into their services. As governments worldwide continue to refine their policies on digital assets, achieving a balanced framework that fosters innovation while ensuring consumer protection remains a critical challenge.
Security Concerns Eroding Trust in Digital Assets
Security remains at the forefront of concerns surrounding cryptocurrency adoption. Despite advancements in blockchain security protocols, high-profile hacks continue to undermine confidence among users and potential adopters.
In March 2025 alone, a major cryptocurrency exchange suffered a significant breach resulting in millions of dollars worth of digital assets being stolen. Such incidents not only cause immediate financial losses but also damage long-term trust in crypto platforms' safety measures.
For broader acceptance—especially among institutional investors—the security infrastructure must be robust enough to prevent future breaches. Ongoing efforts include implementing multi-signature wallets, decentralized exchanges with enhanced security features—and increasing transparency around cybersecurity practices are vital steps forward.
Failure to address these concerns could lead users toward more traditional financial systems or alternative investments perceived as safer options—hindering overall growth within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Market Volatility as an Adoption Barrier
Cryptocurrency markets are notorious for their extreme price fluctuations over short periods—a characteristic that can deter both individual traders and large-scale enterprises from embracing digital currencies fully.
In early 2025 alone, Bitcoin and Ethereum experienced substantial swings causing major losses for some investors; Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy), which holds large Bitcoin reserves as part of its corporate strategy reported a $4.2 billion net loss due to volatile price movements during Q1 2025.
This volatility complicates use cases such as daily transactions or business payments where stable value is crucial. Companies may hesitate to accept cryptocurrencies if they fear rapid devaluation affecting profitability or operational costs significantly.
To mitigate this issue:
- Stablecoins pegged against fiat currencies are gaining popularity.
- Derivative products offer hedging options.
- Developing more mature markets with higher liquidity can reduce volatility over time.However—as long as speculative trading dominates crypto markets—the risk associated with sudden price swings will remain an obstacle for mass adoption.
Infrastructure Development: Building Reliable Payment Ecosystems
A well-developed infrastructure is fundamental for seamless cryptocurrency transactions—from user-friendly wallets to integrated payment systems capable of handling high transaction volumes efficiently.
Recent initiatives demonstrate progress: In April 2025 , firms like Cantor Financial Group partnered with Tether and SoftBank launching Twenty One Capital—aimingto become oneoftheworld’s largest bitcoin treasuries—which underscores ongoing efforts toward infrastructure expansion[3].
Despite such developments:
- Many regions still lack reliable payment gateways supporting cryptocurrencies.
- Transaction speeds remain inconsistent across networks.
- High fees during peak times hinder usability at scale.These limitations restrict everyday use cases like retail shopping or remittances—key drivers needed for mainstream acceptance—and highlight areas requiring further technological innovation such as layer 2 scaling solutions (e.g., Lightning Network)and sharding techniquesto improve throughputand reduce costs .
Education Gaps Hindering Broader Public Understanding
A significant portion of potential users still lacks foundational knowledge about how cryptocurrencies work—including blockchain technology's benefits versus risks—which hampers wider acceptance beyond tech-savvy communities .
Efforts are underway globally through educational campaigns aimed at demystifying cryptos’ mechanicsand promoting responsible investing practices . Nonetheless , misconceptions persist regarding issues like decentralization , privacy , taxation,and environmental impact .
Bridging this knowledge gap is crucial because informed consumers tendto make better decisions —whether adopting new payment methodsor investing responsibly —ultimately fostering trustand encouraging broader participationincryptocurrency ecosystems .
Environmental Concerns Affecting Regulatory Policies
The energy consumption associated with mining certain proof-of-work cryptocurrencies has sparked environmental debates worldwide . Critics argue that large-scale mining operations consume vast amountsof electricity —sometimes sourcedfrom fossil fuels—raising sustainability questions .
Some countries have responded by exploring greener alternatives:
- Transitioning towards renewable energy-powered mining farms
- Promoting proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms which require less energyNegative perceptions about environmental impact could influence future regulations , potentially leading tomore restrictive policiesthat limit mining activitiesor impose carbon taxeson miners[6].
Addressing these concerns involves balancing technological innovationwith ecological responsibility—to ensure sustainable growth without compromising environmental integrity .
Scalability Challenges Limiting Transaction Capacity
As demand increases,the current capacity limitsof many blockchain networks become apparent . High transaction feesand slow confirmation times during peak periods hinder practical usage scenarios like retail paymentsor microtransactions .
Research teams are actively working on solutions:1.Layer 2 scaling solutionssuch as state channelsand sidechains aimto offload transactionsfrom main chains .2.Sharding techniques distribute network loadacross multiple segmentsfor increased throughput .3.Blockchain interoperability protocols facilitate communication between different networks,to create unified ecosystems capableof handling larger volumes seamlessly[7].
Without effective scalability improvements,this bottleneck could resultin user frustration,reduced transaction speed,and higher costs—all factors discouraging mass adoption across diverse sectors including finance,e-commerce,and remittances.
Navigating Future Pathways Toward Widespread Adoption
Overcoming these multifaceted challenges requires coordinated efforts among regulators,businesses,and technologists alike.To foster trust,safety,and efficiency within cryptocurrency ecosystems,the industry must prioritize transparent regulation development,enforce rigorous security standards,and invest heavilyin infrastructural upgrades alongwith public education initiatives .
Furthermore,the evolution towards sustainable practices addressing environmental impacts will be critical—not only ethically but also politically—to avoid restrictive legislation that might stifle innovation.[8] As research progresseson scalability solutions,the promise remains high: creating faster,morereliable,inclusivecrypto networks capableof supporting global economic integration.
Final Thoughts
While numerous hurdles stand between current state-of-the-art blockchain applicationsand full-fledged global crypto adoption,it’s evident that proactive strategies targeting regulation clarity,safety enhancements,infrastructure robustness,population education,sustainability measures,and scalable technology development will shape future success stories . The path forward involves collaborative effortsto unlockcryptocurrencies’ transformative potential while mitigating risks inherent within emerging technologies.
References
1. [Link]
2. [Link]
3. [Link]
4. [Link]
5. [Link]
6. [Link]
7. [Link]
8. [Link]


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-11 14:02
What are the future challenges for global crypto adoption?
Future Challenges for Global Crypto Adoption
As the world increasingly integrates digital currencies into everyday life, understanding the hurdles that could impede widespread crypto adoption becomes essential. While blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies have made significant strides, several persistent challenges threaten to slow or even halt their mainstream acceptance. This article explores these obstacles in detail, providing insights into regulatory, security, market, infrastructural, educational, environmental, and scalability issues that lie ahead.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Its Impact on Cryptocurrency Growth
One of the most significant barriers to global crypto adoption is the lack of clear and consistent regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. Countries vary widely in how they approach digital assets—some embrace cryptocurrencies with open arms; others impose strict bans or ambiguous rules. This patchwork creates a landscape fraught with legal ambiguity for investors and businesses alike.
Recent developments highlight this ongoing uncertainty. For instance, in April 2025, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued a statement clarifying its stance on digital asset regulation—a move met with mixed reactions from industry stakeholders. Such regulatory ambiguity can deter institutional investors who seek clarity before committing substantial capital to crypto markets.
The absence of comprehensive regulations can lead to legal risks for companies operating within this space—potentially resulting in fines or shutdowns—and discourage mainstream financial institutions from integrating cryptocurrencies into their services. As governments worldwide continue to refine their policies on digital assets, achieving a balanced framework that fosters innovation while ensuring consumer protection remains a critical challenge.
Security Concerns Eroding Trust in Digital Assets
Security remains at the forefront of concerns surrounding cryptocurrency adoption. Despite advancements in blockchain security protocols, high-profile hacks continue to undermine confidence among users and potential adopters.
In March 2025 alone, a major cryptocurrency exchange suffered a significant breach resulting in millions of dollars worth of digital assets being stolen. Such incidents not only cause immediate financial losses but also damage long-term trust in crypto platforms' safety measures.
For broader acceptance—especially among institutional investors—the security infrastructure must be robust enough to prevent future breaches. Ongoing efforts include implementing multi-signature wallets, decentralized exchanges with enhanced security features—and increasing transparency around cybersecurity practices are vital steps forward.
Failure to address these concerns could lead users toward more traditional financial systems or alternative investments perceived as safer options—hindering overall growth within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Market Volatility as an Adoption Barrier
Cryptocurrency markets are notorious for their extreme price fluctuations over short periods—a characteristic that can deter both individual traders and large-scale enterprises from embracing digital currencies fully.
In early 2025 alone, Bitcoin and Ethereum experienced substantial swings causing major losses for some investors; Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy), which holds large Bitcoin reserves as part of its corporate strategy reported a $4.2 billion net loss due to volatile price movements during Q1 2025.
This volatility complicates use cases such as daily transactions or business payments where stable value is crucial. Companies may hesitate to accept cryptocurrencies if they fear rapid devaluation affecting profitability or operational costs significantly.
To mitigate this issue:
- Stablecoins pegged against fiat currencies are gaining popularity.
- Derivative products offer hedging options.
- Developing more mature markets with higher liquidity can reduce volatility over time.However—as long as speculative trading dominates crypto markets—the risk associated with sudden price swings will remain an obstacle for mass adoption.
Infrastructure Development: Building Reliable Payment Ecosystems
A well-developed infrastructure is fundamental for seamless cryptocurrency transactions—from user-friendly wallets to integrated payment systems capable of handling high transaction volumes efficiently.
Recent initiatives demonstrate progress: In April 2025 , firms like Cantor Financial Group partnered with Tether and SoftBank launching Twenty One Capital—aimingto become oneoftheworld’s largest bitcoin treasuries—which underscores ongoing efforts toward infrastructure expansion[3].
Despite such developments:
- Many regions still lack reliable payment gateways supporting cryptocurrencies.
- Transaction speeds remain inconsistent across networks.
- High fees during peak times hinder usability at scale.These limitations restrict everyday use cases like retail shopping or remittances—key drivers needed for mainstream acceptance—and highlight areas requiring further technological innovation such as layer 2 scaling solutions (e.g., Lightning Network)and sharding techniquesto improve throughputand reduce costs .
Education Gaps Hindering Broader Public Understanding
A significant portion of potential users still lacks foundational knowledge about how cryptocurrencies work—including blockchain technology's benefits versus risks—which hampers wider acceptance beyond tech-savvy communities .
Efforts are underway globally through educational campaigns aimed at demystifying cryptos’ mechanicsand promoting responsible investing practices . Nonetheless , misconceptions persist regarding issues like decentralization , privacy , taxation,and environmental impact .
Bridging this knowledge gap is crucial because informed consumers tendto make better decisions —whether adopting new payment methodsor investing responsibly —ultimately fostering trustand encouraging broader participationincryptocurrency ecosystems .
Environmental Concerns Affecting Regulatory Policies
The energy consumption associated with mining certain proof-of-work cryptocurrencies has sparked environmental debates worldwide . Critics argue that large-scale mining operations consume vast amountsof electricity —sometimes sourcedfrom fossil fuels—raising sustainability questions .
Some countries have responded by exploring greener alternatives:
- Transitioning towards renewable energy-powered mining farms
- Promoting proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms which require less energyNegative perceptions about environmental impact could influence future regulations , potentially leading tomore restrictive policiesthat limit mining activitiesor impose carbon taxeson miners[6].
Addressing these concerns involves balancing technological innovationwith ecological responsibility—to ensure sustainable growth without compromising environmental integrity .
Scalability Challenges Limiting Transaction Capacity
As demand increases,the current capacity limitsof many blockchain networks become apparent . High transaction feesand slow confirmation times during peak periods hinder practical usage scenarios like retail paymentsor microtransactions .
Research teams are actively working on solutions:1.Layer 2 scaling solutionssuch as state channelsand sidechains aimto offload transactionsfrom main chains .2.Sharding techniques distribute network loadacross multiple segmentsfor increased throughput .3.Blockchain interoperability protocols facilitate communication between different networks,to create unified ecosystems capableof handling larger volumes seamlessly[7].
Without effective scalability improvements,this bottleneck could resultin user frustration,reduced transaction speed,and higher costs—all factors discouraging mass adoption across diverse sectors including finance,e-commerce,and remittances.
Navigating Future Pathways Toward Widespread Adoption
Overcoming these multifaceted challenges requires coordinated efforts among regulators,businesses,and technologists alike.To foster trust,safety,and efficiency within cryptocurrency ecosystems,the industry must prioritize transparent regulation development,enforce rigorous security standards,and invest heavilyin infrastructural upgrades alongwith public education initiatives .
Furthermore,the evolution towards sustainable practices addressing environmental impacts will be critical—not only ethically but also politically—to avoid restrictive legislation that might stifle innovation.[8] As research progresseson scalability solutions,the promise remains high: creating faster,morereliable,inclusivecrypto networks capableof supporting global economic integration.
Final Thoughts
While numerous hurdles stand between current state-of-the-art blockchain applicationsand full-fledged global crypto adoption,it’s evident that proactive strategies targeting regulation clarity,safety enhancements,infrastructure robustness,population education,sustainability measures,and scalable technology development will shape future success stories . The path forward involves collaborative effortsto unlockcryptocurrencies’ transformative potential while mitigating risks inherent within emerging technologies.
References
1. [Link]
2. [Link]
3. [Link]
4. [Link]
5. [Link]
6. [Link]
7. [Link]
8. [Link]
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
$JU Savings arrive demain ! Ne clignez pas des yeux — saisissez-le. verrouillez-le. faites-le croître. https://jucoin.online/en/accounts/register?ref=USJYGL



Carmelita
2025-09-01 22:54
Tick. Tock.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Effective Strategies for Managing Risk When Investing in Cryptocurrency
Investing in cryptocurrencies offers exciting opportunities but also comes with significant risks. As the market remains highly volatile, understanding and implementing effective risk management strategies is essential for protecting your investments and maximizing potential returns. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of proven methods to manage crypto investment risks effectively.
Understanding the Risks of Cryptocurrency Investment
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their rapid price fluctuations, which can lead to substantial gains or losses within short periods. Several factors contribute to this volatility, including regulatory developments, technological innovations, market sentiment shifts, and liquidity issues. Recognizing these risks helps investors develop appropriate strategies to navigate the unpredictable landscape.
Regulatory uncertainty is a prominent concern; governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding digital assets. Changes in regulations can significantly impact cryptocurrency prices—either boosting confidence or causing sharp declines. Security threats also pose serious challenges; hacking incidents on exchanges or wallets have resulted in irreversible losses for many investors. Additionally, low liquidity in certain cryptocurrencies makes it difficult to buy or sell large amounts without affecting prices adversely.
Key Risk Management Strategies for Crypto Investors
Implementing structured risk management techniques can help mitigate potential losses while allowing investors to participate actively in the market's growth prospects.
Diversification remains one of the most fundamental strategies—spreading investments across various cryptocurrencies and other asset classes reduces exposure to any single asset’s downturns. For example, holding a mix of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and emerging altcoins can balance out volatility inherent in individual tokens.
Stop-loss orders are automated instructions that trigger sales when an asset reaches a predetermined price point. This approach limits downside risk by ensuring that losses do not escalate beyond acceptable levels during sudden market drops.
Regular portfolio rebalancing involves reviewing your holdings periodically and adjusting allocations based on current market conditions or changing investment goals. This practice maintains an optimal risk-return profile over time.
Staying informed through educational research is vital—keeping up with news about regulatory changes, technological advancements like blockchain upgrades, and security best practices helps make informed decisions rather than reacting impulsively during volatile periods.
Utilizing risk assessment tools, such as analytics platforms that evaluate historical data trends or simulate different scenarios based on current conditions, enables more precise evaluation of potential risks associated with specific assets or portfolios.
Recent Developments Impacting Crypto Risk Management
The introduction of financial products like Bitcoin ETFs has increased institutional interest but also added layers of complexity concerning regulation and market behavior. While ETFs facilitate easier access for traditional investors—and potentially stabilize some aspects—they may also introduce new vulnerabilities if not managed carefully due to increased inflows leading to heightened volatility during certain periods [2].
Industry forecasts suggest Bitcoin could reach $200,000 or more by 2025 as adoption expands and volatility decreases [3]. Such optimistic projections highlight both opportunity and caution: rapid growth could attract new investors but might also lead to speculative bubbles if not tempered by prudent risk controls.
Furthermore, recent trends emphasize the importance of close monitoring—especially amid ongoing regulatory discussions—that could influence overall sentiment negatively if policies become restrictive [1].
The Potential Fallout from Poor Risk Management
Failure to implement proper risk mitigation measures can result in severe consequences:
- Increased Market Volatility: Without safeguards like stop-loss orders or diversification strategies, investors may suffer outsized losses during sudden downturns.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of awareness about evolving legal frameworks might expose investors to compliance issues or forced liquidations.
- Security Breaches: Inadequate security practices increase vulnerability; hacking incidents have led many into losing their crypto holdings permanently unless proper safeguards are employed (e.g., hardware wallets).
Being proactive about these risks ensures resilience against adverse events while positioning oneself advantageously within this dynamic environment.
Practical Tips for Managing Crypto Investment Risks
To build a robust approach toward managing cryptocurrency risks effectively:
- Diversify your portfolio across multiple digital assets rather than concentrating holdings solely on one coin.
- Use stop-loss orders strategically—set them at levels aligned with your risk tolerance.
- Regularly review your portfolio’s composition; rebalance as needed based on performance metrics.
- Stay updated through reputable sources about regulatory changes impacting cryptocurrencies.
- Prioritize secure storage solutions such as hardware wallets instead of leaving funds exposed on exchanges prone to hacks.
- Leverage analytical tools designed specifically for crypto markets that assess historical data patterns and forecast potential movements.
- Avoid emotional decision-making; develop clear investment plans grounded in research rather than speculation alone.
By integrating these practices into your investment routine—and continuously educating yourself—you enhance your ability not only to survive turbulent markets but potentially thrive amid them.
Navigating Future Risks & Opportunities in Cryptocurrency Markets
As industry forecasts project continued growth alongside increasing adoption rates [3], it’s crucial for investors always remain vigilant regarding emerging threats such as evolving regulations—or technological vulnerabilities—and capitalize on opportunities through disciplined strategy implementation today.
Understanding how recent developments influence overall stability allows you better prepare against unforeseen shocks while positioning yourself advantageously within this rapidly changing ecosystem.
Final Thoughts: Building Resilience Through Knowledge & Strategy
Effective risk management isn’t just about avoiding losses—it’s about creating sustainable investing habits rooted in knowledge-based decision-making processes tailored specifically toward cryptocurrency's unique landscape . By diversifying investments wisely , employing protective order types , staying informed via credible sources , securing assets properly , leveraging analytical tools ,and maintaining discipline throughout fluctuating markets —you set yourself up not only for survival but long-term success amidst inherent uncertainties.
Remember: The key lies in balancing opportunity with caution — embracing innovation responsibly while safeguarding against its pitfalls ensures you’re well-positioned today—and tomorrow—in the exciting world of crypto investing


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 18:42
What are effective strategies for managing risk when investing in crypto?
Effective Strategies for Managing Risk When Investing in Cryptocurrency
Investing in cryptocurrencies offers exciting opportunities but also comes with significant risks. As the market remains highly volatile, understanding and implementing effective risk management strategies is essential for protecting your investments and maximizing potential returns. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of proven methods to manage crypto investment risks effectively.
Understanding the Risks of Cryptocurrency Investment
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their rapid price fluctuations, which can lead to substantial gains or losses within short periods. Several factors contribute to this volatility, including regulatory developments, technological innovations, market sentiment shifts, and liquidity issues. Recognizing these risks helps investors develop appropriate strategies to navigate the unpredictable landscape.
Regulatory uncertainty is a prominent concern; governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding digital assets. Changes in regulations can significantly impact cryptocurrency prices—either boosting confidence or causing sharp declines. Security threats also pose serious challenges; hacking incidents on exchanges or wallets have resulted in irreversible losses for many investors. Additionally, low liquidity in certain cryptocurrencies makes it difficult to buy or sell large amounts without affecting prices adversely.
Key Risk Management Strategies for Crypto Investors
Implementing structured risk management techniques can help mitigate potential losses while allowing investors to participate actively in the market's growth prospects.
Diversification remains one of the most fundamental strategies—spreading investments across various cryptocurrencies and other asset classes reduces exposure to any single asset’s downturns. For example, holding a mix of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and emerging altcoins can balance out volatility inherent in individual tokens.
Stop-loss orders are automated instructions that trigger sales when an asset reaches a predetermined price point. This approach limits downside risk by ensuring that losses do not escalate beyond acceptable levels during sudden market drops.
Regular portfolio rebalancing involves reviewing your holdings periodically and adjusting allocations based on current market conditions or changing investment goals. This practice maintains an optimal risk-return profile over time.
Staying informed through educational research is vital—keeping up with news about regulatory changes, technological advancements like blockchain upgrades, and security best practices helps make informed decisions rather than reacting impulsively during volatile periods.
Utilizing risk assessment tools, such as analytics platforms that evaluate historical data trends or simulate different scenarios based on current conditions, enables more precise evaluation of potential risks associated with specific assets or portfolios.
Recent Developments Impacting Crypto Risk Management
The introduction of financial products like Bitcoin ETFs has increased institutional interest but also added layers of complexity concerning regulation and market behavior. While ETFs facilitate easier access for traditional investors—and potentially stabilize some aspects—they may also introduce new vulnerabilities if not managed carefully due to increased inflows leading to heightened volatility during certain periods [2].
Industry forecasts suggest Bitcoin could reach $200,000 or more by 2025 as adoption expands and volatility decreases [3]. Such optimistic projections highlight both opportunity and caution: rapid growth could attract new investors but might also lead to speculative bubbles if not tempered by prudent risk controls.
Furthermore, recent trends emphasize the importance of close monitoring—especially amid ongoing regulatory discussions—that could influence overall sentiment negatively if policies become restrictive [1].
The Potential Fallout from Poor Risk Management
Failure to implement proper risk mitigation measures can result in severe consequences:
- Increased Market Volatility: Without safeguards like stop-loss orders or diversification strategies, investors may suffer outsized losses during sudden downturns.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of awareness about evolving legal frameworks might expose investors to compliance issues or forced liquidations.
- Security Breaches: Inadequate security practices increase vulnerability; hacking incidents have led many into losing their crypto holdings permanently unless proper safeguards are employed (e.g., hardware wallets).
Being proactive about these risks ensures resilience against adverse events while positioning oneself advantageously within this dynamic environment.
Practical Tips for Managing Crypto Investment Risks
To build a robust approach toward managing cryptocurrency risks effectively:
- Diversify your portfolio across multiple digital assets rather than concentrating holdings solely on one coin.
- Use stop-loss orders strategically—set them at levels aligned with your risk tolerance.
- Regularly review your portfolio’s composition; rebalance as needed based on performance metrics.
- Stay updated through reputable sources about regulatory changes impacting cryptocurrencies.
- Prioritize secure storage solutions such as hardware wallets instead of leaving funds exposed on exchanges prone to hacks.
- Leverage analytical tools designed specifically for crypto markets that assess historical data patterns and forecast potential movements.
- Avoid emotional decision-making; develop clear investment plans grounded in research rather than speculation alone.
By integrating these practices into your investment routine—and continuously educating yourself—you enhance your ability not only to survive turbulent markets but potentially thrive amid them.
Navigating Future Risks & Opportunities in Cryptocurrency Markets
As industry forecasts project continued growth alongside increasing adoption rates [3], it’s crucial for investors always remain vigilant regarding emerging threats such as evolving regulations—or technological vulnerabilities—and capitalize on opportunities through disciplined strategy implementation today.
Understanding how recent developments influence overall stability allows you better prepare against unforeseen shocks while positioning yourself advantageously within this rapidly changing ecosystem.
Final Thoughts: Building Resilience Through Knowledge & Strategy
Effective risk management isn’t just about avoiding losses—it’s about creating sustainable investing habits rooted in knowledge-based decision-making processes tailored specifically toward cryptocurrency's unique landscape . By diversifying investments wisely , employing protective order types , staying informed via credible sources , securing assets properly , leveraging analytical tools ,and maintaining discipline throughout fluctuating markets —you set yourself up not only for survival but long-term success amidst inherent uncertainties.
Remember: The key lies in balancing opportunity with caution — embracing innovation responsibly while safeguarding against its pitfalls ensures you’re well-positioned today—and tomorrow—in the exciting world of crypto investing
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
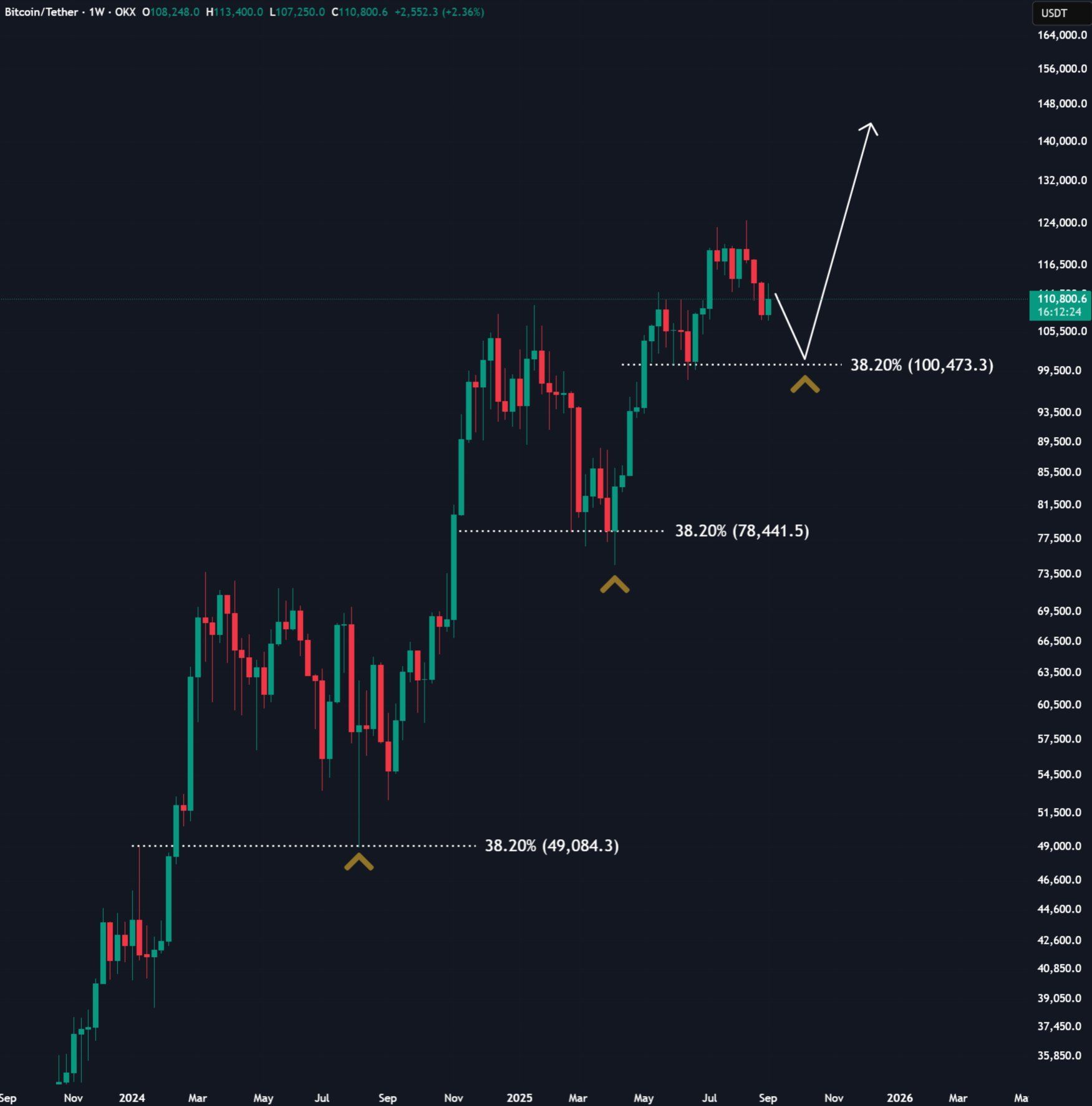
$BTC/USDT vient de clôturer au-dessus de $111K. 👉 Les analystes fixent le pire scénario à ~$100K (-10%).
⚡ Petit rappel historique : lors des cycles passés, Bitcoin encaissait des corrections de 30–40% avant de repartir en orbite.
➡️ Si -10% est désormais le maximum de douleur… alors les taureaux mènent la danse.
#Bitcoin #BTC #crypto #CryptoMarkets


Carmelita
2025-09-07 22:38
📊 Bitcoin bulls flexing their dominance
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Sharding in Blockchain?
Sharding is a transformative scalability solution designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of blockchain networks. As blockchain technology gains widespread adoption, the need to process increasing numbers of transactions quickly and securely becomes critical. Sharding addresses this challenge by dividing the entire network into smaller, manageable segments called shards, each capable of processing transactions independently. This division allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing congestion and improving overall throughput.
In essence, sharding enables a blockchain network to operate more like a distributed database rather than a single monolithic ledger. Each shard functions as its own mini-blockchain with its unique state and transaction history but remains interconnected within the larger network framework. This structure not only boosts transaction speeds but also helps in scaling blockchain solutions for real-world applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and enterprise solutions.
How Does Sharding Work in Blockchain Networks?
The core idea behind sharding involves splitting the workload across various smaller components—shards—that work concurrently. Each shard processes a subset of all transactions based on specific criteria such as user accounts or data types. For example, one shard might handle payment transactions while another manages smart contract interactions.
To maintain consistency across these independent shards, mechanisms like cross-shard communication are implemented. These protocols ensure that when users perform transactions involving multiple shards—say transferring assets from one account managed by one shard to another managed by different shards—the system can verify and record these operations accurately without compromising security or integrity.
Shards typically operate as separate blockchains known as "shard chains." They maintain their own states—such as account balances or smart contract data—and process their designated set of transactions independently before periodically syncing with other shards through consensus protocols designed for cross-shard validation.
Types of Sharding
There are primarily two types of sharding used in blockchain systems:
Horizontal Sharding: This approach divides the network based on transaction types or user groups—for instance, separating payment processing from smart contract execution.
Vertical Sharding: Here, data is partitioned based on storage needs or data categories—for example, storing different kinds of information (user profiles vs transactional logs) separately across various shards.
Both methods aim to optimize resource utilization while maintaining security and decentralization principles inherent in blockchain technology.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Implementing sharding offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By distributing transaction loads across multiple shards, networks can handle many more operations per second compared to traditional single-chain architectures.
Reduced Transaction Fees: Faster processing times mean less congestion; consequently, users often experience lower fees during peak usage periods.
Improved Network Efficiency: Smaller nodes manage fewer tasks within each shard—they require less computational power and storage capacity—making participation easier for more validators.
Parallel Processing: Multiple parts of the network work simultaneously rather than sequentially; this parallelism accelerates overall throughput significantly.
These benefits make sharded blockchains suitable for large-scale applications where high speed and low latency are essential requirements.
Challenges Associated With Blockchain Sharding
Despite its promising potential, implementing sharding introduces complex technical challenges that must be addressed:
Inter-Shard Communication
Ensuring seamless communication between different shards is vital yet difficult. Transactions involving multiple shards require secure protocols that prevent double-spending or inconsistencies—a problem known as cross-shard communication complexity.
Consensus Mechanisms Across Multiple Shards
Traditional consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) are not inherently designed for multi-shard environments. Developing efficient consensus models that work reliably across numerous independent chains remains an ongoing research area within blockchain development communities.
Security Concerns
Dividing a network into smaller segments increases vulnerability risks; if one shard becomes compromised due to an attack or bug exploitation—a scenario called "shard takeover"—it could threaten the entire ecosystem's security integrity unless robust safeguards are implemented effectively throughout all parts of the system.
Standardization & Adoption Barriers
For widespread adoption beyond experimental phases requires industry-wide standards governing how sharded networks communicate and interoperate seamlessly. Without standardization efforts among developers and stakeholders worldwide—including major platforms like Ethereum—the risk exists that fragmentation could hinder progress rather than accelerate it.
Recent Developments in Blockchain Sharding Technology
Major projects have made notable strides toward integrating sharding into their ecosystems:
Ethereum 2.0 has been at the forefront with plans for scalable upgrades through its phased rollout strategy involving beacon chains (launched December 2020). The next steps include deploying dedicated shard chains alongside cross-shard communication protocols aimed at enabling Ethereum’s massive ecosystem to scale efficiently without sacrificing decentralization or security standards.
Polkadot employs relay chains connecting parachains—independent blockchains optimized for specific use cases—that communicate via shared security models facilitating interoperability among diverse networks.
Cosmos, utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithm architecture allows developers to create zones (independent blockchains) capable of interoperation within an overarching hub-and-spoke model similar to Polkadot’s relay chain approach.
Research continues globally exploring innovative techniques such as state sharding, which aims at optimizing how state information is stored across nodes—a crucial factor influencing scalability limits further improvements.
Potential Risks Impacting Future Adoption
While promising solutions exist today—and ongoing research promises even better approaches—the path forward faces hurdles related mainly to:
Security Risks: Smaller individual shards may become targets due to reduced validation power compared with full nodes operating on entire networks.
Interoperability Challenges: Achieving flawless interaction between diverse systems requires standardized protocols; otherwise fragmentation may occur leading toward isolated ecosystems instead of unified platforms.
Adoption Hurdles & Industry Standardization
Without broad agreement on technical standards governing cross-shard communications—as well as regulatory considerations—widespread deployment might slow down considerably despite technological readiness.
Understanding How Blockchain Scaling Evolves Through Sharding
As demand grows exponentially—from DeFi applications demanding rapid trades versus enterprise-level integrations requiring high throughput—the importance lies not just in creating faster blockchains but ensuring they remain secure against evolving threats while interoperable enough for global adoption.
By addressing current limitations through continuous innovation—in protocol design improvements like state sharing techniques—and fostering collaboration among industry leaders worldwide who develop open standards —the future landscape looks promising: scalable yet secure decentralized systems capable enough for mainstream use.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what sharding entails within blockchain technology: how it works technically; why it matters; what benefits it offers; what challenges lie ahead; along with recent advancements shaping its future trajectory—all aligned towards helping users understand both foundational concepts and cutting-edge developments effectively.


Lo
2025-05-15 02:38
What is sharding in blockchain?
What Is Sharding in Blockchain?
Sharding is a transformative scalability solution designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of blockchain networks. As blockchain technology gains widespread adoption, the need to process increasing numbers of transactions quickly and securely becomes critical. Sharding addresses this challenge by dividing the entire network into smaller, manageable segments called shards, each capable of processing transactions independently. This division allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing congestion and improving overall throughput.
In essence, sharding enables a blockchain network to operate more like a distributed database rather than a single monolithic ledger. Each shard functions as its own mini-blockchain with its unique state and transaction history but remains interconnected within the larger network framework. This structure not only boosts transaction speeds but also helps in scaling blockchain solutions for real-world applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and enterprise solutions.
How Does Sharding Work in Blockchain Networks?
The core idea behind sharding involves splitting the workload across various smaller components—shards—that work concurrently. Each shard processes a subset of all transactions based on specific criteria such as user accounts or data types. For example, one shard might handle payment transactions while another manages smart contract interactions.
To maintain consistency across these independent shards, mechanisms like cross-shard communication are implemented. These protocols ensure that when users perform transactions involving multiple shards—say transferring assets from one account managed by one shard to another managed by different shards—the system can verify and record these operations accurately without compromising security or integrity.
Shards typically operate as separate blockchains known as "shard chains." They maintain their own states—such as account balances or smart contract data—and process their designated set of transactions independently before periodically syncing with other shards through consensus protocols designed for cross-shard validation.
Types of Sharding
There are primarily two types of sharding used in blockchain systems:
Horizontal Sharding: This approach divides the network based on transaction types or user groups—for instance, separating payment processing from smart contract execution.
Vertical Sharding: Here, data is partitioned based on storage needs or data categories—for example, storing different kinds of information (user profiles vs transactional logs) separately across various shards.
Both methods aim to optimize resource utilization while maintaining security and decentralization principles inherent in blockchain technology.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Implementing sharding offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By distributing transaction loads across multiple shards, networks can handle many more operations per second compared to traditional single-chain architectures.
Reduced Transaction Fees: Faster processing times mean less congestion; consequently, users often experience lower fees during peak usage periods.
Improved Network Efficiency: Smaller nodes manage fewer tasks within each shard—they require less computational power and storage capacity—making participation easier for more validators.
Parallel Processing: Multiple parts of the network work simultaneously rather than sequentially; this parallelism accelerates overall throughput significantly.
These benefits make sharded blockchains suitable for large-scale applications where high speed and low latency are essential requirements.
Challenges Associated With Blockchain Sharding
Despite its promising potential, implementing sharding introduces complex technical challenges that must be addressed:
Inter-Shard Communication
Ensuring seamless communication between different shards is vital yet difficult. Transactions involving multiple shards require secure protocols that prevent double-spending or inconsistencies—a problem known as cross-shard communication complexity.
Consensus Mechanisms Across Multiple Shards
Traditional consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) are not inherently designed for multi-shard environments. Developing efficient consensus models that work reliably across numerous independent chains remains an ongoing research area within blockchain development communities.
Security Concerns
Dividing a network into smaller segments increases vulnerability risks; if one shard becomes compromised due to an attack or bug exploitation—a scenario called "shard takeover"—it could threaten the entire ecosystem's security integrity unless robust safeguards are implemented effectively throughout all parts of the system.
Standardization & Adoption Barriers
For widespread adoption beyond experimental phases requires industry-wide standards governing how sharded networks communicate and interoperate seamlessly. Without standardization efforts among developers and stakeholders worldwide—including major platforms like Ethereum—the risk exists that fragmentation could hinder progress rather than accelerate it.
Recent Developments in Blockchain Sharding Technology
Major projects have made notable strides toward integrating sharding into their ecosystems:
Ethereum 2.0 has been at the forefront with plans for scalable upgrades through its phased rollout strategy involving beacon chains (launched December 2020). The next steps include deploying dedicated shard chains alongside cross-shard communication protocols aimed at enabling Ethereum’s massive ecosystem to scale efficiently without sacrificing decentralization or security standards.
Polkadot employs relay chains connecting parachains—independent blockchains optimized for specific use cases—that communicate via shared security models facilitating interoperability among diverse networks.
Cosmos, utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithm architecture allows developers to create zones (independent blockchains) capable of interoperation within an overarching hub-and-spoke model similar to Polkadot’s relay chain approach.
Research continues globally exploring innovative techniques such as state sharding, which aims at optimizing how state information is stored across nodes—a crucial factor influencing scalability limits further improvements.
Potential Risks Impacting Future Adoption
While promising solutions exist today—and ongoing research promises even better approaches—the path forward faces hurdles related mainly to:
Security Risks: Smaller individual shards may become targets due to reduced validation power compared with full nodes operating on entire networks.
Interoperability Challenges: Achieving flawless interaction between diverse systems requires standardized protocols; otherwise fragmentation may occur leading toward isolated ecosystems instead of unified platforms.
Adoption Hurdles & Industry Standardization
Without broad agreement on technical standards governing cross-shard communications—as well as regulatory considerations—widespread deployment might slow down considerably despite technological readiness.
Understanding How Blockchain Scaling Evolves Through Sharding
As demand grows exponentially—from DeFi applications demanding rapid trades versus enterprise-level integrations requiring high throughput—the importance lies not just in creating faster blockchains but ensuring they remain secure against evolving threats while interoperable enough for global adoption.
By addressing current limitations through continuous innovation—in protocol design improvements like state sharing techniques—and fostering collaboration among industry leaders worldwide who develop open standards —the future landscape looks promising: scalable yet secure decentralized systems capable enough for mainstream use.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what sharding entails within blockchain technology: how it works technically; why it matters; what benefits it offers; what challenges lie ahead; along with recent advancements shaping its future trajectory—all aligned towards helping users understand both foundational concepts and cutting-edge developments effectively.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Impermanent Loss in Crypto?
Impermanent loss is a fundamental concept in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem that every liquidity provider (LP) should understand. It refers to the potential financial loss that can occur when providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange (DEX). While offering liquidity can generate passive income through trading fees, impermanent loss highlights the risks involved, especially during volatile market conditions.
Understanding Impermanent Loss
At its core, impermanent loss happens because of price fluctuations between two tokens within a liquidity pool. When LPs deposit tokens into a pool—say ETH and USDT—they are effectively supplying both assets to facilitate trades on platforms like Uniswap or SushiSwap. The pool uses an automated market maker (AMM) algorithm to maintain balance and enable seamless trading.
However, if one token's price changes significantly relative to the other after your deposit, the value of your pooled assets may be less than simply holding those tokens outside the pool. This discrepancy is what we call "impermanent" because it isn't realized as an actual loss until you withdraw your funds; if prices revert or stabilize before withdrawal, some or all of this potential loss can be mitigated.
Why Does Impermanent Loss Occur?
Impermanent loss results from how AMMs manage token ratios based on current prices rather than fixed quantities. When traders swap tokens within a pool, they cause shifts in token balances which impact LPs' holdings. For example:
- If Token A's price increases significantly compared to Token B,
- The AMM automatically adjusts by selling some of Token A for more of Token B,
- Leading to an imbalance where LPs hold fewer high-value tokens and more low-value ones upon withdrawal.
This process means that even though trading fees earned might offset some losses, substantial price swings can still lead LPs into negative returns relative to simply holding their original assets.
Factors That Influence Impermanent Loss
Several factors determine how much impermanent loss an LP might experience:
Market Volatility: High volatility causes larger price swings and increases risk.
Token Pair Correlation: Well-correlated pairs like stablecoins tend to have lower impermanence risk compared with volatile pairs such as ETH/ALT coins.
Pool Size and Liquidity Depth: Larger pools with deep liquidity tend to absorb shocks better; smaller pools are more susceptible to manipulation or large swings.
Market Trends: Rapid upward or downward trends amplify potential losses during periods of significant movement.
Understanding these factors helps LPs assess whether providing liquidity aligns with their risk appetite and investment goals.
Strategies for Managing Impermanent Loss
While impermanent loss cannot be entirely eliminated without sacrificing potential earnings from trading fees, several strategies help mitigate its impact:
Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple pools reduces exposure concentrated in one asset pair.
Choosing Stablecoin Pairs: Pools involving stablecoins like USDC/USDT minimize volatility-related risks.
Monitoring Market Conditions: Staying informed about market trends allows timely decisions about adding or removing liquidity.
Utilizing Risk Management Tools: Some DeFi platforms offer features such as dynamic fee adjustments or insurance options designed specifically for reducing impermanence risks.
Yield Farming & Incentives: Combining staking rewards with fee earnings can offset potential losses over time.
By applying these approaches thoughtfully, users can better balance earning opportunities against associated risks.
Recent Developments Addressing Impermanent Loss
The DeFi sector has seen ongoing innovation aimed at reducing impermanence concerns:
Several platforms now incorporate dynamic fee structures that increase transaction costs during high volatility periods—compensating LPs for increased risk.
New protocols are experimenting with hybrid models combining AMMs with order book mechanisms for improved stability.
Education initiatives focus on increasing user awareness around impermanent loss so investors make informed decisions rather than relying solely on platform marketing claims.
Additionally, regulatory scrutiny has increased transparency requirements around disclosures related to impermanence risks—a move aimed at protecting retail investors from unexpected losses while fostering trust in DeFi ecosystems.
Potential Risks Beyond Financial Losses
Impermanent loss not only affects individual users but also has broader implications:
Reduced user confidence could slow down adoption if participants perceive high risks without adequate safeguards.
Lack of transparency regarding possible losses may attract regulatory attention—potentially leading toward stricter compliance standards across jurisdictions.
Furthermore, significant instances of large-scale withdrawals due to perceived unrecoverable losses could contribute negatively toward overall market stability within DeFi ecosystems.
Navigating Impermanent Loss Effectively
For anyone considering participating as an LP in crypto markets via DEXes, understanding how impermanent loss works is crucial for making informed decisions aligned with personal investment strategies. While it presents inherent risks tied closely with market volatility and asset selection choices, ongoing innovations aim at minimizing its impact through smarter protocol design and better educational resources.
By staying updated on recent developments—and employing sound risk management practices—investors can enjoy the benefits offered by DeFi’s yield opportunities while safeguarding their capital against unnecessary exposure.
Keywords: Imper permanentloss crypto | Decentralized Finance Risks | Liquidity Pool Management | Crypto Market Volatility | DeFi Investment Strategies


Lo
2025-05-14 06:40
What is impermanent loss?
What Is Impermanent Loss in Crypto?
Impermanent loss is a fundamental concept in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem that every liquidity provider (LP) should understand. It refers to the potential financial loss that can occur when providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange (DEX). While offering liquidity can generate passive income through trading fees, impermanent loss highlights the risks involved, especially during volatile market conditions.
Understanding Impermanent Loss
At its core, impermanent loss happens because of price fluctuations between two tokens within a liquidity pool. When LPs deposit tokens into a pool—say ETH and USDT—they are effectively supplying both assets to facilitate trades on platforms like Uniswap or SushiSwap. The pool uses an automated market maker (AMM) algorithm to maintain balance and enable seamless trading.
However, if one token's price changes significantly relative to the other after your deposit, the value of your pooled assets may be less than simply holding those tokens outside the pool. This discrepancy is what we call "impermanent" because it isn't realized as an actual loss until you withdraw your funds; if prices revert or stabilize before withdrawal, some or all of this potential loss can be mitigated.
Why Does Impermanent Loss Occur?
Impermanent loss results from how AMMs manage token ratios based on current prices rather than fixed quantities. When traders swap tokens within a pool, they cause shifts in token balances which impact LPs' holdings. For example:
- If Token A's price increases significantly compared to Token B,
- The AMM automatically adjusts by selling some of Token A for more of Token B,
- Leading to an imbalance where LPs hold fewer high-value tokens and more low-value ones upon withdrawal.
This process means that even though trading fees earned might offset some losses, substantial price swings can still lead LPs into negative returns relative to simply holding their original assets.
Factors That Influence Impermanent Loss
Several factors determine how much impermanent loss an LP might experience:
Market Volatility: High volatility causes larger price swings and increases risk.
Token Pair Correlation: Well-correlated pairs like stablecoins tend to have lower impermanence risk compared with volatile pairs such as ETH/ALT coins.
Pool Size and Liquidity Depth: Larger pools with deep liquidity tend to absorb shocks better; smaller pools are more susceptible to manipulation or large swings.
Market Trends: Rapid upward or downward trends amplify potential losses during periods of significant movement.
Understanding these factors helps LPs assess whether providing liquidity aligns with their risk appetite and investment goals.
Strategies for Managing Impermanent Loss
While impermanent loss cannot be entirely eliminated without sacrificing potential earnings from trading fees, several strategies help mitigate its impact:
Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple pools reduces exposure concentrated in one asset pair.
Choosing Stablecoin Pairs: Pools involving stablecoins like USDC/USDT minimize volatility-related risks.
Monitoring Market Conditions: Staying informed about market trends allows timely decisions about adding or removing liquidity.
Utilizing Risk Management Tools: Some DeFi platforms offer features such as dynamic fee adjustments or insurance options designed specifically for reducing impermanence risks.
Yield Farming & Incentives: Combining staking rewards with fee earnings can offset potential losses over time.
By applying these approaches thoughtfully, users can better balance earning opportunities against associated risks.
Recent Developments Addressing Impermanent Loss
The DeFi sector has seen ongoing innovation aimed at reducing impermanence concerns:
Several platforms now incorporate dynamic fee structures that increase transaction costs during high volatility periods—compensating LPs for increased risk.
New protocols are experimenting with hybrid models combining AMMs with order book mechanisms for improved stability.
Education initiatives focus on increasing user awareness around impermanent loss so investors make informed decisions rather than relying solely on platform marketing claims.
Additionally, regulatory scrutiny has increased transparency requirements around disclosures related to impermanence risks—a move aimed at protecting retail investors from unexpected losses while fostering trust in DeFi ecosystems.
Potential Risks Beyond Financial Losses
Impermanent loss not only affects individual users but also has broader implications:
Reduced user confidence could slow down adoption if participants perceive high risks without adequate safeguards.
Lack of transparency regarding possible losses may attract regulatory attention—potentially leading toward stricter compliance standards across jurisdictions.
Furthermore, significant instances of large-scale withdrawals due to perceived unrecoverable losses could contribute negatively toward overall market stability within DeFi ecosystems.
Navigating Impermanent Loss Effectively
For anyone considering participating as an LP in crypto markets via DEXes, understanding how impermanent loss works is crucial for making informed decisions aligned with personal investment strategies. While it presents inherent risks tied closely with market volatility and asset selection choices, ongoing innovations aim at minimizing its impact through smarter protocol design and better educational resources.
By staying updated on recent developments—and employing sound risk management practices—investors can enjoy the benefits offered by DeFi’s yield opportunities while safeguarding their capital against unnecessary exposure.
Keywords: Imper permanentloss crypto | Decentralized Finance Risks | Liquidity Pool Management | Crypto Market Volatility | DeFi Investment Strategies
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
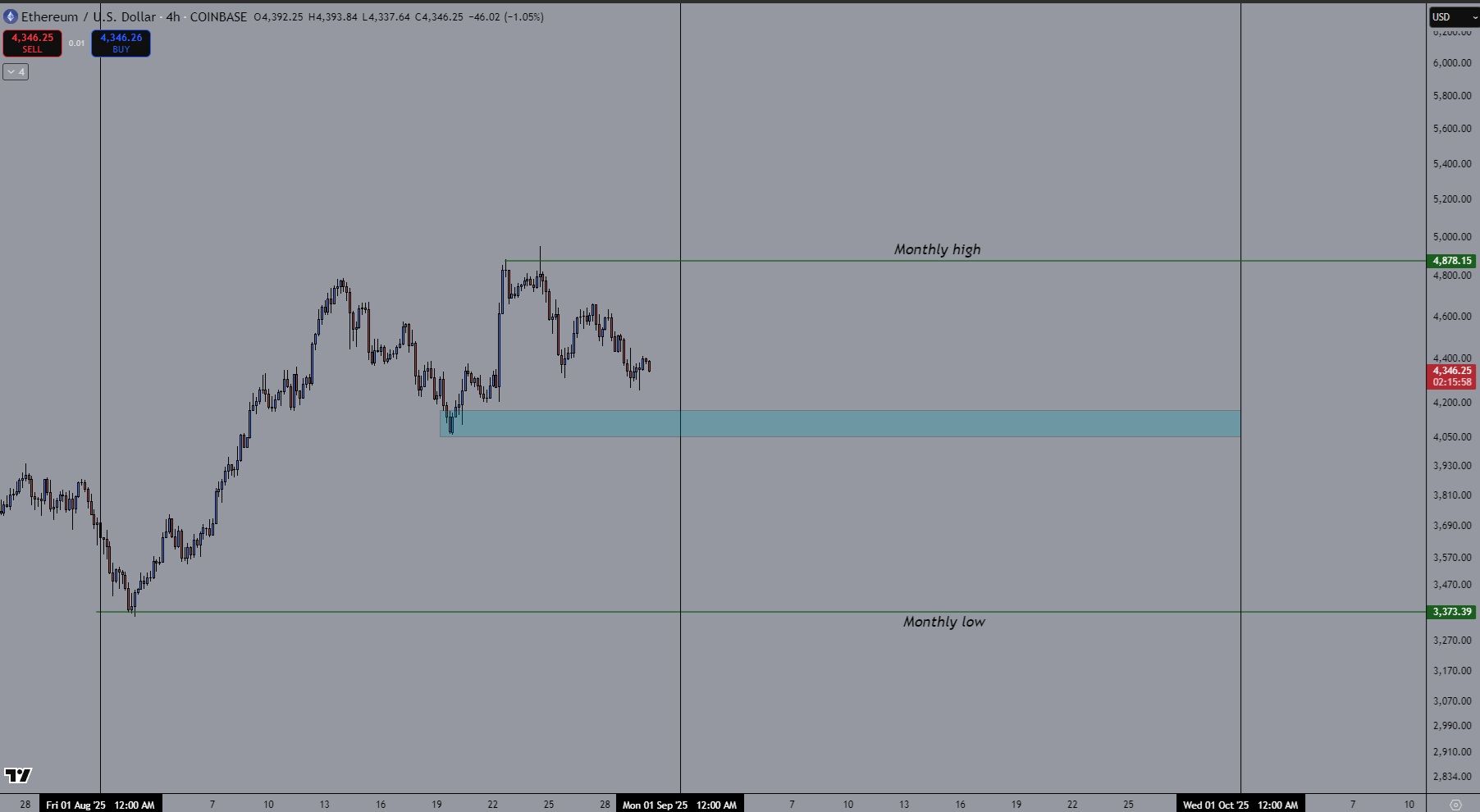
Début de mois = possible dip 📉 2ᵉ moitié = éventuelle étincelle si la Fed coupe les taux 🔥
👉 Septembre pourrait être le mois pour se positionner avant le prochain leg haussier. 🚀
#Ethereum #crypto


Carmelita
2025-08-30 23:40
$ETH – Septembre en ligne de mire
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Nous sommes désormais intégrés à @BitgetWallet, l’un des leaders mondiaux des portefeuilles Web3, utilisé par plus de 20M d’utilisateurs 🌍💎
💡 Pourquoi c’est important : ✅ Accès simplifié pour des millions de nouveaux utilisateurs ✅ Barrière d’entrée réduite pour l’adoption on-chain ✅ Expansion de JuChain au cœur de la communauté Web3
🔥 Une étape majeure vers la scalabilité et l’adoption de masse. L’avenir du Web3 se construit ensemble.
#JuChain #crypto #BitgetWallet #Adoption



Carmelita
2025-08-22 09:47
Grande nouvelle pour l’écosystème #JuChain !
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
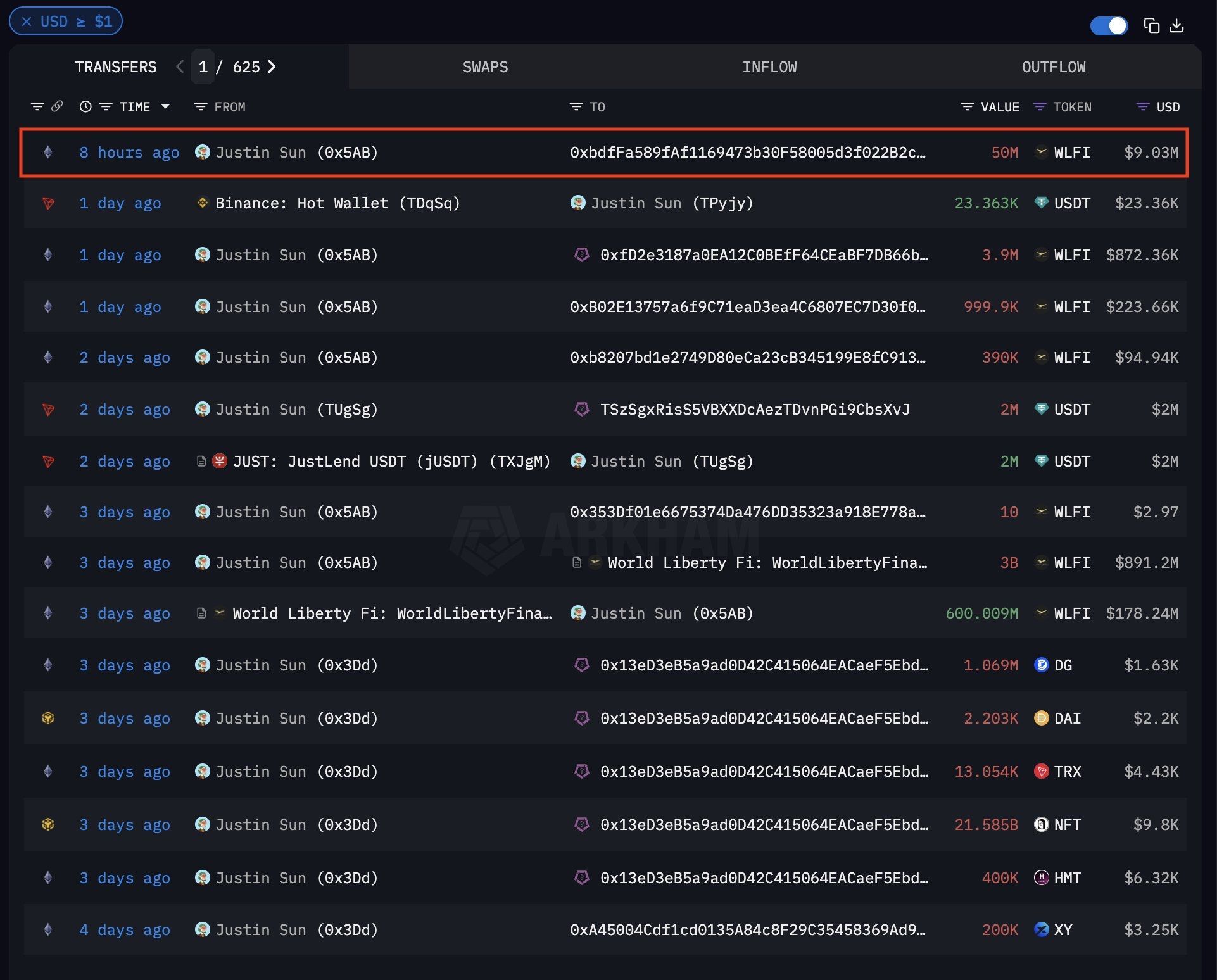
👉 Quand une baleine de ce calibre bouge, tout l’écosystème s’interroge. Le fait que Justin affirme “ne pas vouloir vendre” ne suffit pas à calmer les spéculations :
Risque de pression réglementaire accrue sur les fondateurs influents. Impact potentiel sur la liquidité et la confiance autour de $WLFI. Opportunité pour ceux qui savent lire au-delà du bruit médiatique.
📊 Le marché crypto ne dort jamais, et chaque mouvement de baleine peut redessiner les équilibres. La vraie question : serez-vous observateur ou acteur quand le prochain signal tombera ?
#crypto #blockchain #WLFI #cryptocurrency #blockchain


Carmelita
2025-09-04 23:06
🔥 “9M$ en $WLFI, wallet de Justin Sun blacklisté : simple transfert ou signal caché pour le march
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
MakerDAO Governance Mechanisms: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding MakerDAO and Its Role in DeFi
MakerDAO is a pioneering decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain. It enables users to generate the DAI stablecoin, which is pegged to the US dollar, through collateralized debt positions (CDPs). As one of the earliest DeFi projects launched in 2017 by Rune Christensen, MakerDAO has played a significant role in shaping decentralized governance and stablecoin ecosystems. Its core mission is to provide a transparent, censorship-resistant financial system where decisions are made collectively by its community of stakeholders.
How Does MakerDAO's Governance Work?
At its core, MakerDAO’s governance model emphasizes decentralization and community participation. The protocol employs several mechanisms that empower MKR token holders—its native governance tokens—to influence key parameters and future development directions.
MKR Tokens as Governance Tools
MKR tokens are central to MakerDAO’s decision-making process. Holders of MKR have voting rights that allow them to approve or reject proposals affecting the protocol’s operations. These tokens are not just voting instruments; their value also reflects confidence in the system's stability and growth prospects. Market dynamics influence MKR prices, aligning stakeholder incentives with long-term health rather than short-term gains.
Proposal Submission System
Anyone with an Ethereum wallet can submit proposals for changes within the ecosystem—be it adjusting stability fees, modifying collateral types, or implementing upgrades. This open approach encourages broad participation from developers, users, investors, and other stakeholders who wish to shape how MakerDAO evolves over time.
Voting Process Dynamics
Once a proposal is submitted, it enters a voting phase where MKR token holders cast their votes during designated periods. Typically conducted via snapshot votes at specific block heights or timestamps—ensuring transparency—the outcome depends on whether proposals meet predefined approval thresholds such as supermajorities or simple majorities depending on their significance.
Emergency Shutdown Protocols
In scenarios where immediate action is necessary—such as security breaches or critical vulnerabilities—MakerDAO incorporates an emergency shutdown mechanism. This feature allows a supermajority of MKR holders to temporarily halt operations for safety reasons until issues are resolved or mitigated effectively.
Recent Developments Enhancing Governance Effectiveness
The evolution of MakerDAO’s governance mechanisms reflects ongoing efforts toward increased efficiency and inclusivity within decentralized decision-making frameworks.
Adjustments to Stability Fees Based on Market Conditions
The stability fee functions akin to interest rates charged on borrowed DAI against collateralized assets like ETH or WBTC. During volatile market periods—for example in 2022—the DAO adjusted these fees upward strategically to maintain DAI's peg amid fluctuating asset prices. Such dynamic management helps stabilize supply-demand balances but also influences borrowing costs for users seeking liquidity through CDPs.
Expansion Through Collateral Type Additions
Diversification remains vital for risk mitigation; hence recent years saw MakerDAO adding new collateral options such as USDC (a fiat-backed stablecoin), WBTC (wrapped Bitcoin), among others. These additions broaden access points for users while increasing liquidity pools within the ecosystem—a move aligned with broader DeFi trends emphasizing interoperability across protocols.
Upgrades in Governance Infrastructure
To improve transparency and user engagement further, recent upgrades introduced more sophisticated voting tools—including better proposal submission interfaces—and enhanced transparency measures like detailed dashboards tracking vote outcomes over time. These improvements aim at fostering higher participation levels among community members while ensuring decisions reflect collective consensus accurately.
Challenges Facing MakerDAO's Governance Model
Despite its strengths, certain risks threaten the robustness of MakerDAO’s governance framework:
Market Volatility: Rapid price swings can necessitate frequent adjustments like changing stability fees—a process that might lead to increased costs for borrowers and reduced activity if not managed carefully.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As regulators worldwide scrutinize DeFi protocols more intensely—including stablecoins like DAI—potential legal challenges could impose restrictions that impact operational flexibility.
Security Concerns: Smart contract vulnerabilities remain an inherent risk; exploits could lead directly to loss of funds or destabilization if malicious actors manipulate protocol parameters before safeguards activate.
These challenges underscore why continuous innovation—not only technologically but also from regulatory compliance perspectives—is essential for maintaining trustworthiness within decentralized communities.
The Future Outlook: Maintaining Decentralized Control Amid Evolving Risks
As DeFi continues expanding rapidly across global markets—with increasing user adoption—the importance of resilient governance mechanisms becomes even more critical for protocols like MakerDAO aiming at long-term sustainability. Ongoing developments include exploring multi-signature approaches for critical decisions alongside automated safeguards driven by smart contracts designed explicitly with security best practices in mind.
By fostering active community engagement through transparent processes—and adapting swiftly when faced with market shifts—they can uphold decentralization principles while mitigating emerging risks effectively.
Keywords: makerdao governance mechanisms | how does makerdao work | mkr token voting | decentralized finance protocols | stablecoin regulation | smart contract security | DAO proposal system | collateral types makerdao


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 13:05
What governance mechanisms does MakerDAO use?
MakerDAO Governance Mechanisms: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding MakerDAO and Its Role in DeFi
MakerDAO is a pioneering decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain. It enables users to generate the DAI stablecoin, which is pegged to the US dollar, through collateralized debt positions (CDPs). As one of the earliest DeFi projects launched in 2017 by Rune Christensen, MakerDAO has played a significant role in shaping decentralized governance and stablecoin ecosystems. Its core mission is to provide a transparent, censorship-resistant financial system where decisions are made collectively by its community of stakeholders.
How Does MakerDAO's Governance Work?
At its core, MakerDAO’s governance model emphasizes decentralization and community participation. The protocol employs several mechanisms that empower MKR token holders—its native governance tokens—to influence key parameters and future development directions.
MKR Tokens as Governance Tools
MKR tokens are central to MakerDAO’s decision-making process. Holders of MKR have voting rights that allow them to approve or reject proposals affecting the protocol’s operations. These tokens are not just voting instruments; their value also reflects confidence in the system's stability and growth prospects. Market dynamics influence MKR prices, aligning stakeholder incentives with long-term health rather than short-term gains.
Proposal Submission System
Anyone with an Ethereum wallet can submit proposals for changes within the ecosystem—be it adjusting stability fees, modifying collateral types, or implementing upgrades. This open approach encourages broad participation from developers, users, investors, and other stakeholders who wish to shape how MakerDAO evolves over time.
Voting Process Dynamics
Once a proposal is submitted, it enters a voting phase where MKR token holders cast their votes during designated periods. Typically conducted via snapshot votes at specific block heights or timestamps—ensuring transparency—the outcome depends on whether proposals meet predefined approval thresholds such as supermajorities or simple majorities depending on their significance.
Emergency Shutdown Protocols
In scenarios where immediate action is necessary—such as security breaches or critical vulnerabilities—MakerDAO incorporates an emergency shutdown mechanism. This feature allows a supermajority of MKR holders to temporarily halt operations for safety reasons until issues are resolved or mitigated effectively.
Recent Developments Enhancing Governance Effectiveness
The evolution of MakerDAO’s governance mechanisms reflects ongoing efforts toward increased efficiency and inclusivity within decentralized decision-making frameworks.
Adjustments to Stability Fees Based on Market Conditions
The stability fee functions akin to interest rates charged on borrowed DAI against collateralized assets like ETH or WBTC. During volatile market periods—for example in 2022—the DAO adjusted these fees upward strategically to maintain DAI's peg amid fluctuating asset prices. Such dynamic management helps stabilize supply-demand balances but also influences borrowing costs for users seeking liquidity through CDPs.
Expansion Through Collateral Type Additions
Diversification remains vital for risk mitigation; hence recent years saw MakerDAO adding new collateral options such as USDC (a fiat-backed stablecoin), WBTC (wrapped Bitcoin), among others. These additions broaden access points for users while increasing liquidity pools within the ecosystem—a move aligned with broader DeFi trends emphasizing interoperability across protocols.
Upgrades in Governance Infrastructure
To improve transparency and user engagement further, recent upgrades introduced more sophisticated voting tools—including better proposal submission interfaces—and enhanced transparency measures like detailed dashboards tracking vote outcomes over time. These improvements aim at fostering higher participation levels among community members while ensuring decisions reflect collective consensus accurately.
Challenges Facing MakerDAO's Governance Model
Despite its strengths, certain risks threaten the robustness of MakerDAO’s governance framework:
Market Volatility: Rapid price swings can necessitate frequent adjustments like changing stability fees—a process that might lead to increased costs for borrowers and reduced activity if not managed carefully.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As regulators worldwide scrutinize DeFi protocols more intensely—including stablecoins like DAI—potential legal challenges could impose restrictions that impact operational flexibility.
Security Concerns: Smart contract vulnerabilities remain an inherent risk; exploits could lead directly to loss of funds or destabilization if malicious actors manipulate protocol parameters before safeguards activate.
These challenges underscore why continuous innovation—not only technologically but also from regulatory compliance perspectives—is essential for maintaining trustworthiness within decentralized communities.
The Future Outlook: Maintaining Decentralized Control Amid Evolving Risks
As DeFi continues expanding rapidly across global markets—with increasing user adoption—the importance of resilient governance mechanisms becomes even more critical for protocols like MakerDAO aiming at long-term sustainability. Ongoing developments include exploring multi-signature approaches for critical decisions alongside automated safeguards driven by smart contracts designed explicitly with security best practices in mind.
By fostering active community engagement through transparent processes—and adapting swiftly when faced with market shifts—they can uphold decentralization principles while mitigating emerging risks effectively.
Keywords: makerdao governance mechanisms | how does makerdao work | mkr token voting | decentralized finance protocols | stablecoin regulation | smart contract security | DAO proposal system | collateral types makerdao
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
La zone des $20 reste notre buy zone stratégique.
⏳ Patience = puissance. On attend le bon signal avant de frapper. 🚀
👉 Tu accumules ou tu restes en sidelines ?
#Chainlink #crypto
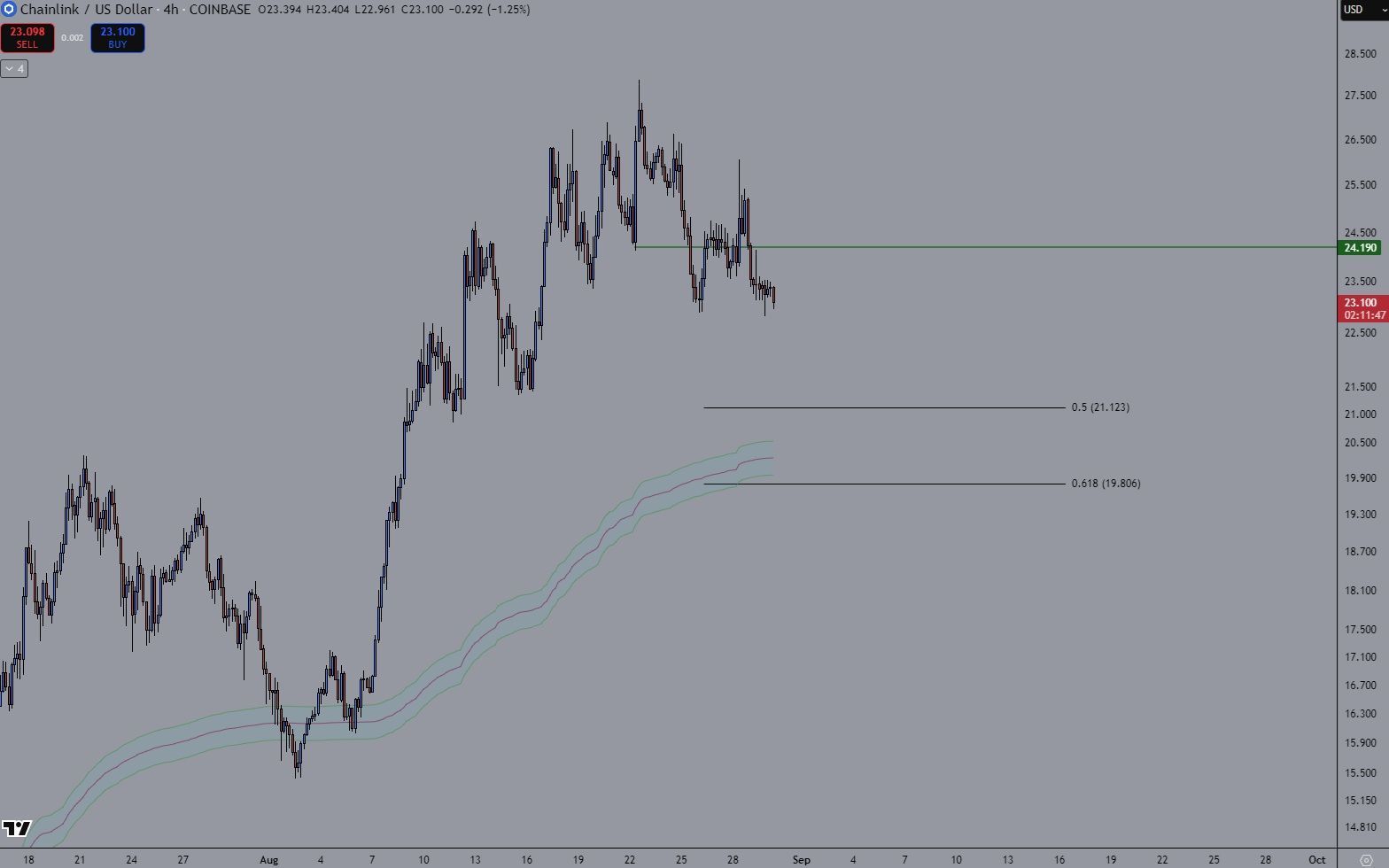


Carmelita
2025-08-30 23:42
$LINK toujours sous surveillance.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Tokens Classified as Securities: What You Need to Know
Understanding the classification of tokens as securities is essential for investors, developers, and regulators involved in the cryptocurrency space. This issue impacts how digital assets are regulated, traded, and integrated into traditional financial systems. As the regulatory environment evolves, clarity around which tokens are considered securities can significantly influence market dynamics and investor protections.
What Does It Mean When a Token Is Classified as a Security?
In financial regulation, a security generally refers to an investment that represents ownership or debt in an entity and is subject to specific legal protections. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a pivotal role in determining whether a token qualifies as a security. The primary legal test used is the Howey Test—a standard established by the Supreme Court in 1946—which assesses whether an asset involves an investment of money in a common enterprise with expectations of profits derived primarily from efforts of others.
When tokens are classified as securities under this framework, they become subject to federal securities laws. This classification requires issuers to register their offerings with regulators unless they qualify for exemptions. It also entails compliance with disclosure requirements designed to protect investors but can complicate issuance processes for blockchain projects.
Tokens Under Scrutiny: Which Have Been Classified?
While many cryptocurrencies operate without explicit classification by authorities, certain tokens have come under increased scrutiny or have been explicitly deemed securities by regulatory agencies. Notably:
Solana (SOL): Although primarily known as a blockchain platform facilitating decentralized applications and smart contracts, Solana's native token SOL has faced questions regarding its status. As of May 2025, there are ongoing discussions about whether SOL should be classified as a security due to its use case and distribution methods.
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs): Many early ICOs involved issuing new tokens that were later considered securities because they met criteria outlined by the Howey Test—particularly when sold with profit expectations based on developer efforts.
Specific Projects: Some projects have explicitly stated their intent not to classify their tokens as securities; however, regulatory agencies may still challenge these claims if certain conditions suggest otherwise.
The SEC’s Approach Toward Token Classification
The SEC’s stance on cryptocurrencies has historically been cautious yet evolving. Recent statements from key figures like SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasize calls for clearer regulations rather than outright bans or classifications without due process. The agency evaluates each token based on its characteristics—such as how it was issued and marketed—to determine if it functions like traditional securities.
For example:
If investors purchase tokens expecting profits primarily from managerial efforts or project development—similar to stocks—they are more likely deemed securities.
Conversely, utility tokens intended solely for accessing services within blockchain ecosystems might not meet this threshold but remain under scrutiny depending on circumstances.
Implications for Investors and Market Participants
Classifying tokens as securities carries significant implications:
Legal Compliance: Issuers must adhere strictly to registration requirements or seek exemptions; failure can lead to legal actions.
Market Access: Tokens deemed securities may face restrictions on trading platforms that do not comply with federal laws—potentially limiting liquidity.
Investment Risks: Investors could encounter delays or denials when attempting ETF conversions or other mainstream financial products involving these assets.
Innovation Challenges: Regulatory uncertainty might hinder new project launches or technological advancements within crypto ecosystems due to fear of non-compliance penalties.
Recent Developments Highlighting Regulatory Trends
Several recent events underscore ongoing shifts toward stricter regulation:
The Grayscale Solana Trust (GSOL), which holds Solana (SOL), faces potential reclassification issues that could delay ETF approval processes—a move closely watched by industry stakeholders aiming for broader institutional adoption.
State-level initiatives like New Hampshire’s Strategic Bitcoin Reserve demonstrate attempts at integrating cryptocurrencies into official government strategies despite federal uncertainties.
Former President Trump’s executive order establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve signals growing interest at governmental levels in leveraging digital assets strategically while navigating complex legal landscapes.
Challenges Posed by Regulatory Uncertainty
One major obstacle remains inconsistent guidance across jurisdictions—creating ambiguity about what constitutes security status for various tokens—and leading some projects either delaying launches or altering their structures altogether. This uncertainty hampers innovation while increasing compliance costs for companies operating within this space.
Moreover, if more tokens get classified under strict regulations similar to traditional equities or bonds—as seen with some high-profile cases—the entire ecosystem risks becoming less accessible especially for smaller investors who rely heavily on decentralized finance platforms outside conventional exchanges.
How Classification Affects Future Cryptocurrency Adoption
Clearer definitions around token classifications could foster greater trust among institutional investors wary of regulatory pitfalls while encouraging mainstream adoption through compliant products such as ETFs backed by digital assets like Solana—or even Bitcoin reserves managed at state levels—as seen recently in New Hampshire's strategic initiatives.
However, overly restrictive policies might stifle innovation within blockchain technology sectors unless balanced carefully through well-defined frameworks that recognize both investor protection needs and technological progress.
Key Takeaways About Tokens Being Considered Securities
To summarize:
Several prominent cryptocurrencies—including Solana—are currently being evaluated regarding their status under U.S law.
The SEC applies criteria similar across jurisdictions but often leaves room for interpretation based on specific project features.
Classifying these assets influences everything from trading practices and product offerings (like ETFs) to broader market acceptance.
As regulators continue refining policies amidst rapid technological developments—and governments explore strategic uses such as state reserves—the landscape surrounding token classification remains dynamic yet crucially impactful.
Staying Informed: Navigating Legal Changes Effectively
For market participants—from individual investors seeking exposure via compliant channels—to developers designing new blockchain solutions understanding evolving regulations is vital:
- Keep abreast of official statements from agencies like the SEC.
- Monitor legislative proposals impacting cryptocurrency classifications nationally and internationally.3.. Consult legal experts specializing in fintech regulation before launching new projects involving digital assets.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:cryptocurrency regulation | security classification | SEC crypto rules | token compliance | blockchain asset regulation | ETF approval process | crypto investment risks | US crypto law updates | digital asset legality


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 15:10
Which tokens have been classified as securities?
Tokens Classified as Securities: What You Need to Know
Understanding the classification of tokens as securities is essential for investors, developers, and regulators involved in the cryptocurrency space. This issue impacts how digital assets are regulated, traded, and integrated into traditional financial systems. As the regulatory environment evolves, clarity around which tokens are considered securities can significantly influence market dynamics and investor protections.
What Does It Mean When a Token Is Classified as a Security?
In financial regulation, a security generally refers to an investment that represents ownership or debt in an entity and is subject to specific legal protections. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a pivotal role in determining whether a token qualifies as a security. The primary legal test used is the Howey Test—a standard established by the Supreme Court in 1946—which assesses whether an asset involves an investment of money in a common enterprise with expectations of profits derived primarily from efforts of others.
When tokens are classified as securities under this framework, they become subject to federal securities laws. This classification requires issuers to register their offerings with regulators unless they qualify for exemptions. It also entails compliance with disclosure requirements designed to protect investors but can complicate issuance processes for blockchain projects.
Tokens Under Scrutiny: Which Have Been Classified?
While many cryptocurrencies operate without explicit classification by authorities, certain tokens have come under increased scrutiny or have been explicitly deemed securities by regulatory agencies. Notably:
Solana (SOL): Although primarily known as a blockchain platform facilitating decentralized applications and smart contracts, Solana's native token SOL has faced questions regarding its status. As of May 2025, there are ongoing discussions about whether SOL should be classified as a security due to its use case and distribution methods.
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs): Many early ICOs involved issuing new tokens that were later considered securities because they met criteria outlined by the Howey Test—particularly when sold with profit expectations based on developer efforts.
Specific Projects: Some projects have explicitly stated their intent not to classify their tokens as securities; however, regulatory agencies may still challenge these claims if certain conditions suggest otherwise.
The SEC’s Approach Toward Token Classification
The SEC’s stance on cryptocurrencies has historically been cautious yet evolving. Recent statements from key figures like SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasize calls for clearer regulations rather than outright bans or classifications without due process. The agency evaluates each token based on its characteristics—such as how it was issued and marketed—to determine if it functions like traditional securities.
For example:
If investors purchase tokens expecting profits primarily from managerial efforts or project development—similar to stocks—they are more likely deemed securities.
Conversely, utility tokens intended solely for accessing services within blockchain ecosystems might not meet this threshold but remain under scrutiny depending on circumstances.
Implications for Investors and Market Participants
Classifying tokens as securities carries significant implications:
Legal Compliance: Issuers must adhere strictly to registration requirements or seek exemptions; failure can lead to legal actions.
Market Access: Tokens deemed securities may face restrictions on trading platforms that do not comply with federal laws—potentially limiting liquidity.
Investment Risks: Investors could encounter delays or denials when attempting ETF conversions or other mainstream financial products involving these assets.
Innovation Challenges: Regulatory uncertainty might hinder new project launches or technological advancements within crypto ecosystems due to fear of non-compliance penalties.
Recent Developments Highlighting Regulatory Trends
Several recent events underscore ongoing shifts toward stricter regulation:
The Grayscale Solana Trust (GSOL), which holds Solana (SOL), faces potential reclassification issues that could delay ETF approval processes—a move closely watched by industry stakeholders aiming for broader institutional adoption.
State-level initiatives like New Hampshire’s Strategic Bitcoin Reserve demonstrate attempts at integrating cryptocurrencies into official government strategies despite federal uncertainties.
Former President Trump’s executive order establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve signals growing interest at governmental levels in leveraging digital assets strategically while navigating complex legal landscapes.
Challenges Posed by Regulatory Uncertainty
One major obstacle remains inconsistent guidance across jurisdictions—creating ambiguity about what constitutes security status for various tokens—and leading some projects either delaying launches or altering their structures altogether. This uncertainty hampers innovation while increasing compliance costs for companies operating within this space.
Moreover, if more tokens get classified under strict regulations similar to traditional equities or bonds—as seen with some high-profile cases—the entire ecosystem risks becoming less accessible especially for smaller investors who rely heavily on decentralized finance platforms outside conventional exchanges.
How Classification Affects Future Cryptocurrency Adoption
Clearer definitions around token classifications could foster greater trust among institutional investors wary of regulatory pitfalls while encouraging mainstream adoption through compliant products such as ETFs backed by digital assets like Solana—or even Bitcoin reserves managed at state levels—as seen recently in New Hampshire's strategic initiatives.
However, overly restrictive policies might stifle innovation within blockchain technology sectors unless balanced carefully through well-defined frameworks that recognize both investor protection needs and technological progress.
Key Takeaways About Tokens Being Considered Securities
To summarize:
Several prominent cryptocurrencies—including Solana—are currently being evaluated regarding their status under U.S law.
The SEC applies criteria similar across jurisdictions but often leaves room for interpretation based on specific project features.
Classifying these assets influences everything from trading practices and product offerings (like ETFs) to broader market acceptance.
As regulators continue refining policies amidst rapid technological developments—and governments explore strategic uses such as state reserves—the landscape surrounding token classification remains dynamic yet crucially impactful.
Staying Informed: Navigating Legal Changes Effectively
For market participants—from individual investors seeking exposure via compliant channels—to developers designing new blockchain solutions understanding evolving regulations is vital:
- Keep abreast of official statements from agencies like the SEC.
- Monitor legislative proposals impacting cryptocurrency classifications nationally and internationally.3.. Consult legal experts specializing in fintech regulation before launching new projects involving digital assets.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:cryptocurrency regulation | security classification | SEC crypto rules | token compliance | blockchain asset regulation | ETF approval process | crypto investment risks | US crypto law updates | digital asset legality
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Beginners Can Achieve Long-Term Success in Cryptocurrency
Entering the world of cryptocurrency can be both exciting and overwhelming for newcomers. With its rapid growth, technological innovations, and market volatility, understanding how to position oneself for sustainable success is essential. This guide provides practical insights and strategies tailored to beginners aiming for long-term stability in the crypto space.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Cryptocurrency Investment
Before diving into trading or investing, it’s crucial to build a solid foundation of knowledge about blockchain technology and how cryptocurrencies work. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions transparently and securely. Recognizing this underlying technology helps investors appreciate the value proposition of various digital assets.
Resources such as CoinDesk, CryptoSlate, Coursera courses, and reputable blogs offer accessible educational content suitable for beginners. Gaining clarity on key concepts like wallets, private keys, public addresses, and transaction processes ensures you make informed decisions rather than impulsive moves driven by market hype.
Prioritize Education and Continuous Research
The crypto landscape evolves rapidly; staying updated is vital for long-term success. Regularly following trusted news sources like Bloomberg Crypto or CNBC Crypto provides insights into regulatory changes, technological advancements, or macroeconomic factors influencing markets.
Additionally, engaging with online communities such as Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency or Telegram groups allows new investors to learn from experienced members’ insights while avoiding misinformation. Developing a habit of research helps identify promising projects based on their use cases, development teams, community support—and not just price movements.
Implement Effective Risk Management Strategies
Cryptocurrency investments are inherently volatile; therefore managing risk should be at the core of your strategy:
- Diversification: Spread investments across multiple cryptocurrencies rather than concentrating funds in one asset class to mitigate potential losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Set predefined exit points to limit downside risk if prices fall unexpectedly.
- Position Sizing: Only allocate what you can afford to lose without impacting your financial stability.
By applying these techniques consistently—especially during turbulent market phases—you protect your capital while maintaining exposure to potential growth opportunities over time.
Adopt a Long-Term Investment Perspective
Short-term trading can be tempting but often leads to emotional decision-making driven by fear or greed. Instead, focus on building wealth through patience by holding quality assets over extended periods—this approach aligns with fundamental value appreciation rather than speculative swings.
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) further supports this mindset by allowing you to invest fixed amounts regularly regardless of market fluctuations. Over time—through disciplined investing—you reduce the impact of short-term volatility while increasing chances for compounding gains aligned with broader adoption trends.
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes
Regulatory environments significantly influence cryptocurrency markets; thus keeping abreast of legal developments helps avoid compliance issues:
- Monitor updates from authorities like the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), European regulators—or relevant local agencies.
- Understand how classifications (e.g., whether certain tokens are securities) affect your holdings.
- Be aware that sudden regulatory shifts can impact prices or restrict access temporarily; proactive awareness minimizes surprises.
Being compliant not only safeguards your investments but also positions you as a responsible participant within an evolving ecosystem that increasingly seeks legitimacy worldwide.
Enhance Security Measures for Your Digital Assets
Security remains paramount when dealing with digital currencies:
- Use hardware wallets such as Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor devices instead of leaving funds on exchanges susceptible to hacking.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) across all accounts involved in transactions.
- Avoid sharing private keys or seed phrases publicly—and store them securely offline.
These practices significantly reduce risks associated with thefts or scams prevalent in crypto markets today. As security threats evolve alongside technological advancements—staying vigilant ensures ongoing protection against malicious actors.
Engage With Community Networks & Mentorship Opportunities
Building relationships within crypto communities offers valuable learning opportunities:
- Join forums like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency or Discord channels dedicated to blockchain discussions.
- Attend webinars/webcasts hosted by industry experts.
Networking facilitates mentorship from seasoned investors who can share practical tips based on real-world experience—a critical advantage especially during bear markets when patience is tested most effectively through peer support systems.
Utilize Market Analysis Tools Effectively
Successful long-term investors leverage both technical analysis (TA) and fundamental analysis (FA):
Technical Analysis:
- Use charting tools like TradingView
- Study indicators such as Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands
- Recognize patterns indicating potential trend reversals
Fundamental Analysis:
- Evaluate project whitepapers
- Assess team credibility
- Review use case viability
Combining these approaches enables more accurate predictions about future price movements while aligning investment choices with underlying project fundamentals.
Understand Tax Implications & Legal Responsibilities
Taxation policies vary globally but generally require reporting gains/losses from crypto activities:
- Keep detailed records including purchase dates/prices/sale proceeds
- Consult tax professionals familiar with local laws regarding cryptocurrency income— this prevents inadvertent legal issues down the line
Being compliant not only avoids penalties but also builds credibility within regulated financial systems increasingly integrating digital assets.
Maintain Emotional Discipline During Market Fluctuations
Crypto markets are known for their dramatic swings which test investor psychology:
– Practice emotional control; avoid impulsive buying during hype cycles – Resist panic selling amid downturns – Focus on long-term goals rather than short-lived price spikes
Maintaining mental resilience reduces costly mistakes caused by fear-driven decisions—a key trait among successful long-term holders.
By integrating education efforts with disciplined risk management strategies—and continuously adapting based on evolving regulations—the beginner investor sets themselves up for sustainable growth in cryptocurrency markets. Patience combined with informed decision-making creates resilience against volatility while positioning portfolios toward future adoption-driven appreciation.
This comprehensive approach empowers newcomers not just to survive but thrive amid one of today’s most dynamic financial landscapes—building wealth responsibly over time through strategic planning rooted in knowledge and prudence


Lo
2025-05-22 14:18
How can beginners position themselves for sustainable, long-term success in the crypto space?
How Beginners Can Achieve Long-Term Success in Cryptocurrency
Entering the world of cryptocurrency can be both exciting and overwhelming for newcomers. With its rapid growth, technological innovations, and market volatility, understanding how to position oneself for sustainable success is essential. This guide provides practical insights and strategies tailored to beginners aiming for long-term stability in the crypto space.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Cryptocurrency Investment
Before diving into trading or investing, it’s crucial to build a solid foundation of knowledge about blockchain technology and how cryptocurrencies work. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions transparently and securely. Recognizing this underlying technology helps investors appreciate the value proposition of various digital assets.
Resources such as CoinDesk, CryptoSlate, Coursera courses, and reputable blogs offer accessible educational content suitable for beginners. Gaining clarity on key concepts like wallets, private keys, public addresses, and transaction processes ensures you make informed decisions rather than impulsive moves driven by market hype.
Prioritize Education and Continuous Research
The crypto landscape evolves rapidly; staying updated is vital for long-term success. Regularly following trusted news sources like Bloomberg Crypto or CNBC Crypto provides insights into regulatory changes, technological advancements, or macroeconomic factors influencing markets.
Additionally, engaging with online communities such as Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency or Telegram groups allows new investors to learn from experienced members’ insights while avoiding misinformation. Developing a habit of research helps identify promising projects based on their use cases, development teams, community support—and not just price movements.
Implement Effective Risk Management Strategies
Cryptocurrency investments are inherently volatile; therefore managing risk should be at the core of your strategy:
- Diversification: Spread investments across multiple cryptocurrencies rather than concentrating funds in one asset class to mitigate potential losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Set predefined exit points to limit downside risk if prices fall unexpectedly.
- Position Sizing: Only allocate what you can afford to lose without impacting your financial stability.
By applying these techniques consistently—especially during turbulent market phases—you protect your capital while maintaining exposure to potential growth opportunities over time.
Adopt a Long-Term Investment Perspective
Short-term trading can be tempting but often leads to emotional decision-making driven by fear or greed. Instead, focus on building wealth through patience by holding quality assets over extended periods—this approach aligns with fundamental value appreciation rather than speculative swings.
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) further supports this mindset by allowing you to invest fixed amounts regularly regardless of market fluctuations. Over time—through disciplined investing—you reduce the impact of short-term volatility while increasing chances for compounding gains aligned with broader adoption trends.
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes
Regulatory environments significantly influence cryptocurrency markets; thus keeping abreast of legal developments helps avoid compliance issues:
- Monitor updates from authorities like the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), European regulators—or relevant local agencies.
- Understand how classifications (e.g., whether certain tokens are securities) affect your holdings.
- Be aware that sudden regulatory shifts can impact prices or restrict access temporarily; proactive awareness minimizes surprises.
Being compliant not only safeguards your investments but also positions you as a responsible participant within an evolving ecosystem that increasingly seeks legitimacy worldwide.
Enhance Security Measures for Your Digital Assets
Security remains paramount when dealing with digital currencies:
- Use hardware wallets such as Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor devices instead of leaving funds on exchanges susceptible to hacking.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) across all accounts involved in transactions.
- Avoid sharing private keys or seed phrases publicly—and store them securely offline.
These practices significantly reduce risks associated with thefts or scams prevalent in crypto markets today. As security threats evolve alongside technological advancements—staying vigilant ensures ongoing protection against malicious actors.
Engage With Community Networks & Mentorship Opportunities
Building relationships within crypto communities offers valuable learning opportunities:
- Join forums like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency or Discord channels dedicated to blockchain discussions.
- Attend webinars/webcasts hosted by industry experts.
Networking facilitates mentorship from seasoned investors who can share practical tips based on real-world experience—a critical advantage especially during bear markets when patience is tested most effectively through peer support systems.
Utilize Market Analysis Tools Effectively
Successful long-term investors leverage both technical analysis (TA) and fundamental analysis (FA):
Technical Analysis:
- Use charting tools like TradingView
- Study indicators such as Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands
- Recognize patterns indicating potential trend reversals
Fundamental Analysis:
- Evaluate project whitepapers
- Assess team credibility
- Review use case viability
Combining these approaches enables more accurate predictions about future price movements while aligning investment choices with underlying project fundamentals.
Understand Tax Implications & Legal Responsibilities
Taxation policies vary globally but generally require reporting gains/losses from crypto activities:
- Keep detailed records including purchase dates/prices/sale proceeds
- Consult tax professionals familiar with local laws regarding cryptocurrency income— this prevents inadvertent legal issues down the line
Being compliant not only avoids penalties but also builds credibility within regulated financial systems increasingly integrating digital assets.
Maintain Emotional Discipline During Market Fluctuations
Crypto markets are known for their dramatic swings which test investor psychology:
– Practice emotional control; avoid impulsive buying during hype cycles – Resist panic selling amid downturns – Focus on long-term goals rather than short-lived price spikes
Maintaining mental resilience reduces costly mistakes caused by fear-driven decisions—a key trait among successful long-term holders.
By integrating education efforts with disciplined risk management strategies—and continuously adapting based on evolving regulations—the beginner investor sets themselves up for sustainable growth in cryptocurrency markets. Patience combined with informed decision-making creates resilience against volatility while positioning portfolios toward future adoption-driven appreciation.
This comprehensive approach empowers newcomers not just to survive but thrive amid one of today’s most dynamic financial landscapes—building wealth responsibly over time through strategic planning rooted in knowledge and prudence
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Gas Fees in Crypto Transactions?
Gas fees are an essential aspect of conducting transactions on blockchain networks, especially on Ethereum. They serve as the cost users pay to miners or validators who process and validate transactions. These fees ensure that the network remains secure, decentralized, and functional by incentivizing participants to include transactions in new blocks. Without gas fees, it would be challenging to prioritize and manage transaction processing efficiently within a decentralized environment.
Understanding Gas Fees: The Basics
In simple terms, gas fees are payments made for computational work performed during a transaction or smart contract execution on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. Unlike traditional banking systems where transaction costs are fixed or vary minimally, gas fees fluctuate based on network demand and complexity of the operation.
On Ethereum, gas is measured in units called "gas units" (Gwei). When initiating a transaction—such as transferring tokens or executing a smart contract—the user specifies two key parameters: the gas limit and the gas price. The gas limit indicates the maximum amount of gas they’re willing to spend for that transaction; meanwhile, the gas price determines how much they’re willing to pay per unit of gas.
The Role of Miners and Validators
Once a user submits a transaction with specified fee parameters, miners (or validators in proof-of-stake systems) compete to include these transactions into upcoming blocks. Typically, those offering higher fees get prioritized because miners earn more from them. This competitive process creates an economic incentive for users who want faster confirmation times—especially during periods when network congestion is high.
Network congestion directly impacts gas prices; when many users submit transactions simultaneously—for example during popular NFT drops or DeFi activity—fees can spike dramatically. This dynamic ensures that only those willing to pay higher costs can have their transactions processed quickly under congested conditions.
Factors Influencing Gas Fees
Several factors influence how much users pay in gas fees:
- Network Demand: High activity levels increase competition among transactions.
- Transaction Complexity: Smart contracts requiring more computational steps consume more gas.
- Gas Price Settings: Users can manually set higher prices for faster processing or accept lower prices risking delays.
- Block Size & Capacity: Limited block space means only so many transactions can be included at once; excess demand drives up costs.
Recent Trends: Rising Costs and Their Impact
In recent years—particularly throughout 2023—Ethereum's network experienced significant congestion due to booming interest in DeFi projects and NFTs. During this period, average gas fees soared past $100 per transaction at peak times—a substantial barrier for casual users or small-scale investors trying to participate without incurring prohibitive costs.
High fee environments not only hinder user participation but also introduce market volatility since uncertainty around transaction costs discourages some from engaging altogether. This situation underscores why scalability solutions are critical for broader adoption of blockchain technology.
Ethereum’s Transition: Aiming To Reduce Gas Fees
To address these challenges, developers have been working towards transitioning Ethereum from its original proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism toward Ethereum 2.0—a move designed primarily to improve scalability through proof-of-stake (PoS). Eth2 aims to reduce energy consumption while increasing throughput capacity significantly.
However, this transition has faced delays due mainly to technical complexities involved with upgrading such a large decentralized system safely. Once fully implemented—and combined with Layer 2 solutions—it promises substantial reductions in average gas prices by offloading part of transactional load away from mainnet operations.
Layer 2 Solutions: Off-Chain Processing To Cut Costs
Layer 2 scaling solutions like Optimism, Polygon (formerly Matic), Arbitrum—and others—are gaining prominence as effective methods for reducing high GAS FEES while maintaining security standards inherent within mainnet blockchains:
- They process most interactions off-chain.
- Only settle final states back onto Ethereum’s mainnet periodically.
This approach alleviates pressure on base layer networks by batching multiple operations into single settlements — thus lowering individual transaction costs substantially without sacrificing decentralization or security guarantees provided by Layer 1 protocols.
Potential Challenges & Future Outlook
While Layer 2 solutions show promise—and ongoing upgrades like Eth2 could further ease fee burdens—the path forward involves navigating several hurdles:
- Security Concerns – Ensuring off-chain solutions remain secure against attacks.
- Interoperability – Seamless integration between different scaling layers requires standardization.
- User Experience – Simplifying interfaces so everyday users can easily choose optimal fee settings without technical knowledge.
- Market Volatility – Managing unpredictable fluctuations driven by external factors such as market sentiment or sudden surges in demand remains complex despite technological advancements.
As blockchain technology matures—with continuous innovation addressing scalability issues—the hope is that future developments will make crypto transactions cheaper and more accessible globally while maintaining robust security standards necessary for widespread trustworthiness.
How High Gas Fees Affect Cryptocurrency Adoption
Elevated GAS FEES pose significant barriers not just economically but also psychologically—they discourage new entrants wary of unpredictable expenses before completing simple transfers or participating actively within DeFi ecosystems . For existing users engaged regularly with complex smart contracts , high operational costs reduce profitability margins which could slow down overall ecosystem growth .
Moreover , excessive reliance on high-fee models may push developers toward alternative chains offering lower-cost environments — creating fragmentation across platforms rather than unified growth . Therefore , balancing scalability improvements with affordability remains central goal within crypto development communities .
Final Thoughts
Gas fees play an indispensable role within blockchain ecosystems—they incentivize participants ensuring decentralization while enabling smooth operation amid growing demand . However , escalating charges during periods of congestion highlight urgent needs for scalable infrastructure upgrades like Eth2 transition coupled with Layer 2 innovations . As these technologies mature , expect lower transactional costs leading toward broader mainstream adoption — making cryptocurrencies more practical tools across diverse sectors worldwide.
References
- "Ethereum Gas Fees Reach Record Highs in 2023." Available at [source URL].
- "Ethereum 2.0: A Guide To The Transition." Available at [source URL].
- "Layer 2 Solutions For Ethereum: A Comprehensive Guide." Available at [source URL].


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-06-09 05:54
What are gas fees in crypto transactions?
What Are Gas Fees in Crypto Transactions?
Gas fees are an essential aspect of conducting transactions on blockchain networks, especially on Ethereum. They serve as the cost users pay to miners or validators who process and validate transactions. These fees ensure that the network remains secure, decentralized, and functional by incentivizing participants to include transactions in new blocks. Without gas fees, it would be challenging to prioritize and manage transaction processing efficiently within a decentralized environment.
Understanding Gas Fees: The Basics
In simple terms, gas fees are payments made for computational work performed during a transaction or smart contract execution on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. Unlike traditional banking systems where transaction costs are fixed or vary minimally, gas fees fluctuate based on network demand and complexity of the operation.
On Ethereum, gas is measured in units called "gas units" (Gwei). When initiating a transaction—such as transferring tokens or executing a smart contract—the user specifies two key parameters: the gas limit and the gas price. The gas limit indicates the maximum amount of gas they’re willing to spend for that transaction; meanwhile, the gas price determines how much they’re willing to pay per unit of gas.
The Role of Miners and Validators
Once a user submits a transaction with specified fee parameters, miners (or validators in proof-of-stake systems) compete to include these transactions into upcoming blocks. Typically, those offering higher fees get prioritized because miners earn more from them. This competitive process creates an economic incentive for users who want faster confirmation times—especially during periods when network congestion is high.
Network congestion directly impacts gas prices; when many users submit transactions simultaneously—for example during popular NFT drops or DeFi activity—fees can spike dramatically. This dynamic ensures that only those willing to pay higher costs can have their transactions processed quickly under congested conditions.
Factors Influencing Gas Fees
Several factors influence how much users pay in gas fees:
- Network Demand: High activity levels increase competition among transactions.
- Transaction Complexity: Smart contracts requiring more computational steps consume more gas.
- Gas Price Settings: Users can manually set higher prices for faster processing or accept lower prices risking delays.
- Block Size & Capacity: Limited block space means only so many transactions can be included at once; excess demand drives up costs.
Recent Trends: Rising Costs and Their Impact
In recent years—particularly throughout 2023—Ethereum's network experienced significant congestion due to booming interest in DeFi projects and NFTs. During this period, average gas fees soared past $100 per transaction at peak times—a substantial barrier for casual users or small-scale investors trying to participate without incurring prohibitive costs.
High fee environments not only hinder user participation but also introduce market volatility since uncertainty around transaction costs discourages some from engaging altogether. This situation underscores why scalability solutions are critical for broader adoption of blockchain technology.
Ethereum’s Transition: Aiming To Reduce Gas Fees
To address these challenges, developers have been working towards transitioning Ethereum from its original proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism toward Ethereum 2.0—a move designed primarily to improve scalability through proof-of-stake (PoS). Eth2 aims to reduce energy consumption while increasing throughput capacity significantly.
However, this transition has faced delays due mainly to technical complexities involved with upgrading such a large decentralized system safely. Once fully implemented—and combined with Layer 2 solutions—it promises substantial reductions in average gas prices by offloading part of transactional load away from mainnet operations.
Layer 2 Solutions: Off-Chain Processing To Cut Costs
Layer 2 scaling solutions like Optimism, Polygon (formerly Matic), Arbitrum—and others—are gaining prominence as effective methods for reducing high GAS FEES while maintaining security standards inherent within mainnet blockchains:
- They process most interactions off-chain.
- Only settle final states back onto Ethereum’s mainnet periodically.
This approach alleviates pressure on base layer networks by batching multiple operations into single settlements — thus lowering individual transaction costs substantially without sacrificing decentralization or security guarantees provided by Layer 1 protocols.
Potential Challenges & Future Outlook
While Layer 2 solutions show promise—and ongoing upgrades like Eth2 could further ease fee burdens—the path forward involves navigating several hurdles:
- Security Concerns – Ensuring off-chain solutions remain secure against attacks.
- Interoperability – Seamless integration between different scaling layers requires standardization.
- User Experience – Simplifying interfaces so everyday users can easily choose optimal fee settings without technical knowledge.
- Market Volatility – Managing unpredictable fluctuations driven by external factors such as market sentiment or sudden surges in demand remains complex despite technological advancements.
As blockchain technology matures—with continuous innovation addressing scalability issues—the hope is that future developments will make crypto transactions cheaper and more accessible globally while maintaining robust security standards necessary for widespread trustworthiness.
How High Gas Fees Affect Cryptocurrency Adoption
Elevated GAS FEES pose significant barriers not just economically but also psychologically—they discourage new entrants wary of unpredictable expenses before completing simple transfers or participating actively within DeFi ecosystems . For existing users engaged regularly with complex smart contracts , high operational costs reduce profitability margins which could slow down overall ecosystem growth .
Moreover , excessive reliance on high-fee models may push developers toward alternative chains offering lower-cost environments — creating fragmentation across platforms rather than unified growth . Therefore , balancing scalability improvements with affordability remains central goal within crypto development communities .
Final Thoughts
Gas fees play an indispensable role within blockchain ecosystems—they incentivize participants ensuring decentralization while enabling smooth operation amid growing demand . However , escalating charges during periods of congestion highlight urgent needs for scalable infrastructure upgrades like Eth2 transition coupled with Layer 2 innovations . As these technologies mature , expect lower transactional costs leading toward broader mainstream adoption — making cryptocurrencies more practical tools across diverse sectors worldwide.
References
- "Ethereum Gas Fees Reach Record Highs in 2023." Available at [source URL].
- "Ethereum 2.0: A Guide To The Transition." Available at [source URL].
- "Layer 2 Solutions For Ethereum: A Comprehensive Guide." Available at [source URL].
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The Role of Institutional Investors in Cryptocurrency Markets
Institutional investors have become increasingly influential players in the cryptocurrency landscape. Their entry into the market has not only driven significant capital inflows but also added a layer of legitimacy and stability to digital assets. Understanding their role is essential for anyone interested in the future trajectory of cryptocurrencies, whether as an investor, regulator, or industry participant.
Who Are Institutional Investors?
Institutional investors are large organizations that manage substantial sums of money on behalf of clients such as pension funds, hedge funds, university endowments, insurance companies, and family offices. Unlike individual retail investors who typically buy smaller amounts directly from exchanges or brokers, institutional investors operate at a much larger scale with sophisticated strategies and risk management protocols.
Historically focused on traditional assets like stocks and bonds, these entities have started exploring cryptocurrencies due to their potential for high returns and portfolio diversification. Their involvement signals a shift toward mainstream acceptance and recognition of digital assets as legitimate investment vehicles.
Why Are Institutional Investors Investing in Crypto?
Several factors have contributed to the increased interest from institutional players:
Market Growth & Volatility: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have experienced exponential growth alongside notable volatility. This environment offers opportunities for high returns but also demands advanced risk management—something institutional investors are equipped to handle.
Regulatory Improvements: Clarification around regulations—such as approval processes for Bitcoin ETFs—has reduced uncertainties that previously hindered large-scale participation.
Technological Innovations: Development of secure custody solutions and sophisticated trading platforms has addressed major concerns about security risks associated with digital asset storage.
Diversification & Hedge Strategies: Cryptocurrencies are increasingly viewed as uncorrelated assets that can serve as hedges against inflation or economic downturns.
Recent Developments Signaling Institutional Engagement
The past few years have seen several landmark events indicating growing institutional involvement:
Introduction of Bitcoin ETFs: Exchange-Traded Funds linked to Bitcoin allow institutions to gain exposure without directly holding the cryptocurrency. This reduces operational risks related to security and custody while providing liquidity advantages.
Corporate Investments: Companies like MicroStrategy have made substantial investments in Bitcoin, positioning it as a treasury reserve asset akin to gold—a move that underscores its perceived store-of-value potential.
State-Level Initiatives: Some U.S. states are exploring innovative ways to integrate crypto into public finance systems; New Hampshire’s establishment of a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve exemplifies this trend by signaling governmental acknowledgment at state levels.
Broader Adoption Beyond Bitcoin: Investment products focusing on alternative cryptocurrencies such as Solana through specialized ETFs demonstrate diversification efforts among institutional portfolios beyond just Bitcoin.
Stablecoins & Digital Currency Use Cases: The emergence of stablecoins linked to prominent figures or institutions highlights evolving use cases—particularly settling large transactions efficiently while maintaining price stability within volatile markets.
How Do Institutional Investors Impact Cryptocurrency Markets?
The influx of institutional capital has had tangible effects:
It has contributed significantly toward pushing prices higher; for example, Bitcoin's value approached $95,000 amid increased buying activity.
Institutions employ diverse strategies—from direct purchases and futures contracts to ETF investments—to optimize risk-adjusted returns.
Their participation lends credibility which can attract further retail interest but also introduces complexities related to market influence by large trades (market impact).
However, this increased participation isn't without challenges:
Market Volatility
Large trades executed by institutions can cause sharp price swings due to liquidity constraints—a phenomenon known as "whale activity." While volatility is inherent in crypto markets anyway, significant institutional moves can amplify fluctuations temporarily.
Regulatory Risks
As more big players enter the space rapidly, regulators face pressure both from within their jurisdictions and globally—to craft frameworks that balance innovation with consumer protection—and this ongoing process may introduce uncertainties affecting market stability.
Security Concerns
With more significant sums involved comes heightened cybersecurity risks—including hacking attempts targeting exchanges or custody solutions—that could threaten investor holdings if not properly managed through robust security measures.
Potential Market Manipulation
The size advantage held by some institutions raises concerns about possible market manipulation practices such as pump-and-dump schemes or coordinated trading activities lacking sufficient oversight mechanisms currently under development worldwide.
Moving Forward: Challenges & Opportunities for Crypto’s Mainstream Adoption
Institutional involvement undeniably accelerates mainstream adoption by providing legitimacy through substantial capital flows; however it also necessitates careful regulation enforcement alongside technological advancements aimed at safeguarding investor interests across all levels—from retail traders up through giant funds managing billions worth of assets.
Efforts towards clearer regulatory frameworks will be crucial moving forward—not only protecting individual investors but ensuring sustainable growth within an evolving ecosystem where transparency becomes paramount.
Furthermore,
- Continued innovation around custody solutions will help mitigate security threats,
- Enhanced oversight mechanisms will reduce manipulation risks,
- And broader education initiatives will foster better understanding among all stakeholders about crypto’s benefits versus its inherent risks.
By addressing these areas proactively—with input from industry leaders alongside policymakers—the cryptocurrency sector can harness the full potential offered by institutional engagement while minimizing adverse fallout.
Final Thoughts on Institutional Influence in Crypto Markets
Institutional investors play an increasingly pivotal role shaping today’s cryptocurrency markets—they bring much-needed liquidity along with credibility but also pose challenges related to volatility control and regulatory compliance. As they continue expanding their footprint—with innovations like ETFs becoming more commonplace—the landscape is poised for further maturation.
For retail traders and smaller firms alike, understanding how these developments unfold remains critical—not just for navigating current conditions but preparing strategically for future shifts driven largely by big-money participants entering what was once considered a niche asset class.
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping readers with insights into how large organizations influence crypto markets today—and what lies ahead—as digital currencies inch closer toward mainstream financial ecosystems worldwide.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 15:56
What role do institutional investors play in crypto?
The Role of Institutional Investors in Cryptocurrency Markets
Institutional investors have become increasingly influential players in the cryptocurrency landscape. Their entry into the market has not only driven significant capital inflows but also added a layer of legitimacy and stability to digital assets. Understanding their role is essential for anyone interested in the future trajectory of cryptocurrencies, whether as an investor, regulator, or industry participant.
Who Are Institutional Investors?
Institutional investors are large organizations that manage substantial sums of money on behalf of clients such as pension funds, hedge funds, university endowments, insurance companies, and family offices. Unlike individual retail investors who typically buy smaller amounts directly from exchanges or brokers, institutional investors operate at a much larger scale with sophisticated strategies and risk management protocols.
Historically focused on traditional assets like stocks and bonds, these entities have started exploring cryptocurrencies due to their potential for high returns and portfolio diversification. Their involvement signals a shift toward mainstream acceptance and recognition of digital assets as legitimate investment vehicles.
Why Are Institutional Investors Investing in Crypto?
Several factors have contributed to the increased interest from institutional players:
Market Growth & Volatility: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have experienced exponential growth alongside notable volatility. This environment offers opportunities for high returns but also demands advanced risk management—something institutional investors are equipped to handle.
Regulatory Improvements: Clarification around regulations—such as approval processes for Bitcoin ETFs—has reduced uncertainties that previously hindered large-scale participation.
Technological Innovations: Development of secure custody solutions and sophisticated trading platforms has addressed major concerns about security risks associated with digital asset storage.
Diversification & Hedge Strategies: Cryptocurrencies are increasingly viewed as uncorrelated assets that can serve as hedges against inflation or economic downturns.
Recent Developments Signaling Institutional Engagement
The past few years have seen several landmark events indicating growing institutional involvement:
Introduction of Bitcoin ETFs: Exchange-Traded Funds linked to Bitcoin allow institutions to gain exposure without directly holding the cryptocurrency. This reduces operational risks related to security and custody while providing liquidity advantages.
Corporate Investments: Companies like MicroStrategy have made substantial investments in Bitcoin, positioning it as a treasury reserve asset akin to gold—a move that underscores its perceived store-of-value potential.
State-Level Initiatives: Some U.S. states are exploring innovative ways to integrate crypto into public finance systems; New Hampshire’s establishment of a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve exemplifies this trend by signaling governmental acknowledgment at state levels.
Broader Adoption Beyond Bitcoin: Investment products focusing on alternative cryptocurrencies such as Solana through specialized ETFs demonstrate diversification efforts among institutional portfolios beyond just Bitcoin.
Stablecoins & Digital Currency Use Cases: The emergence of stablecoins linked to prominent figures or institutions highlights evolving use cases—particularly settling large transactions efficiently while maintaining price stability within volatile markets.
How Do Institutional Investors Impact Cryptocurrency Markets?
The influx of institutional capital has had tangible effects:
It has contributed significantly toward pushing prices higher; for example, Bitcoin's value approached $95,000 amid increased buying activity.
Institutions employ diverse strategies—from direct purchases and futures contracts to ETF investments—to optimize risk-adjusted returns.
Their participation lends credibility which can attract further retail interest but also introduces complexities related to market influence by large trades (market impact).
However, this increased participation isn't without challenges:
Market Volatility
Large trades executed by institutions can cause sharp price swings due to liquidity constraints—a phenomenon known as "whale activity." While volatility is inherent in crypto markets anyway, significant institutional moves can amplify fluctuations temporarily.
Regulatory Risks
As more big players enter the space rapidly, regulators face pressure both from within their jurisdictions and globally—to craft frameworks that balance innovation with consumer protection—and this ongoing process may introduce uncertainties affecting market stability.
Security Concerns
With more significant sums involved comes heightened cybersecurity risks—including hacking attempts targeting exchanges or custody solutions—that could threaten investor holdings if not properly managed through robust security measures.
Potential Market Manipulation
The size advantage held by some institutions raises concerns about possible market manipulation practices such as pump-and-dump schemes or coordinated trading activities lacking sufficient oversight mechanisms currently under development worldwide.
Moving Forward: Challenges & Opportunities for Crypto’s Mainstream Adoption
Institutional involvement undeniably accelerates mainstream adoption by providing legitimacy through substantial capital flows; however it also necessitates careful regulation enforcement alongside technological advancements aimed at safeguarding investor interests across all levels—from retail traders up through giant funds managing billions worth of assets.
Efforts towards clearer regulatory frameworks will be crucial moving forward—not only protecting individual investors but ensuring sustainable growth within an evolving ecosystem where transparency becomes paramount.
Furthermore,
- Continued innovation around custody solutions will help mitigate security threats,
- Enhanced oversight mechanisms will reduce manipulation risks,
- And broader education initiatives will foster better understanding among all stakeholders about crypto’s benefits versus its inherent risks.
By addressing these areas proactively—with input from industry leaders alongside policymakers—the cryptocurrency sector can harness the full potential offered by institutional engagement while minimizing adverse fallout.
Final Thoughts on Institutional Influence in Crypto Markets
Institutional investors play an increasingly pivotal role shaping today’s cryptocurrency markets—they bring much-needed liquidity along with credibility but also pose challenges related to volatility control and regulatory compliance. As they continue expanding their footprint—with innovations like ETFs becoming more commonplace—the landscape is poised for further maturation.
For retail traders and smaller firms alike, understanding how these developments unfold remains critical—not just for navigating current conditions but preparing strategically for future shifts driven largely by big-money participants entering what was once considered a niche asset class.
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping readers with insights into how large organizations influence crypto markets today—and what lies ahead—as digital currencies inch closer toward mainstream financial ecosystems worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👀 Les regards sont braqués sur $0.20 comme zone d’accumulation idéale.
✅ R/R setup explosif : les acheteurs pourraient déclencher le breakout attendu. 🚀
👉 Tu stackes $HBAR ou tu attends le décollage ?
#HBAR #crypto
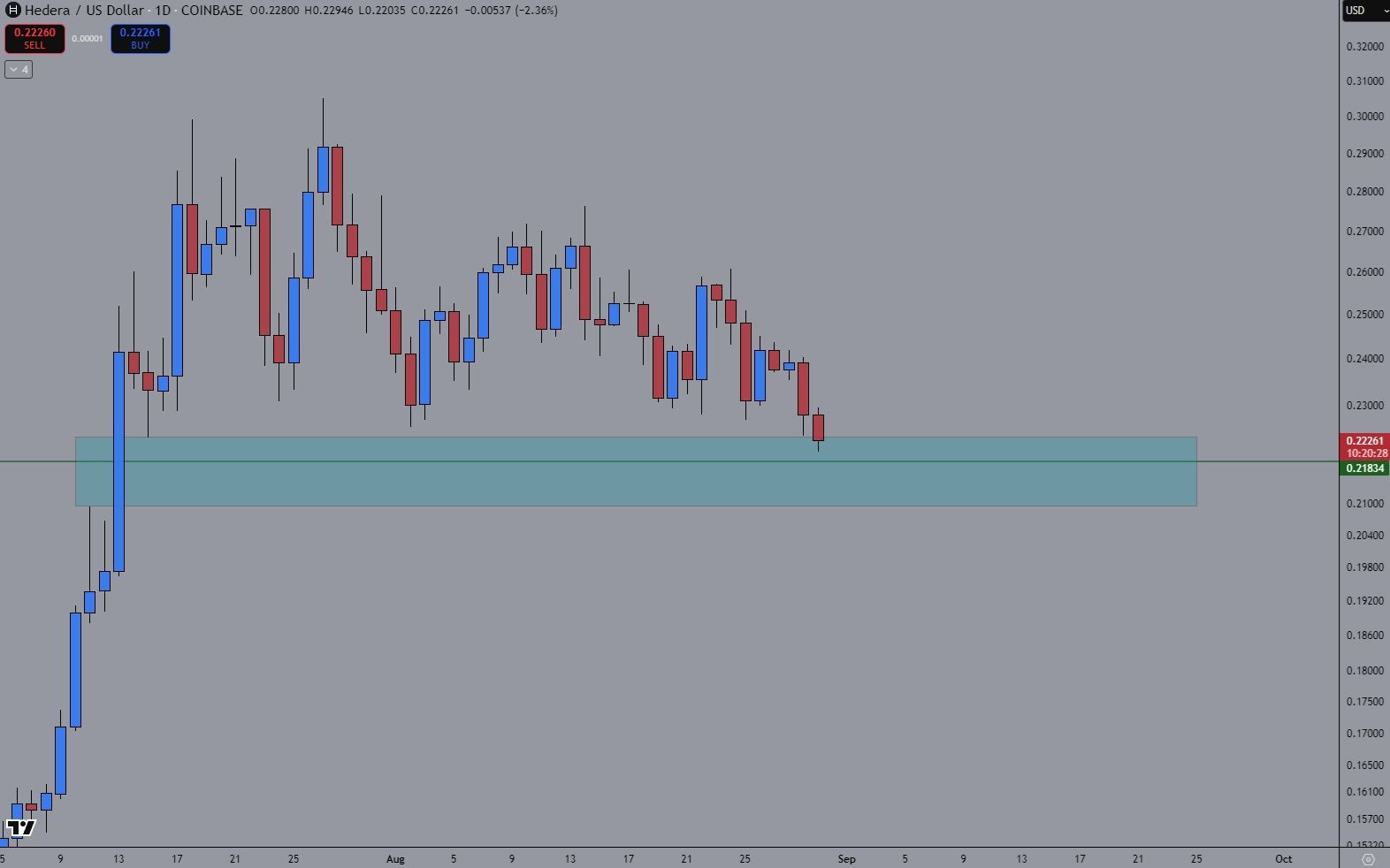


Carmelita
2025-08-30 23:41
$HBAR se resserre dans une zone clé de volume.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.