How Is Dogecoin Different from Bitcoin?
Understanding the differences between Dogecoin and Bitcoin is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrencies, whether you're a new investor or an experienced trader. Both digital currencies have unique features, origins, and market behaviors that influence their roles within the broader crypto ecosystem. This article explores these distinctions in detail to help clarify how each operates and what sets them apart.
Origins of Bitcoin and Dogecoin
Bitcoin was created in 2008 by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It was launched in January 2009 with the goal of establishing a decentralized digital currency free from government control. As the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin introduced blockchain technology—a transparent ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers—laying the foundation for countless other cryptocurrencies.
Dogecoin, on the other hand, emerged much later in December 2013. It was developed by Jackson Palmer and Billy Markus as a lighthearted alternative to Bitcoin, inspired by the popular "Doge" meme featuring a Shiba Inu dog. Initially conceived as a joke or parody cryptocurrency, Dogecoin quickly gained popularity due to its fun branding and active community support.
Technical Specifications: Blockchain & Transaction Mechanics
One of the key differences between these two cryptocurrencies lies in their technical architecture:
Blockchain Technology: Both use proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithms that require miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. However, their implementation details differ significantly.
Block Time:
- Bitcoin: Processes new blocks approximately every 10 minutes.
- Dogecoin: Has a faster block time of about one minute, enabling quicker transaction confirmation.
Supply Limits:
- Bitcoin: Has a fixed supply cap at 21 million coins—this scarcity has contributed heavily to its value proposition.
- Dogecoin: Does not have such strict scarcity; its total supply is capped at around 10 billion coins initially but continues to be mined indefinitely without an upper limit.
Transaction Speed & Costs: Due to its faster block time, Dogecoin generally offers quicker transaction processing with lower fees compared to Bitcoin’s slower network which can sometimes lead to higher transaction costs during peak times.
These technical differences influence how each currency is used—Bitcoin often functions as digital gold or store of value due to its limited supply and security features; meanwhile, Dogecoin's speed makes it suitable for tipping content creators or small transactions within online communities.
Market Dynamics & Adoption Trends
Market behavior reflects both technological attributes and community engagement:
Market Capitalization & Value:
Bitcoin dominates as the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization globally. Its widespread adoption among institutional investors has cemented its status as "digital gold." Its high volatility presents risks but also opportunities for significant gains.
Conversely, Dogecoin's market cap remains substantially smaller but has experienced notable surges driven largely by social media hype rather than institutional backing alone.
Volatility & Community Influence:
While both are volatile assets—common among cryptocurrencies—Dogecoin tends toward less extreme swings compared with Bitcoin’s rapid price fluctuations during bull markets. The strength behind Dogecoin lies heavily in its active community which frequently promotes it through platforms like Reddit and Twitter; this grassroots support often results in sudden price movements based on social sentiment rather than fundamental financial metrics.
In contrast, Bitcoin’s adoption rate among mainstream financial institutions lends it more stability over time despite short-term volatility spikes.
Recent Developments Impacting Both Cryptocurrencies
Recent news highlights ongoing regulatory scrutiny affecting both assets:
On May 10th ,2025—the SEC delayed approval for Bitwise's proposed Dogecoin ETF until June 15th . This move underscores increasing regulatory oversight aimed at protecting investors but also introduces uncertainty into how regulators will treat various crypto products moving forward.
Community-driven initiatives continue shaping public perception around both currencies; however,regulatory delays could hinder further mainstream acceptance especially if governments impose stricter rules on trading platforms or token offerings.
Regulatory Environment & Future Outlook
The evolving regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping future prospects for both cryptocurrencies:
- Increased scrutiny from authorities like SEC may lead toward tighter regulations on crypto exchanges and investment vehicles such as ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds). Such measures could impact liquidity levels or restrict certain trading activities involving tokens like Dogecoin.
- Competition between established players like Bitcoin versus newer entrants such as Dogecoin influences overall market dynamics; while some see potential growth driven by community support (as seen with meme coins), others emphasize security standards rooted in proven blockchain technology.
- Institutional interest remains pivotal: While institutions have shown growing interest primarily towards Bitcoin due to perceived stability and recognition from major companies—including Tesla—their stance on meme-based coins remains cautious yet open-minded depending on regulatory developments.
Key Takeaways About How They Differ
To summarize some core distinctions:
Origins: Created nearly five years apart with different initial purposes—Bitcoin aiming for decentralization; Doge starting as satire/community project.
Technical Specs: Faster block times (1 minute vs ~10 minutes), differing supply caps (21 million vs ~10 billion), varying transaction speeds/costs.
Market Role: Dominant store of value versus niche internet culture asset supported strongly by communities rather than institutional backing alone.
By understanding these fundamental differences—and considering ongoing developments—you can better evaluate each cryptocurrency's potential role within your investment strategy or usage scenario while appreciating their unique contributions within blockchain innovation efforts worldwide.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-29 05:45
How is Dogecoin different from Bitcoin?
How Is Dogecoin Different from Bitcoin?
Understanding the differences between Dogecoin and Bitcoin is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrencies, whether you're a new investor or an experienced trader. Both digital currencies have unique features, origins, and market behaviors that influence their roles within the broader crypto ecosystem. This article explores these distinctions in detail to help clarify how each operates and what sets them apart.
Origins of Bitcoin and Dogecoin
Bitcoin was created in 2008 by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It was launched in January 2009 with the goal of establishing a decentralized digital currency free from government control. As the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin introduced blockchain technology—a transparent ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers—laying the foundation for countless other cryptocurrencies.
Dogecoin, on the other hand, emerged much later in December 2013. It was developed by Jackson Palmer and Billy Markus as a lighthearted alternative to Bitcoin, inspired by the popular "Doge" meme featuring a Shiba Inu dog. Initially conceived as a joke or parody cryptocurrency, Dogecoin quickly gained popularity due to its fun branding and active community support.
Technical Specifications: Blockchain & Transaction Mechanics
One of the key differences between these two cryptocurrencies lies in their technical architecture:
Blockchain Technology: Both use proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithms that require miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. However, their implementation details differ significantly.
Block Time:
- Bitcoin: Processes new blocks approximately every 10 minutes.
- Dogecoin: Has a faster block time of about one minute, enabling quicker transaction confirmation.
Supply Limits:
- Bitcoin: Has a fixed supply cap at 21 million coins—this scarcity has contributed heavily to its value proposition.
- Dogecoin: Does not have such strict scarcity; its total supply is capped at around 10 billion coins initially but continues to be mined indefinitely without an upper limit.
Transaction Speed & Costs: Due to its faster block time, Dogecoin generally offers quicker transaction processing with lower fees compared to Bitcoin’s slower network which can sometimes lead to higher transaction costs during peak times.
These technical differences influence how each currency is used—Bitcoin often functions as digital gold or store of value due to its limited supply and security features; meanwhile, Dogecoin's speed makes it suitable for tipping content creators or small transactions within online communities.
Market Dynamics & Adoption Trends
Market behavior reflects both technological attributes and community engagement:
Market Capitalization & Value:
Bitcoin dominates as the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization globally. Its widespread adoption among institutional investors has cemented its status as "digital gold." Its high volatility presents risks but also opportunities for significant gains.
Conversely, Dogecoin's market cap remains substantially smaller but has experienced notable surges driven largely by social media hype rather than institutional backing alone.
Volatility & Community Influence:
While both are volatile assets—common among cryptocurrencies—Dogecoin tends toward less extreme swings compared with Bitcoin’s rapid price fluctuations during bull markets. The strength behind Dogecoin lies heavily in its active community which frequently promotes it through platforms like Reddit and Twitter; this grassroots support often results in sudden price movements based on social sentiment rather than fundamental financial metrics.
In contrast, Bitcoin’s adoption rate among mainstream financial institutions lends it more stability over time despite short-term volatility spikes.
Recent Developments Impacting Both Cryptocurrencies
Recent news highlights ongoing regulatory scrutiny affecting both assets:
On May 10th ,2025—the SEC delayed approval for Bitwise's proposed Dogecoin ETF until June 15th . This move underscores increasing regulatory oversight aimed at protecting investors but also introduces uncertainty into how regulators will treat various crypto products moving forward.
Community-driven initiatives continue shaping public perception around both currencies; however,regulatory delays could hinder further mainstream acceptance especially if governments impose stricter rules on trading platforms or token offerings.
Regulatory Environment & Future Outlook
The evolving regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping future prospects for both cryptocurrencies:
- Increased scrutiny from authorities like SEC may lead toward tighter regulations on crypto exchanges and investment vehicles such as ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds). Such measures could impact liquidity levels or restrict certain trading activities involving tokens like Dogecoin.
- Competition between established players like Bitcoin versus newer entrants such as Dogecoin influences overall market dynamics; while some see potential growth driven by community support (as seen with meme coins), others emphasize security standards rooted in proven blockchain technology.
- Institutional interest remains pivotal: While institutions have shown growing interest primarily towards Bitcoin due to perceived stability and recognition from major companies—including Tesla—their stance on meme-based coins remains cautious yet open-minded depending on regulatory developments.
Key Takeaways About How They Differ
To summarize some core distinctions:
Origins: Created nearly five years apart with different initial purposes—Bitcoin aiming for decentralization; Doge starting as satire/community project.
Technical Specs: Faster block times (1 minute vs ~10 minutes), differing supply caps (21 million vs ~10 billion), varying transaction speeds/costs.
Market Role: Dominant store of value versus niche internet culture asset supported strongly by communities rather than institutional backing alone.
By understanding these fundamental differences—and considering ongoing developments—you can better evaluate each cryptocurrency's potential role within your investment strategy or usage scenario while appreciating their unique contributions within blockchain innovation efforts worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can Bollinger Bands Be Used in Trading?
Understanding Bollinger Bands and Their Role in Technical Analysis
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool designed to measure market volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, these bands consist of a simple moving average (SMA) and two standard deviations plotted above and below it. The primary purpose of Bollinger Bands is to provide traders with insights into whether an asset is overbought or oversold, as well as to detect possible trend reversals or breakouts.
The typical setup involves a 20-period SMA, which smooths out price fluctuations over that timeframe. The upper band is calculated by adding twice the standard deviation to the SMA, while the lower band subtracts twice the standard deviation from it. Because these bands are dynamic—they expand and contract based on market volatility—they adapt to changing market conditions, making them particularly useful across different asset classes such as stocks, forex, commodities, and increasingly in cryptocurrencies.
Practical Applications of Bollinger Bands in Trading Strategies
Traders utilize Bollinger Bands for various purposes within their trading strategies:
Identifying Overbought or Oversold Conditions: When prices touch or cross above the upper band, it may suggest that an asset is overbought—potentially signaling a forthcoming reversal downward. Conversely, when prices reach or dip below the lower band, it could indicate oversold conditions—possibly hinting at an upward bounce.
Spotting Trend Reversals: Persistent touches of one band followed by a reversal can signal changes in trend direction. For example, if prices consistently hit the upper band but fail to break through convincingly before reversing downward, this might be indicative of weakening bullish momentum.
Detecting Breakouts: Significant price movements outside of the bands often precede strong trends or breakout scenarios. Traders watch for such breakouts as signals for entering new positions aligned with emerging trends.
Setting Stop-Losses: Many traders use Bollinger Bands to determine optimal stop-loss levels—for instance, placing stops just outside the bands when entering trades near support (lower band) or resistance (upper band).
Interpreting Volatility with Band Width
One key feature of Bollinger Bands is their ability to reflect market volatility through their width:
When markets are calm with low volatility—such as during sideways trading—the bands tend to contract closely together.
During periods of high volatility—like sudden price spikes—the bands widen significantly.
This characteristic helps traders anticipate potential breakout points; narrow bands often precede sharp moves once volatility increases again. Recognizing these phases allows traders to prepare for upcoming significant price actions rather than reacting impulsively after they occur.
Using Bollinger Bands Effectively in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility compared to traditional assets like stocks or forex pairs. This makes Bollinger Bands especially valuable here because they can help identify rapid shifts in sentiment and trend reversals more precisely than some other indicators.
In crypto trading:
Traders often look for "band squeezes" where both upper and lower bands converge tightly—a sign that a major move might be imminent.
Breakouts beyond either band can signal strong directional moves; however, caution should be exercised since false signals are common due to crypto's unpredictable nature.
To improve accuracy when applying Bollinger Bands within crypto markets:
- Combine them with volume analysis — increased volume during breakouts adds confirmation.
- Use additional indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) for better validation.
- Adjust parameters if necessary—for example adjusting period lengths—to suit specific cryptocurrencies' behavior patterns.
Limitations and Risks Associated With Using Bollinger Bands
While widely used among professional traders—and suitable across multiple markets—BollingerBands have limitations that must be acknowledged:
Overreliance on Technical Signals: Relying solely on Band signals without considering fundamental factors can lead traders astray during unexpected news events affecting asset prices.
False Breakouts: Price may temporarily breach outer bands without establishing a sustained trend change—a phenomenon known as false signals—which could result in premature entries/exits.
Market Manipulation Risks: In highly volatile assets like cryptocurrencies—with less regulation—market manipulation can distort indicator readings leading traders into misleading positions.
Parameter Sensitivity: Default settings may not suit all assets; adjusting periods or standard deviations requires experience and testing for optimal results under different conditions.
To mitigate these risks: combine BollINGER Band analysis with other technical tools; stay updated on fundamental developments; practice disciplined risk management strategies including stop-loss orders; continually refine your approach based on historical performance data.
By understanding how bollINGER BANDS function—and integrating them thoughtfully into broader trading frameworks—you enhance your ability not only to spot potential entry points but also manage risk effectively amid volatile markets like cryptocurrencies today’s trader faces complex challenges but also exciting opportunities when leveraging robust tools like bollINGER BANDS intelligently


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-29 04:57
How can Bollinger Bands be used in trading?
How Can Bollinger Bands Be Used in Trading?
Understanding Bollinger Bands and Their Role in Technical Analysis
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool designed to measure market volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, these bands consist of a simple moving average (SMA) and two standard deviations plotted above and below it. The primary purpose of Bollinger Bands is to provide traders with insights into whether an asset is overbought or oversold, as well as to detect possible trend reversals or breakouts.
The typical setup involves a 20-period SMA, which smooths out price fluctuations over that timeframe. The upper band is calculated by adding twice the standard deviation to the SMA, while the lower band subtracts twice the standard deviation from it. Because these bands are dynamic—they expand and contract based on market volatility—they adapt to changing market conditions, making them particularly useful across different asset classes such as stocks, forex, commodities, and increasingly in cryptocurrencies.
Practical Applications of Bollinger Bands in Trading Strategies
Traders utilize Bollinger Bands for various purposes within their trading strategies:
Identifying Overbought or Oversold Conditions: When prices touch or cross above the upper band, it may suggest that an asset is overbought—potentially signaling a forthcoming reversal downward. Conversely, when prices reach or dip below the lower band, it could indicate oversold conditions—possibly hinting at an upward bounce.
Spotting Trend Reversals: Persistent touches of one band followed by a reversal can signal changes in trend direction. For example, if prices consistently hit the upper band but fail to break through convincingly before reversing downward, this might be indicative of weakening bullish momentum.
Detecting Breakouts: Significant price movements outside of the bands often precede strong trends or breakout scenarios. Traders watch for such breakouts as signals for entering new positions aligned with emerging trends.
Setting Stop-Losses: Many traders use Bollinger Bands to determine optimal stop-loss levels—for instance, placing stops just outside the bands when entering trades near support (lower band) or resistance (upper band).
Interpreting Volatility with Band Width
One key feature of Bollinger Bands is their ability to reflect market volatility through their width:
When markets are calm with low volatility—such as during sideways trading—the bands tend to contract closely together.
During periods of high volatility—like sudden price spikes—the bands widen significantly.
This characteristic helps traders anticipate potential breakout points; narrow bands often precede sharp moves once volatility increases again. Recognizing these phases allows traders to prepare for upcoming significant price actions rather than reacting impulsively after they occur.
Using Bollinger Bands Effectively in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility compared to traditional assets like stocks or forex pairs. This makes Bollinger Bands especially valuable here because they can help identify rapid shifts in sentiment and trend reversals more precisely than some other indicators.
In crypto trading:
Traders often look for "band squeezes" where both upper and lower bands converge tightly—a sign that a major move might be imminent.
Breakouts beyond either band can signal strong directional moves; however, caution should be exercised since false signals are common due to crypto's unpredictable nature.
To improve accuracy when applying Bollinger Bands within crypto markets:
- Combine them with volume analysis — increased volume during breakouts adds confirmation.
- Use additional indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) for better validation.
- Adjust parameters if necessary—for example adjusting period lengths—to suit specific cryptocurrencies' behavior patterns.
Limitations and Risks Associated With Using Bollinger Bands
While widely used among professional traders—and suitable across multiple markets—BollingerBands have limitations that must be acknowledged:
Overreliance on Technical Signals: Relying solely on Band signals without considering fundamental factors can lead traders astray during unexpected news events affecting asset prices.
False Breakouts: Price may temporarily breach outer bands without establishing a sustained trend change—a phenomenon known as false signals—which could result in premature entries/exits.
Market Manipulation Risks: In highly volatile assets like cryptocurrencies—with less regulation—market manipulation can distort indicator readings leading traders into misleading positions.
Parameter Sensitivity: Default settings may not suit all assets; adjusting periods or standard deviations requires experience and testing for optimal results under different conditions.
To mitigate these risks: combine BollINGER Band analysis with other technical tools; stay updated on fundamental developments; practice disciplined risk management strategies including stop-loss orders; continually refine your approach based on historical performance data.
By understanding how bollINGER BANDS function—and integrating them thoughtfully into broader trading frameworks—you enhance your ability not only to spot potential entry points but also manage risk effectively amid volatile markets like cryptocurrencies today’s trader faces complex challenges but also exciting opportunities when leveraging robust tools like bollINGER BANDS intelligently
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are the Advantages of Using a Market Order?
When engaging in financial trading, understanding different order types is essential for executing strategies effectively. Among these, the market order stands out as one of the most straightforward and widely used tools. Its simplicity and immediacy make it particularly appealing to traders who prioritize quick execution over price precision. This article explores the key advantages of using a market order, providing insights into why traders across various markets—stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities—prefer this type of instruction.
Immediate Execution Ensures Quick Entry and Exit
One of the primary benefits of a market order is its ability to execute immediately upon placement. When a trader submits a market order, it is sent directly to the exchange or broker for instant processing. This feature is especially valuable in fast-moving markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly within seconds. For traders aiming to capitalize on short-term movements or needing to exit positions swiftly to limit losses, immediate execution can be critical.
In volatile environments like cryptocurrency markets or during significant news events affecting stock prices, delays in execution could mean missing out on optimal entry or exit points. Market orders eliminate this concern by prioritizing speed over price specificity.
Flexibility Across Asset Classes
Market orders are versatile and applicable across various asset classes including stocks, bonds, commodities, ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds), and cryptocurrencies. Whether an investor wants to buy shares in a company during an IPO or sell Bitcoin quickly during sudden price swings—market orders facilitate these transactions seamlessly.
This flexibility simplifies trading strategies because traders do not need to specify complex parameters such as limit prices unless they wish to do so later with other types of orders like limit or stop-loss orders. The ease of use makes market orders suitable for both novice investors learning about trading mechanics and experienced professionals executing rapid trades.
Simplicity Makes Trading More Accessible
Placing a market order requires minimal input: typically just specifying what security you want to buy or sell and how much you want involved. Unlike more complex instructions that involve setting specific target prices (limit orders) or conditional triggers (stop-loss), market orders are straightforward commands that anyone can understand easily.
This simplicity reduces potential errors during trade placement—a crucial factor for beginners who may find detailed instructions intimidating at first glance—and speeds up decision-making processes when quick action is needed.
Risk Management Through Speed
While some might assume that placing an immediate buy or sell exposes traders solely to risks related to unfavorable prices due to volatility; many see it as part of effective risk management when used appropriately. By executing trades instantly at current market conditions, traders avoid situations where their intended transaction gets delayed due to network issues or hesitation that could lead them into worse pricing scenarios later on.
Furthermore, combining market orders with other risk mitigation tools such as stop-losses allows traders not only for swift entry/exit but also controlled risk exposure based on predefined thresholds rather than waiting indefinitely for ideal conditions which may never materialize amid turbulent markets.
Cost Efficiency Compared To Limit Orders
In some cases—particularly in highly liquid markets—market orders can be more cost-effective than limit orders because they guarantee execution without additional fees associated with setting specific price points that might not be reached promptly—or at all—in volatile conditions.
Since limit orders require patience until your specified price level is hit—which might never happen if the asset's price moves away quickly—a market order ensures your trade goes through immediately without waiting for favorable pricing conditions that may no longer exist by then.
However, it's important for traders aware of potential slippage—the difference between expected transaction prices and actual executed prices—to weigh whether immediate execution outweighs possible costs from less favorable fill rates during periods of high volatility.
Contexts Where Market Orders Are Particularly Useful
Market orders are especially advantageous under certain circumstances:
- High Volatility Markets: During rapid price changes—as seen frequently in cryptocurrency exchanges—they allow quick entry/exit before significant shifts occur.
- Time-Sensitive Trades: When timing matters most—for example: reacting swiftly after earnings reports—they enable prompt action.
- Liquidity-Rich Environments: In highly traded assets like major stocks listed on prominent exchanges where bid-ask spreads are narrow.
Despite their advantages, users should remain cautious about potential drawbacks such as slippage—the difference between expected purchase/sale price versus actual executed rate—which becomes more pronounced during low liquidity periods.
Recent Trends Enhancing Market Order Utility
Advancements in technology have significantly improved how efficiently investors utilize market orders today:
- Automated Trading Algorithms: High-frequency trading systems execute thousands of transactions per second using algorithms optimized around immediate executions.
- Enhanced Trading Platforms: Modern online brokers provide intuitive interfaces allowing even novice users instant access with minimal delay.
- Regulatory Oversight: Authorities have implemented guidelines aimed at protecting investors from manipulative practices involving rapid-fire trades driven by high-frequency algorithms utilizing large volumes of market-orders.
These developments ensure that while risks remain—especially concerning flash crashes caused by algorithmic trading—the overall utility and safety profile surrounding well-managed use cases continue improving.
Key Considerations When Using Market Orders
While offering many benefits—including speed and simplicity—it’s vital for traders employing market orders also consider certain factors:
- Slippage Risks: During volatile periods or low liquidity times (e.g., after-hours trading), actual fill prices may differ significantly from current quotes.
- Overtrading Potential: The ease with which one can place multiple rapid-fire trades might lead inexperienced investors toward impulsive decisions lacking strategic planning.
- Market Manipulation Concerns: In less regulated environments like some cryptocurrency exchanges—or through tactics such as quote stuffing—high volumes of aggressive-market-orders could distort true supply/demand signals if unchecked.
Final Thoughts on Using Market Orders Effectively
Market orders serve as powerful tools within any trader’s arsenal due primarily to their ability to deliver swift transaction executions across diverse financial instruments worldwide. Their inherent simplicity makes them accessible even for newcomers while providing seasoned professionals with rapid response capabilities essential amid dynamic markets characterized by high volatility—and increasingly sophisticated technological infrastructure supporting these operations globally.
To maximize benefits while mitigating risks associated with slippage and overtrading requires understanding when best suited—for instance: urgent entries/exits versus strategic positioning requiring precise control over purchase/sale levels—and integrating them thoughtfully within broader risk management frameworks such as stop-losses combined with other advanced order types.
By grasping both their strengths and limitations comprehensively—from immediate execution advantages through technological trends shaping modern trading environments—you position yourself better equipped either as an active trader seeking efficiency or an investor aiming informed decision-making aligned with evolving global markets' realities


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-29 02:01
What are the advantages of using a market order?
What Are the Advantages of Using a Market Order?
When engaging in financial trading, understanding different order types is essential for executing strategies effectively. Among these, the market order stands out as one of the most straightforward and widely used tools. Its simplicity and immediacy make it particularly appealing to traders who prioritize quick execution over price precision. This article explores the key advantages of using a market order, providing insights into why traders across various markets—stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities—prefer this type of instruction.
Immediate Execution Ensures Quick Entry and Exit
One of the primary benefits of a market order is its ability to execute immediately upon placement. When a trader submits a market order, it is sent directly to the exchange or broker for instant processing. This feature is especially valuable in fast-moving markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly within seconds. For traders aiming to capitalize on short-term movements or needing to exit positions swiftly to limit losses, immediate execution can be critical.
In volatile environments like cryptocurrency markets or during significant news events affecting stock prices, delays in execution could mean missing out on optimal entry or exit points. Market orders eliminate this concern by prioritizing speed over price specificity.
Flexibility Across Asset Classes
Market orders are versatile and applicable across various asset classes including stocks, bonds, commodities, ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds), and cryptocurrencies. Whether an investor wants to buy shares in a company during an IPO or sell Bitcoin quickly during sudden price swings—market orders facilitate these transactions seamlessly.
This flexibility simplifies trading strategies because traders do not need to specify complex parameters such as limit prices unless they wish to do so later with other types of orders like limit or stop-loss orders. The ease of use makes market orders suitable for both novice investors learning about trading mechanics and experienced professionals executing rapid trades.
Simplicity Makes Trading More Accessible
Placing a market order requires minimal input: typically just specifying what security you want to buy or sell and how much you want involved. Unlike more complex instructions that involve setting specific target prices (limit orders) or conditional triggers (stop-loss), market orders are straightforward commands that anyone can understand easily.
This simplicity reduces potential errors during trade placement—a crucial factor for beginners who may find detailed instructions intimidating at first glance—and speeds up decision-making processes when quick action is needed.
Risk Management Through Speed
While some might assume that placing an immediate buy or sell exposes traders solely to risks related to unfavorable prices due to volatility; many see it as part of effective risk management when used appropriately. By executing trades instantly at current market conditions, traders avoid situations where their intended transaction gets delayed due to network issues or hesitation that could lead them into worse pricing scenarios later on.
Furthermore, combining market orders with other risk mitigation tools such as stop-losses allows traders not only for swift entry/exit but also controlled risk exposure based on predefined thresholds rather than waiting indefinitely for ideal conditions which may never materialize amid turbulent markets.
Cost Efficiency Compared To Limit Orders
In some cases—particularly in highly liquid markets—market orders can be more cost-effective than limit orders because they guarantee execution without additional fees associated with setting specific price points that might not be reached promptly—or at all—in volatile conditions.
Since limit orders require patience until your specified price level is hit—which might never happen if the asset's price moves away quickly—a market order ensures your trade goes through immediately without waiting for favorable pricing conditions that may no longer exist by then.
However, it's important for traders aware of potential slippage—the difference between expected transaction prices and actual executed prices—to weigh whether immediate execution outweighs possible costs from less favorable fill rates during periods of high volatility.
Contexts Where Market Orders Are Particularly Useful
Market orders are especially advantageous under certain circumstances:
- High Volatility Markets: During rapid price changes—as seen frequently in cryptocurrency exchanges—they allow quick entry/exit before significant shifts occur.
- Time-Sensitive Trades: When timing matters most—for example: reacting swiftly after earnings reports—they enable prompt action.
- Liquidity-Rich Environments: In highly traded assets like major stocks listed on prominent exchanges where bid-ask spreads are narrow.
Despite their advantages, users should remain cautious about potential drawbacks such as slippage—the difference between expected purchase/sale price versus actual executed rate—which becomes more pronounced during low liquidity periods.
Recent Trends Enhancing Market Order Utility
Advancements in technology have significantly improved how efficiently investors utilize market orders today:
- Automated Trading Algorithms: High-frequency trading systems execute thousands of transactions per second using algorithms optimized around immediate executions.
- Enhanced Trading Platforms: Modern online brokers provide intuitive interfaces allowing even novice users instant access with minimal delay.
- Regulatory Oversight: Authorities have implemented guidelines aimed at protecting investors from manipulative practices involving rapid-fire trades driven by high-frequency algorithms utilizing large volumes of market-orders.
These developments ensure that while risks remain—especially concerning flash crashes caused by algorithmic trading—the overall utility and safety profile surrounding well-managed use cases continue improving.
Key Considerations When Using Market Orders
While offering many benefits—including speed and simplicity—it’s vital for traders employing market orders also consider certain factors:
- Slippage Risks: During volatile periods or low liquidity times (e.g., after-hours trading), actual fill prices may differ significantly from current quotes.
- Overtrading Potential: The ease with which one can place multiple rapid-fire trades might lead inexperienced investors toward impulsive decisions lacking strategic planning.
- Market Manipulation Concerns: In less regulated environments like some cryptocurrency exchanges—or through tactics such as quote stuffing—high volumes of aggressive-market-orders could distort true supply/demand signals if unchecked.
Final Thoughts on Using Market Orders Effectively
Market orders serve as powerful tools within any trader’s arsenal due primarily to their ability to deliver swift transaction executions across diverse financial instruments worldwide. Their inherent simplicity makes them accessible even for newcomers while providing seasoned professionals with rapid response capabilities essential amid dynamic markets characterized by high volatility—and increasingly sophisticated technological infrastructure supporting these operations globally.
To maximize benefits while mitigating risks associated with slippage and overtrading requires understanding when best suited—for instance: urgent entries/exits versus strategic positioning requiring precise control over purchase/sale levels—and integrating them thoughtfully within broader risk management frameworks such as stop-losses combined with other advanced order types.
By grasping both their strengths and limitations comprehensively—from immediate execution advantages through technological trends shaping modern trading environments—you position yourself better equipped either as an active trader seeking efficiency or an investor aiming informed decision-making aligned with evolving global markets' realities
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Place a Limit Order on TradingView: A Step-by-Step Guide
Placing a limit order is a fundamental strategy for traders looking to execute trades at specific prices. Whether you are trading stocks, cryptocurrencies, or other assets on TradingView, understanding how to effectively set and manage limit orders can significantly improve your trading outcomes. This guide provides a clear overview of the process, recent platform updates, and potential risks involved.
What Is a Limit Order?
A limit order is an instruction to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price or better. Unlike market orders that execute immediately at the current market price, limit orders only trigger when the asset reaches your specified price point. For example, if you want to buy Bitcoin at $30,000 but not higher, you would place a buy limit order with that exact price. The order remains pending until the market hits that level or your specified expiration time.
Limit orders are especially useful in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies where prices can fluctuate rapidly within short periods. They allow traders to control entry and exit points more precisely while avoiding unfavorable execution prices often associated with market orders.
Accessing TradingView for Limit Orders
TradingView offers both web-based and mobile platforms designed for user-friendly navigation and comprehensive chart analysis. To place a limit order:
- Log into your TradingView account via their website or mobile app.
- Navigate through the interface to select your desired financial instrument—be it stocks, crypto assets, forex pairs, etc.
- Use the search bar by entering the asset’s symbol (e.g., BTCUSD) or browse through available markets.
Once you've selected an asset:
- Click on "Trade" or "Order" buttons typically located near charts.
- Open the order window where you'll specify trade details such as quantity and price.
This streamlined process ensures traders can quickly move from analysis to execution without unnecessary delays.
How To Set Up Your Limit Order
After accessing the trading interface:
1. Choose 'Limit' as Your Order Type
Most platforms default to 'Market' orders; ensure you switch this setting explicitly to 'Limit.' This indicates you're setting specific conditions under which your trade will execute rather than accepting current market prices.
2. Enter Quantity
Specify how many units of an asset you'd like to buy or sell—this could be shares in stocks or units in cryptocurrencies.
3. Set Your Price
Input your desired execution price—the maximum you're willing (for buys) or minimum you're willing (for sells). Be precise here; small differences can impact whether your order gets filled quickly.
4. Select Time-in-Force Options
Decide how long your limit order remains active:
- GTC (Good Till Cancelled): Remains until manually canceled.
- GTD (Good Till Date): Expires after set date/time.
- Day: Cancels automatically if not filled during trading day.
Review all details carefully before submitting because once placed, these parameters govern how and when your trade executes.
Recent Platform Enhancements & Market Dynamics
TradingView has continually upgraded its features over recent years—adding advanced charting tools like drawing tools for technical analysis and improved risk management options such as stop-loss/take-profit settings integrated directly into their platform interface. These enhancements help traders make more informed decisions when placing limit orders based on real-time data insights rather than guesswork alone.
The cryptocurrency sector has experienced heightened volatility lately due to macroeconomic factors and regulatory shifts worldwide—a situation that amplifies reliance on strategic entry/exit points provided by limit orders for managing risk effectively amid rapid swings in prices across exchanges globally.
Additionally, regulatory changes have influenced how exchanges handle different types of orders including limits; some jurisdictions now impose stricter rules around execution times which may affect overall trading strategies involving these instructions.
Risks Associated With Limit Orders
While placing limits offers precision control over trades:
Market Liquidity: Large volumes of pending limit orders can temporarily distort supply-demand dynamics within certain assets’ markets leading potentially unpredictable short-term movements.
Order Execution Failures: If market conditions do not reach specified levels before expiration—or if they change suddenly—you might miss out entirely on intended trades resulting in opportunity costs.
Technological Glitches: Technical issues such as server outages during high-volatility periods could prevent timely placement/execution of critical trades—highlighting importance of choosing reliable platforms like TradingView with robust infrastructure.
Understanding these risks helps traders develop contingency plans—for example using alerts alongside limits—to mitigate potential downsides effectively.
Managing Expectations When Using Limit Orders
Successful use of limited instructions requires patience and strategic planning:
- Always monitor broader market trends alongside individual asset behavior before setting target prices.
- Use supplementary tools such as alerts so you're notified when assets approach desired levels—even if initial limits aren’t triggered immediately.
- Regularly review open positions; adjust limits based on evolving technical signals or fundamental news events impacting markets.
By combining disciplined planning with real-time data insights offered by platforms like TradingView—and staying aware of potential pitfalls—you enhance chances for successful trade executions aligned with personal investment goals.
Placing a limit order via TradingView is straightforward once familiarized with its interface features—from selecting appropriate assets and specifying precise parameters down to understanding recent platform updates and inherent risks involved in this strategy type. Mastery over this tool empowers traders seeking greater control over their entries/exits while navigating complex financial landscapes efficiently—and ultimately supports building resilient trading practices grounded in informed decision-making processes.


kai
2025-05-26 21:38
How do I place a limit order via TradingView?
How to Place a Limit Order on TradingView: A Step-by-Step Guide
Placing a limit order is a fundamental strategy for traders looking to execute trades at specific prices. Whether you are trading stocks, cryptocurrencies, or other assets on TradingView, understanding how to effectively set and manage limit orders can significantly improve your trading outcomes. This guide provides a clear overview of the process, recent platform updates, and potential risks involved.
What Is a Limit Order?
A limit order is an instruction to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price or better. Unlike market orders that execute immediately at the current market price, limit orders only trigger when the asset reaches your specified price point. For example, if you want to buy Bitcoin at $30,000 but not higher, you would place a buy limit order with that exact price. The order remains pending until the market hits that level or your specified expiration time.
Limit orders are especially useful in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies where prices can fluctuate rapidly within short periods. They allow traders to control entry and exit points more precisely while avoiding unfavorable execution prices often associated with market orders.
Accessing TradingView for Limit Orders
TradingView offers both web-based and mobile platforms designed for user-friendly navigation and comprehensive chart analysis. To place a limit order:
- Log into your TradingView account via their website or mobile app.
- Navigate through the interface to select your desired financial instrument—be it stocks, crypto assets, forex pairs, etc.
- Use the search bar by entering the asset’s symbol (e.g., BTCUSD) or browse through available markets.
Once you've selected an asset:
- Click on "Trade" or "Order" buttons typically located near charts.
- Open the order window where you'll specify trade details such as quantity and price.
This streamlined process ensures traders can quickly move from analysis to execution without unnecessary delays.
How To Set Up Your Limit Order
After accessing the trading interface:
1. Choose 'Limit' as Your Order Type
Most platforms default to 'Market' orders; ensure you switch this setting explicitly to 'Limit.' This indicates you're setting specific conditions under which your trade will execute rather than accepting current market prices.
2. Enter Quantity
Specify how many units of an asset you'd like to buy or sell—this could be shares in stocks or units in cryptocurrencies.
3. Set Your Price
Input your desired execution price—the maximum you're willing (for buys) or minimum you're willing (for sells). Be precise here; small differences can impact whether your order gets filled quickly.
4. Select Time-in-Force Options
Decide how long your limit order remains active:
- GTC (Good Till Cancelled): Remains until manually canceled.
- GTD (Good Till Date): Expires after set date/time.
- Day: Cancels automatically if not filled during trading day.
Review all details carefully before submitting because once placed, these parameters govern how and when your trade executes.
Recent Platform Enhancements & Market Dynamics
TradingView has continually upgraded its features over recent years—adding advanced charting tools like drawing tools for technical analysis and improved risk management options such as stop-loss/take-profit settings integrated directly into their platform interface. These enhancements help traders make more informed decisions when placing limit orders based on real-time data insights rather than guesswork alone.
The cryptocurrency sector has experienced heightened volatility lately due to macroeconomic factors and regulatory shifts worldwide—a situation that amplifies reliance on strategic entry/exit points provided by limit orders for managing risk effectively amid rapid swings in prices across exchanges globally.
Additionally, regulatory changes have influenced how exchanges handle different types of orders including limits; some jurisdictions now impose stricter rules around execution times which may affect overall trading strategies involving these instructions.
Risks Associated With Limit Orders
While placing limits offers precision control over trades:
Market Liquidity: Large volumes of pending limit orders can temporarily distort supply-demand dynamics within certain assets’ markets leading potentially unpredictable short-term movements.
Order Execution Failures: If market conditions do not reach specified levels before expiration—or if they change suddenly—you might miss out entirely on intended trades resulting in opportunity costs.
Technological Glitches: Technical issues such as server outages during high-volatility periods could prevent timely placement/execution of critical trades—highlighting importance of choosing reliable platforms like TradingView with robust infrastructure.
Understanding these risks helps traders develop contingency plans—for example using alerts alongside limits—to mitigate potential downsides effectively.
Managing Expectations When Using Limit Orders
Successful use of limited instructions requires patience and strategic planning:
- Always monitor broader market trends alongside individual asset behavior before setting target prices.
- Use supplementary tools such as alerts so you're notified when assets approach desired levels—even if initial limits aren’t triggered immediately.
- Regularly review open positions; adjust limits based on evolving technical signals or fundamental news events impacting markets.
By combining disciplined planning with real-time data insights offered by platforms like TradingView—and staying aware of potential pitfalls—you enhance chances for successful trade executions aligned with personal investment goals.
Placing a limit order via TradingView is straightforward once familiarized with its interface features—from selecting appropriate assets and specifying precise parameters down to understanding recent platform updates and inherent risks involved in this strategy type. Mastery over this tool empowers traders seeking greater control over their entries/exits while navigating complex financial landscapes efficiently—and ultimately supports building resilient trading practices grounded in informed decision-making processes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Risks and Considerations When Buying NFTs
The rise of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) has transformed how we think about digital ownership, art, and collectibles. While many see NFTs as a promising investment or a way to support creators, it's essential to understand the potential risks involved before diving into this rapidly evolving market. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common risks and key considerations for anyone interested in acquiring NFTs.
What Are NFTs and Why Are They Popular?
NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of specific items such as artwork, music, videos, or in-game items. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum—which are interchangeable—NFTs are one-of-a-kind tokens stored on blockchain networks. This uniqueness makes them attractive for collectors and investors seeking exclusive digital assets.
The popularity of NFTs surged due to blockchain technology's transparency and security features. Platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, and SuperRare have made it easier than ever to buy, sell, and trade these tokens globally. However, despite their appeal, potential buyers must be aware of various risks associated with NFT transactions.
Market Volatility: Prices Can Fluctuate Rapidly
One of the most significant concerns with NFTs is their high market volatility. Prices can skyrocket during hype cycles but also plummet unexpectedly. For example, some artworks sold for millions during peak periods but later experienced sharp declines when market sentiment shifted.
This volatility means that investing in NFTs carries substantial risk; what seems like an appreciating asset today might lose value tomorrow. Buyers should approach NFT investments cautiously—considering long-term value rather than short-term gains—and avoid investing more than they can afford to lose.
Lack of Regulation Increases Fraud Risks
Unlike traditional financial markets governed by strict regulations, the NFT space remains largely unregulated in many jurisdictions. This regulatory gap creates opportunities for scams such as fake listings or impersonation schemes targeting unsuspecting buyers.
In recent years alone (notably 2022), numerous reports emerged about fraudulent marketplaces or counterfeit artists selling fake works under legitimate-looking profiles. Buyers must verify authenticity carefully by checking creator credentials and using reputable platforms with robust security measures.
Technical Risks: Blockchain Vulnerabilities
NFTs rely on blockchain technology; however, this infrastructure isn't immune to technical issues. Network congestion can delay transactions or cause failures during high-traffic periods—a problem seen during major sales events.
Smart contract bugs pose another concern—they are self-executing code governing NFT transactions that could contain vulnerabilities exploitable by malicious actors—potentially leading to loss or theft of assets. Additionally (as seen in 2023), attacks like 51% breaches on certain blockchains temporarily halted operations and raised questions about long-term security stability.
Intellectual Property Challenges
Ownership rights associated with NFTs often involve complex legal considerations around intellectual property (IP). While purchasing an NFT may grant ownership over a digital token linked to an artwork or media file—the actual copyright may still belong to the creator unless explicitly transferred through licensing agreements.
This ambiguity has led to disputes; for instance (in 2024), lawsuits emerged over unauthorized use rights tied to certain high-profile NFT artworks—highlighting the importance of clear legal documentation when acquiring these assets.
Environmental Impact Concerns
Blockchain networks require significant energy consumption—particularly those based on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms—which raises environmental sustainability issues linked directly with minting and trading NFTs.
In response (by 2023), several major marketplaces announced initiatives aimed at transitioning toward more energy-efficient blockchains such as proof-of-stake models that consume less power while maintaining security standards—a positive step toward reducing ecological footprints within this industry sector.
Investment Risks: Speculation Can Lead To Losses
Many marketing narratives promote NFTs as lucrative investments; however—and unlike traditional assets—their values are highly speculative driven by trends rather than intrinsic worth alone.For example (in 2022), some projects collapsed after hype faded away quickly causing investors who bought into early enthusiasm suffering substantial losses.Potential buyers should conduct thorough research before investing heavily in any project—and consider whether they’re comfortable with high-risk speculative behavior typical within this space.
Taxation & Legal Uncertainties
Tax laws surrounding NFT transactions remain ambiguous across different countries—posing challenges related either to reporting gains/losses accurately or understanding applicable liabilities.In 2024—for instance—the IRS issued guidelines clarifying some aspects but left many questions unanswered regarding valuation methods or taxable events involving gifting/selling tokens.Legal status varies widely depending on jurisdiction; therefore consulting tax professionals familiar with local laws is advisable prior to engaging extensively in buying/selling activities.
Scams & Phishing Attacks Targeting Buyers
Scammers frequently exploit newcomers through phishing emails pretending to be legitimate platforms—or create fake marketplaces mimicking real ones—to steal funds from unsuspecting users.In one notable case from 2023—a widespread phishing campaign resulted in significant financial losses when victims unwittingly shared private keys or authorized malicious contracts.To protect oneself:
- Always verify website URLs
- Use two-factor authentication
- Avoid sharing private keys
- Purchase only from trusted sources
Storage Security: Protect Your Digital Assets
Once you acquire an NFT—it’s crucial not only how you buy it but also how you store it securely afterward.Hacking incidents have led several prominent collections—including valuable CryptoPunks—to be stolen due primarily to insecure wallets or compromised accounts.Using hardware wallets—or secure custodial services—is recommended for safeguarding valuable holdings against theft.
Recent Developments Shaping the Future Landscape
Recent legal actions highlight ongoing scrutiny within the industry:
- Nike Class Action Lawsuit: In 2025, Nike faced allegations over its proprietary NFT platform amid claims seeking damages exceeding $5 million [1]. Such cases underscore increasing regulatory attention towards marketplace practices.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are beginning efforts:
- The SEC issued new guidelines around 2024 aimed at protecting investors while clarifying compliance expectations for creators and platforms alike [2].
Technological innovations continue improving:
- Transition toward energy-efficient blockchains reduces environmental impact,
- Advanced storage solutions enhance asset security,which collectively contribute toward making future participation safer yet still cautious engagement remains essential due diligence is vital when navigating this dynamic environment.
Navigating Risks Effectively When Acquiring NFTs
Understanding these risks helps prospective buyers make informed decisions aligned with their risk tolerance levels:
- Research Thoroughly — Verify artist credentials & platform reputation
- Use Reputable Marketplaces — Prefer established sites known for security
- Secure Storage Solutions — Invest in hardware wallets if holding valuable assets
- Stay Updated on Regulations — Follow legal developments relevant locally
5.. Be Skeptical About Hype — Avoid impulsive purchases driven solely by FOMO
By staying informed about potential pitfalls—from technical vulnerabilities through legal uncertainties—you can better safeguard your investments while participating responsibly within this innovative space.
[1] Source: Industry News - Nike Lawsuit Highlights Regulatory Scrutiny
[2] Source: Government Guidelines - SEC Regulations on Digital Assets


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 20:31
What are the common risks or considerations when acquiring NFTs?
Understanding the Risks and Considerations When Buying NFTs
The rise of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) has transformed how we think about digital ownership, art, and collectibles. While many see NFTs as a promising investment or a way to support creators, it's essential to understand the potential risks involved before diving into this rapidly evolving market. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common risks and key considerations for anyone interested in acquiring NFTs.
What Are NFTs and Why Are They Popular?
NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of specific items such as artwork, music, videos, or in-game items. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum—which are interchangeable—NFTs are one-of-a-kind tokens stored on blockchain networks. This uniqueness makes them attractive for collectors and investors seeking exclusive digital assets.
The popularity of NFTs surged due to blockchain technology's transparency and security features. Platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, and SuperRare have made it easier than ever to buy, sell, and trade these tokens globally. However, despite their appeal, potential buyers must be aware of various risks associated with NFT transactions.
Market Volatility: Prices Can Fluctuate Rapidly
One of the most significant concerns with NFTs is their high market volatility. Prices can skyrocket during hype cycles but also plummet unexpectedly. For example, some artworks sold for millions during peak periods but later experienced sharp declines when market sentiment shifted.
This volatility means that investing in NFTs carries substantial risk; what seems like an appreciating asset today might lose value tomorrow. Buyers should approach NFT investments cautiously—considering long-term value rather than short-term gains—and avoid investing more than they can afford to lose.
Lack of Regulation Increases Fraud Risks
Unlike traditional financial markets governed by strict regulations, the NFT space remains largely unregulated in many jurisdictions. This regulatory gap creates opportunities for scams such as fake listings or impersonation schemes targeting unsuspecting buyers.
In recent years alone (notably 2022), numerous reports emerged about fraudulent marketplaces or counterfeit artists selling fake works under legitimate-looking profiles. Buyers must verify authenticity carefully by checking creator credentials and using reputable platforms with robust security measures.
Technical Risks: Blockchain Vulnerabilities
NFTs rely on blockchain technology; however, this infrastructure isn't immune to technical issues. Network congestion can delay transactions or cause failures during high-traffic periods—a problem seen during major sales events.
Smart contract bugs pose another concern—they are self-executing code governing NFT transactions that could contain vulnerabilities exploitable by malicious actors—potentially leading to loss or theft of assets. Additionally (as seen in 2023), attacks like 51% breaches on certain blockchains temporarily halted operations and raised questions about long-term security stability.
Intellectual Property Challenges
Ownership rights associated with NFTs often involve complex legal considerations around intellectual property (IP). While purchasing an NFT may grant ownership over a digital token linked to an artwork or media file—the actual copyright may still belong to the creator unless explicitly transferred through licensing agreements.
This ambiguity has led to disputes; for instance (in 2024), lawsuits emerged over unauthorized use rights tied to certain high-profile NFT artworks—highlighting the importance of clear legal documentation when acquiring these assets.
Environmental Impact Concerns
Blockchain networks require significant energy consumption—particularly those based on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms—which raises environmental sustainability issues linked directly with minting and trading NFTs.
In response (by 2023), several major marketplaces announced initiatives aimed at transitioning toward more energy-efficient blockchains such as proof-of-stake models that consume less power while maintaining security standards—a positive step toward reducing ecological footprints within this industry sector.
Investment Risks: Speculation Can Lead To Losses
Many marketing narratives promote NFTs as lucrative investments; however—and unlike traditional assets—their values are highly speculative driven by trends rather than intrinsic worth alone.For example (in 2022), some projects collapsed after hype faded away quickly causing investors who bought into early enthusiasm suffering substantial losses.Potential buyers should conduct thorough research before investing heavily in any project—and consider whether they’re comfortable with high-risk speculative behavior typical within this space.
Taxation & Legal Uncertainties
Tax laws surrounding NFT transactions remain ambiguous across different countries—posing challenges related either to reporting gains/losses accurately or understanding applicable liabilities.In 2024—for instance—the IRS issued guidelines clarifying some aspects but left many questions unanswered regarding valuation methods or taxable events involving gifting/selling tokens.Legal status varies widely depending on jurisdiction; therefore consulting tax professionals familiar with local laws is advisable prior to engaging extensively in buying/selling activities.
Scams & Phishing Attacks Targeting Buyers
Scammers frequently exploit newcomers through phishing emails pretending to be legitimate platforms—or create fake marketplaces mimicking real ones—to steal funds from unsuspecting users.In one notable case from 2023—a widespread phishing campaign resulted in significant financial losses when victims unwittingly shared private keys or authorized malicious contracts.To protect oneself:
- Always verify website URLs
- Use two-factor authentication
- Avoid sharing private keys
- Purchase only from trusted sources
Storage Security: Protect Your Digital Assets
Once you acquire an NFT—it’s crucial not only how you buy it but also how you store it securely afterward.Hacking incidents have led several prominent collections—including valuable CryptoPunks—to be stolen due primarily to insecure wallets or compromised accounts.Using hardware wallets—or secure custodial services—is recommended for safeguarding valuable holdings against theft.
Recent Developments Shaping the Future Landscape
Recent legal actions highlight ongoing scrutiny within the industry:
- Nike Class Action Lawsuit: In 2025, Nike faced allegations over its proprietary NFT platform amid claims seeking damages exceeding $5 million [1]. Such cases underscore increasing regulatory attention towards marketplace practices.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are beginning efforts:
- The SEC issued new guidelines around 2024 aimed at protecting investors while clarifying compliance expectations for creators and platforms alike [2].
Technological innovations continue improving:
- Transition toward energy-efficient blockchains reduces environmental impact,
- Advanced storage solutions enhance asset security,which collectively contribute toward making future participation safer yet still cautious engagement remains essential due diligence is vital when navigating this dynamic environment.
Navigating Risks Effectively When Acquiring NFTs
Understanding these risks helps prospective buyers make informed decisions aligned with their risk tolerance levels:
- Research Thoroughly — Verify artist credentials & platform reputation
- Use Reputable Marketplaces — Prefer established sites known for security
- Secure Storage Solutions — Invest in hardware wallets if holding valuable assets
- Stay Updated on Regulations — Follow legal developments relevant locally
5.. Be Skeptical About Hype — Avoid impulsive purchases driven solely by FOMO
By staying informed about potential pitfalls—from technical vulnerabilities through legal uncertainties—you can better safeguard your investments while participating responsibly within this innovative space.
[1] Source: Industry News - Nike Lawsuit Highlights Regulatory Scrutiny
[2] Source: Government Guidelines - SEC Regulations on Digital Assets
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Common Services and Platforms in the DeFi Ecosystem
The decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem has revolutionized traditional financial services by leveraging blockchain technology to create open, transparent, and permissionless platforms. As DeFi continues to grow rapidly, understanding its core services and key platforms is essential for users, investors, and developers alike. This article explores the most common offerings within DeFi, providing a comprehensive overview of how these components work together to shape the future of finance.
What Are DeFi Services?
DeFi services encompass a broad range of financial activities that operate without centralized intermediaries like banks or brokerages. Instead, smart contracts—self-executing code stored on blockchains—automate transactions and enforce rules transparently. These services aim to democratize access to financial tools by making them accessible globally and removing barriers such as geographic restrictions or credit checks.
The primary categories include lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming protocols, stablecoins, and prediction markets. Each serves a specific purpose but often integrates with others within the ecosystem to provide seamless user experiences.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
Lending protocols are among the earliest innovations in DeFi that mirror traditional banking functions but operate in a decentralized manner. They enable users to lend their crypto assets out for interest or borrow against collateral without involving banks or other intermediaries.
Aave is one of the most prominent examples; it allows users to lend various cryptocurrencies while earning interest or borrow assets at variable rates based on market conditions. Its flexible features include flash loans—unsecured loans executed within a single transaction—which have opened new possibilities for arbitrageurs and developers.
Similarly, Compound offers an algorithmic money market where supply rates fluctuate depending on supply-demand dynamics. Users can earn interest by supplying assets or take out loans using their crypto holdings as collateral.
MakerDAO, distinct from pure lending platforms, provides stability through its governance model that issues DAI—a decentralized stablecoin pegged 1:1 with USD. Users can lock collateral into Maker vaults to generate DAI tokens used across various DeFi applications.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges facilitate peer-to-peer trading directly from user wallets without relying on centralized order books or custodianship of funds. They use automated market makers (AMMs), which rely on liquidity pools instead of traditional order matching systems.
Uniswap, arguably the most popular DEX globally, exemplifies this model with its simple interface allowing anyone to swap tokens instantly via liquidity pools funded by other users who earn fees proportional to their contribution’s size.
Other notable DEXs include SushiSwap, which originated as a fork of Uniswap but added community-driven features like staking rewards for liquidity providers; it has gained significant traction due partly due to its governance token SUSHI.
Curve Finance specializes in stablecoin trading with low slippage thanks to optimized algorithms tailored for assets pegged closely together—ideal for traders seeking minimal price impact when swapping USDC for USDT or similar pairs.
Yield Farming & Liquidity Provision
Yield farming involves providing liquidity—depositing tokens into protocols—to earn returns often higher than traditional savings accounts but accompanied by increased risk levels such as impermanent loss or smart contract vulnerabilities.
Platforms like Yearn.finance aggregate multiple yield opportunities across different protocols automatically optimizing yields based on current conditions. Users deposit tokens into Yearn vaults that deploy funds into various strategies aiming at maximizing returns while managing risks effectively.
SushiSwap also offers yield farming options through its liquidity pools where participants stake pairs like ETH/USDT earning transaction fees plus additional incentives via SUSHI tokens—a process incentivizing active participation in maintaining healthy markets within the ecosystem.
Stablecoins: The Cornerstone Assets
Stablecoins are digital assets designed explicitly for stability—they maintain peg values close enough that they serve as reliable mediums of exchange within DeFi environments rather than volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC).
- DAI, created by MakerDAO’s protocol using overcollateralized crypto assets such as ETH; it maintains decentralization while offering stability.
- USDC, issued jointly by Circle Financial and Coinbase; widely adopted due to regulatory compliance.
- Tether (USDT) remains one of the most traded stablecoins despite ongoing debates about transparency because of its extensive adoption across exchanges worldwide.
These coins underpin many DeFi activities—from trading pairs on DEXs—and serve as safe havens during volatile periods when traders seek refuge from price swings elsewhere in crypto markets.
Prediction Markets & Oracles
Prediction markets allow participants betting on future events’ outcomes—for example election results—or even sports scores—all conducted securely via blockchain-based smart contracts ensuring transparency around odds-setting processes.
Platforms like Augur enable users not only bet but also create custom markets covering diverse topics ranging from politics' outcomes till economic indicators’ movements—all settled automatically once event results are verified externally through oracle feeds provided primarily by Chainlink's network infrastructure.
Oracles play an essential role here—they bridge real-world data with blockchain environments ensuring accurate information feeds necessary for fair settlement processes in prediction markets.
Recent Trends Shaping Core Platforms
Over recent years, regulatory scrutiny has intensified globally—with agencies like SEC scrutinizing certain projects suspected of unregistered securities issuance—and this has prompted many platforms toward increased transparency standards including audits and compliance measures aimed at safeguarding investor interests while maintaining decentralization principles effectively balancing innovation versus regulation adherence.
Security remains paramount amid frequent high-profile hacks exposing vulnerabilities inherent in complex smart contracts architectures leading developers investing heavily into security audits alongside bug bounty programs designed explicitly toward identifying potential flaws before exploitation occurs.
Market volatility continues influencing platform operations significantly; sharp price swings impact liquidity levels adversely affecting yields especially during downturn phases which may lead some investors toward more conservative strategies involving stable asset holdings rather than high-risk yield farming endeavors.
Risks & Future Outlook
While these core services form robust pillars supporting DeFi’s growth trajectory today—including innovative products such as flash loans—the space faces challenges ahead:
- Regulatory actions could tighten restrictions impacting service availability.
- Security improvements require continuous investment amidst evolving threat landscapes.
- Market volatility necessitates developing mechanisms capable of stabilizing ecosystems against sudden shocks.
Despite these hurdles, ongoing technological advancements coupled with increasing institutional interest suggest promising prospects if stakeholders prioritize security enhancements alongside clear regulatory frameworks fostering sustainable growth.
Navigating Key Components Within The DeFi Ecosystem
Understanding common services offered within de-fi helps both newcomers navigate this complex landscape efficiently while enabling experienced participants optimize their strategies responsibly. From lending protocols offering passive income streams through borrowing mechanisms facilitating capital efficiency—to decentralized exchanges democratizing trade access—the diversity ensures broad utility aligned with user needs.
By staying informed about developments across these core areas—including emerging trends such as integrated insurance solutions or cross-chain interoperability—users can better position themselves amidst rapid innovation shaping tomorrow's financial landscape.
This overview aims not only at informing readers about prevalent de-fi platforms but also emphasizes responsible participation rooted in awareness about risks involved.


kai
2025-05-22 19:56
What are some common services or platforms found within the DeFi ecosystem?
Common Services and Platforms in the DeFi Ecosystem
The decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem has revolutionized traditional financial services by leveraging blockchain technology to create open, transparent, and permissionless platforms. As DeFi continues to grow rapidly, understanding its core services and key platforms is essential for users, investors, and developers alike. This article explores the most common offerings within DeFi, providing a comprehensive overview of how these components work together to shape the future of finance.
What Are DeFi Services?
DeFi services encompass a broad range of financial activities that operate without centralized intermediaries like banks or brokerages. Instead, smart contracts—self-executing code stored on blockchains—automate transactions and enforce rules transparently. These services aim to democratize access to financial tools by making them accessible globally and removing barriers such as geographic restrictions or credit checks.
The primary categories include lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming protocols, stablecoins, and prediction markets. Each serves a specific purpose but often integrates with others within the ecosystem to provide seamless user experiences.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
Lending protocols are among the earliest innovations in DeFi that mirror traditional banking functions but operate in a decentralized manner. They enable users to lend their crypto assets out for interest or borrow against collateral without involving banks or other intermediaries.
Aave is one of the most prominent examples; it allows users to lend various cryptocurrencies while earning interest or borrow assets at variable rates based on market conditions. Its flexible features include flash loans—unsecured loans executed within a single transaction—which have opened new possibilities for arbitrageurs and developers.
Similarly, Compound offers an algorithmic money market where supply rates fluctuate depending on supply-demand dynamics. Users can earn interest by supplying assets or take out loans using their crypto holdings as collateral.
MakerDAO, distinct from pure lending platforms, provides stability through its governance model that issues DAI—a decentralized stablecoin pegged 1:1 with USD. Users can lock collateral into Maker vaults to generate DAI tokens used across various DeFi applications.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges facilitate peer-to-peer trading directly from user wallets without relying on centralized order books or custodianship of funds. They use automated market makers (AMMs), which rely on liquidity pools instead of traditional order matching systems.
Uniswap, arguably the most popular DEX globally, exemplifies this model with its simple interface allowing anyone to swap tokens instantly via liquidity pools funded by other users who earn fees proportional to their contribution’s size.
Other notable DEXs include SushiSwap, which originated as a fork of Uniswap but added community-driven features like staking rewards for liquidity providers; it has gained significant traction due partly due to its governance token SUSHI.
Curve Finance specializes in stablecoin trading with low slippage thanks to optimized algorithms tailored for assets pegged closely together—ideal for traders seeking minimal price impact when swapping USDC for USDT or similar pairs.
Yield Farming & Liquidity Provision
Yield farming involves providing liquidity—depositing tokens into protocols—to earn returns often higher than traditional savings accounts but accompanied by increased risk levels such as impermanent loss or smart contract vulnerabilities.
Platforms like Yearn.finance aggregate multiple yield opportunities across different protocols automatically optimizing yields based on current conditions. Users deposit tokens into Yearn vaults that deploy funds into various strategies aiming at maximizing returns while managing risks effectively.
SushiSwap also offers yield farming options through its liquidity pools where participants stake pairs like ETH/USDT earning transaction fees plus additional incentives via SUSHI tokens—a process incentivizing active participation in maintaining healthy markets within the ecosystem.
Stablecoins: The Cornerstone Assets
Stablecoins are digital assets designed explicitly for stability—they maintain peg values close enough that they serve as reliable mediums of exchange within DeFi environments rather than volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC).
- DAI, created by MakerDAO’s protocol using overcollateralized crypto assets such as ETH; it maintains decentralization while offering stability.
- USDC, issued jointly by Circle Financial and Coinbase; widely adopted due to regulatory compliance.
- Tether (USDT) remains one of the most traded stablecoins despite ongoing debates about transparency because of its extensive adoption across exchanges worldwide.
These coins underpin many DeFi activities—from trading pairs on DEXs—and serve as safe havens during volatile periods when traders seek refuge from price swings elsewhere in crypto markets.
Prediction Markets & Oracles
Prediction markets allow participants betting on future events’ outcomes—for example election results—or even sports scores—all conducted securely via blockchain-based smart contracts ensuring transparency around odds-setting processes.
Platforms like Augur enable users not only bet but also create custom markets covering diverse topics ranging from politics' outcomes till economic indicators’ movements—all settled automatically once event results are verified externally through oracle feeds provided primarily by Chainlink's network infrastructure.
Oracles play an essential role here—they bridge real-world data with blockchain environments ensuring accurate information feeds necessary for fair settlement processes in prediction markets.
Recent Trends Shaping Core Platforms
Over recent years, regulatory scrutiny has intensified globally—with agencies like SEC scrutinizing certain projects suspected of unregistered securities issuance—and this has prompted many platforms toward increased transparency standards including audits and compliance measures aimed at safeguarding investor interests while maintaining decentralization principles effectively balancing innovation versus regulation adherence.
Security remains paramount amid frequent high-profile hacks exposing vulnerabilities inherent in complex smart contracts architectures leading developers investing heavily into security audits alongside bug bounty programs designed explicitly toward identifying potential flaws before exploitation occurs.
Market volatility continues influencing platform operations significantly; sharp price swings impact liquidity levels adversely affecting yields especially during downturn phases which may lead some investors toward more conservative strategies involving stable asset holdings rather than high-risk yield farming endeavors.
Risks & Future Outlook
While these core services form robust pillars supporting DeFi’s growth trajectory today—including innovative products such as flash loans—the space faces challenges ahead:
- Regulatory actions could tighten restrictions impacting service availability.
- Security improvements require continuous investment amidst evolving threat landscapes.
- Market volatility necessitates developing mechanisms capable of stabilizing ecosystems against sudden shocks.
Despite these hurdles, ongoing technological advancements coupled with increasing institutional interest suggest promising prospects if stakeholders prioritize security enhancements alongside clear regulatory frameworks fostering sustainable growth.
Navigating Key Components Within The DeFi Ecosystem
Understanding common services offered within de-fi helps both newcomers navigate this complex landscape efficiently while enabling experienced participants optimize their strategies responsibly. From lending protocols offering passive income streams through borrowing mechanisms facilitating capital efficiency—to decentralized exchanges democratizing trade access—the diversity ensures broad utility aligned with user needs.
By staying informed about developments across these core areas—including emerging trends such as integrated insurance solutions or cross-chain interoperability—users can better position themselves amidst rapid innovation shaping tomorrow's financial landscape.
This overview aims not only at informing readers about prevalent de-fi platforms but also emphasizes responsible participation rooted in awareness about risks involved.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Trading Platform?
A cryptocurrency trading platform, often referred to as a crypto exchange, is an online marketplace where individuals and institutions can buy, sell, and trade digital currencies. These platforms serve as the primary interface for accessing the rapidly growing world of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, and many others. They provide a secure environment that facilitates transactions while offering tools for managing digital assets efficiently.
Understanding how these platforms work is essential for anyone interested in investing or trading cryptocurrencies. They operate similarly to traditional stock exchanges but are tailored specifically for digital assets. Users create accounts on these platforms, deposit funds—either fiat currency or cryptocurrencies—and execute trades through user-friendly interfaces or advanced trading tools.
Types of Cryptocurrency Trading Platforms
There are three main categories of cryptocurrency trading platforms:
Centralized Exchanges (CEXs):
These are the most prevalent type of crypto exchanges. Centralized exchanges act as intermediaries that hold users’ funds and facilitate trades between buyers and sellers. They typically offer high liquidity, fast transaction speeds, and user-friendly interfaces suitable for beginners. Examples include Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Bitstamp.Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs):
Operating directly on blockchain networks without an intermediary authority distinguishes DEXs from CEXs. They enable peer-to-peer trading where users retain control over their private keys until they execute a trade. While DEXs generally offer enhanced security due to their decentralized nature—reducing risks like hacking—they tend to have steeper learning curves and lower liquidity levels compared to centralized counterparts. Notable examples include Uniswap and SushiSwap.Hybrid Exchanges:
Combining features from both CEXs and DEXs, hybrid platforms aim to balance security with usability by offering some centralized features alongside decentralized elements such as non-custodial wallets or smart contract-based transactions.
Key Features Offered by Crypto Trading Platforms
Most cryptocurrency exchanges provide several core features designed to enhance user experience:
Trading Pairs:
Platforms support various pairs allowing traders to swap one cryptocurrency for another—for example BTC/USDT or ETH/BTC—enabling diverse trading strategies based on market conditions.Fiat Currency Support:
Many exchanges allow direct fiat-to-crypto transactions using currencies like USD, EUR, JPY etc., making it easier for new investors to enter the market without needing prior crypto holdings.Derivatives & Margin Trading:
Advanced traders can access derivatives such as futures contracts or options which enable speculation on price movements with leverage—though this involves higher risk levels requiring careful risk management strategies.Security Measures:
To protect assets against theft or hacking incidents—which have occurred historically—platform providers implement robust security protocols including two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage solutions (offline wallets), encryption standards,and insurance policies where applicable.
Regulatory Environment & Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrency trading platforms remains complex worldwide due to varying legal frameworks across jurisdictions; this influences how these entities operate legally within different countries.In regions like the United States , authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) actively scrutinize operations—including recent enforcement actions against firms involved in alleged fraud—to ensure compliance with financial laws.Other nations like Japan , Singapore ,and Switzerland have established clearer guidelines aimed at fostering innovation while safeguarding consumers through licensing requirementsand anti-money laundering measures.However , regulatory uncertainty continues to pose challenges: stricter rules could lead some unregulated platforms out of business while also increasing compliance costs even among compliant operators.
Recent Industry Developments & Risks
The industry has experienced notable events impacting trustworthiness:
- Data breaches remain a significant concern; Coinbase disclosed in May 2025 that cybercriminals bribed support agents overseas leading to sensitive customer data being compromised—a reminder of ongoing cybersecurity threats.
- Market volatility persists; rapid price swings can result in substantial gains but also severe losses if traders do not employ proper risk management techniques.
- Technological advancements such as blockchain upgrades improve transaction efficiency but also introduce new vulnerabilities if not properly implemented.These developments underscore why users must prioritize security practices—including enabling two-factor authentication—and stay informed about industry news.
Potential Risks Facing Traders & Platforms
While cryptocurrency trading offers lucrative opportunities,it carries inherent risks:• Regulatory changes may restrict accessor impose additional compliance burdens• Security breaches could leadto lossof fundsor personal information• Market volatility increases unpredictabilityand potential financial losses• Lack of transparencyin some unregulated markets heightens exposureto scamsor fraudulent schemesTo mitigate these risks,the best approach involves thorough research before engaging with any platform,persistent vigilance regarding cybersecurity,and adherenceto sound investment principles.
Future Outlook & Industry Trends
Industry forecasts suggest continued growth driven by mainstream adoption,favorable regulation,and technological innovations:By 2025,the price of Bitcoin might double reaching $200000 amid increased institutional interestand ETF approvals[2]. Such developments could further legitimizecryptocurrency markets,making them more accessiblefor retail investors.Moreover,the integrationof artificial intelligence(AI) into trading algorithms,predictive analytics,and improved blockchain scalability will likely enhance platform performanceand security measures[4].However,such progress must be balanced against evolving regulatory scrutinyand persistent cybersecurity threats,to ensure sustainable growth within this dynamic sector.
Who Should Use Cryptocurrency Trading Platforms?
Cryptocurrency trading platforms cater primarily tohobbyist investors,securities traders seeking diversification,and institutional players exploring digital asset portfolios.They are suitablefor those willingto learn about blockchain technology,risk-tolerant individuals aimingfor high returns,and tech-savvy users comfortable navigating complex interfaces when necessary.
How To Choose The Right Platform?
Selecting an appropriate crypto exchange depends on several factors:1 . Security protocols: Ensure robust protection measuresare in place2 . Regulatory compliance: Verify licensing statusin your jurisdiction3 . User interface: Choose between beginner-friendlyor advanced tools basedon your experience level4 . Supported assets: Confirm availabilityof desired cryptocurrenciesand fiat pairs5 . Fees structure: Comparetransaction fees,taker/maker spreads,and withdrawal costs
Staying Informed Is Key
As the industry evolves rapidly,new regulations emerge,and technological improvements occur,it’s vital for users tomaintain awareness through reputable news sources,research reports,and community discussions.This proactive approach helps safeguard investmentswhile maximizing opportunities within this innovative financial landscape.
Optimizing Your Search Experience
For those seeking information about what constitutes a cryptocurrency trading platform,this guide provides comprehensive insights into its types,functionality,risk factors,current trends,and future prospects—all essential knowledge areas needed before entering this space confidently.
This detailed overview aims at equipping readers with foundational understanding along with practical considerations necessary when engaging with cryptocurrency markets via various types of online platforms.. Staying informed about ongoing developments ensures better decision-making amid an ever-changing environment marked by technological progress but also heightened risks associated with cyber threats and regulatory shifts


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 16:14
What is a cryptocurrency trading platform?
What Is a Cryptocurrency Trading Platform?
A cryptocurrency trading platform, often referred to as a crypto exchange, is an online marketplace where individuals and institutions can buy, sell, and trade digital currencies. These platforms serve as the primary interface for accessing the rapidly growing world of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, and many others. They provide a secure environment that facilitates transactions while offering tools for managing digital assets efficiently.
Understanding how these platforms work is essential for anyone interested in investing or trading cryptocurrencies. They operate similarly to traditional stock exchanges but are tailored specifically for digital assets. Users create accounts on these platforms, deposit funds—either fiat currency or cryptocurrencies—and execute trades through user-friendly interfaces or advanced trading tools.
Types of Cryptocurrency Trading Platforms
There are three main categories of cryptocurrency trading platforms:
Centralized Exchanges (CEXs):
These are the most prevalent type of crypto exchanges. Centralized exchanges act as intermediaries that hold users’ funds and facilitate trades between buyers and sellers. They typically offer high liquidity, fast transaction speeds, and user-friendly interfaces suitable for beginners. Examples include Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Bitstamp.Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs):
Operating directly on blockchain networks without an intermediary authority distinguishes DEXs from CEXs. They enable peer-to-peer trading where users retain control over their private keys until they execute a trade. While DEXs generally offer enhanced security due to their decentralized nature—reducing risks like hacking—they tend to have steeper learning curves and lower liquidity levels compared to centralized counterparts. Notable examples include Uniswap and SushiSwap.Hybrid Exchanges:
Combining features from both CEXs and DEXs, hybrid platforms aim to balance security with usability by offering some centralized features alongside decentralized elements such as non-custodial wallets or smart contract-based transactions.
Key Features Offered by Crypto Trading Platforms
Most cryptocurrency exchanges provide several core features designed to enhance user experience:
Trading Pairs:
Platforms support various pairs allowing traders to swap one cryptocurrency for another—for example BTC/USDT or ETH/BTC—enabling diverse trading strategies based on market conditions.Fiat Currency Support:
Many exchanges allow direct fiat-to-crypto transactions using currencies like USD, EUR, JPY etc., making it easier for new investors to enter the market without needing prior crypto holdings.Derivatives & Margin Trading:
Advanced traders can access derivatives such as futures contracts or options which enable speculation on price movements with leverage—though this involves higher risk levels requiring careful risk management strategies.Security Measures:
To protect assets against theft or hacking incidents—which have occurred historically—platform providers implement robust security protocols including two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage solutions (offline wallets), encryption standards,and insurance policies where applicable.
Regulatory Environment & Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrency trading platforms remains complex worldwide due to varying legal frameworks across jurisdictions; this influences how these entities operate legally within different countries.In regions like the United States , authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) actively scrutinize operations—including recent enforcement actions against firms involved in alleged fraud—to ensure compliance with financial laws.Other nations like Japan , Singapore ,and Switzerland have established clearer guidelines aimed at fostering innovation while safeguarding consumers through licensing requirementsand anti-money laundering measures.However , regulatory uncertainty continues to pose challenges: stricter rules could lead some unregulated platforms out of business while also increasing compliance costs even among compliant operators.
Recent Industry Developments & Risks
The industry has experienced notable events impacting trustworthiness:
- Data breaches remain a significant concern; Coinbase disclosed in May 2025 that cybercriminals bribed support agents overseas leading to sensitive customer data being compromised—a reminder of ongoing cybersecurity threats.
- Market volatility persists; rapid price swings can result in substantial gains but also severe losses if traders do not employ proper risk management techniques.
- Technological advancements such as blockchain upgrades improve transaction efficiency but also introduce new vulnerabilities if not properly implemented.These developments underscore why users must prioritize security practices—including enabling two-factor authentication—and stay informed about industry news.
Potential Risks Facing Traders & Platforms
While cryptocurrency trading offers lucrative opportunities,it carries inherent risks:• Regulatory changes may restrict accessor impose additional compliance burdens• Security breaches could leadto lossof fundsor personal information• Market volatility increases unpredictabilityand potential financial losses• Lack of transparencyin some unregulated markets heightens exposureto scamsor fraudulent schemesTo mitigate these risks,the best approach involves thorough research before engaging with any platform,persistent vigilance regarding cybersecurity,and adherenceto sound investment principles.
Future Outlook & Industry Trends
Industry forecasts suggest continued growth driven by mainstream adoption,favorable regulation,and technological innovations:By 2025,the price of Bitcoin might double reaching $200000 amid increased institutional interestand ETF approvals[2]. Such developments could further legitimizecryptocurrency markets,making them more accessiblefor retail investors.Moreover,the integrationof artificial intelligence(AI) into trading algorithms,predictive analytics,and improved blockchain scalability will likely enhance platform performanceand security measures[4].However,such progress must be balanced against evolving regulatory scrutinyand persistent cybersecurity threats,to ensure sustainable growth within this dynamic sector.
Who Should Use Cryptocurrency Trading Platforms?
Cryptocurrency trading platforms cater primarily tohobbyist investors,securities traders seeking diversification,and institutional players exploring digital asset portfolios.They are suitablefor those willingto learn about blockchain technology,risk-tolerant individuals aimingfor high returns,and tech-savvy users comfortable navigating complex interfaces when necessary.
How To Choose The Right Platform?
Selecting an appropriate crypto exchange depends on several factors:1 . Security protocols: Ensure robust protection measuresare in place2 . Regulatory compliance: Verify licensing statusin your jurisdiction3 . User interface: Choose between beginner-friendlyor advanced tools basedon your experience level4 . Supported assets: Confirm availabilityof desired cryptocurrenciesand fiat pairs5 . Fees structure: Comparetransaction fees,taker/maker spreads,and withdrawal costs
Staying Informed Is Key
As the industry evolves rapidly,new regulations emerge,and technological improvements occur,it’s vital for users tomaintain awareness through reputable news sources,research reports,and community discussions.This proactive approach helps safeguard investmentswhile maximizing opportunities within this innovative financial landscape.
Optimizing Your Search Experience
For those seeking information about what constitutes a cryptocurrency trading platform,this guide provides comprehensive insights into its types,functionality,risk factors,current trends,and future prospects—all essential knowledge areas needed before entering this space confidently.
This detailed overview aims at equipping readers with foundational understanding along with practical considerations necessary when engaging with cryptocurrency markets via various types of online platforms.. Staying informed about ongoing developments ensures better decision-making amid an ever-changing environment marked by technological progress but also heightened risks associated with cyber threats and regulatory shifts
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Who Created Bitcoin (BTC)?
Understanding the origins of Bitcoin is essential for grasping its significance in the digital currency landscape. Bitcoin was created by an individual or a group operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Despite extensive speculation and numerous claims, Nakamoto’s true identity remains unknown, adding an element of mystery that has fueled both intrigue and debate within the cryptocurrency community. This anonymity has contributed to Bitcoin’s decentralized ethos, emphasizing that no single entity controls it.
The creation of Bitcoin marked a revolutionary shift in how we perceive money and financial transactions. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments or central banks, Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network without intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. This decentralization aims to provide users with greater control over their assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
The story begins with Nakamoto publishing the whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" on October 31, 2008. This document laid out the technical blueprint for a new kind of digital currency that could facilitate secure, transparent transactions without third-party oversight. The whitepaper detailed innovative concepts like blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system—and proof-of-work consensus mechanisms that underpin Bitcoin's security.
When Was Bitcoin Launched?
Bitcoin officially came into existence on January 3, 2009, with the mining of its first block known as the Genesis Block. Embedded within this initial block was a message referencing contemporary economic concerns: "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks." This message not only timestamped its creation but also subtly critiqued traditional banking systems and monetary policies—highlighting one of Bitcoin’s core motivations: providing an alternative to fiat currencies susceptible to inflation and government control.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, Bitcoin relies heavily on blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger maintained collectively by thousands of computers worldwide called nodes. Each transaction is verified through cryptographic processes and added as a block linked sequentially to previous blocks—forming an immutable chain accessible publicly for transparency purposes.
This open-source nature ensures no single authority can alter transaction history unilaterally, fostering trust among participants despite lacking central oversight. Blockchain's resilience against tampering makes it highly secure but also requires significant computational power—especially during mining—to validate new transactions efficiently.
How Does Mining Work?
Mining is fundamental to how new Bitcoins are created and how transaction integrity is maintained within the network. Miners use powerful hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work—which validates transactions before they are recorded onto the blockchain.
Successful miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins; this process introduces new coins into circulation while incentivizing miners’ participation in maintaining network security. Initially set at 50 BTC per block when launched in 2009, this reward halves approximately every four years during scheduled “halving” events—reducing supply inflation over time.
Recent Developments in Bitcoin
Halving Events
Bitcoin's protocol includes programmed halving events designed to control supply growth systematically:
- The third halving occurred on May 11, 2020 — reducing rewards from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC per block.
- The upcoming fourth halving is expected around mid-2024 — further decreasing rewards to approximately 3.125 BTC per block.
These halvings tend to influence market dynamics significantly by constraining supply growth amid increasing demand.
Regulatory Environment
Globally, regulatory attitudes toward cryptocurrencies vary widely:
- El Salvador made headlines as it became the first country officially adopting Bitcoin as legal tender in September 2021.
- In contrast, countries like China have imposed strict bans on crypto trading and mining activities.
In jurisdictions like the United States, agencies such as SEC actively regulate aspects related to cryptocurrencies—including enforcement actions against entities involved in securities violations related to tokens like XRP issued by Ripple Labs.
Market Volatility & Institutional Adoption
Bitcoin remains highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically due primarily to regulatory news or macroeconomic factors affecting investor sentiment globally—for example:
- Price surges driven by institutional interest from firms like Fidelity or PayPal offering integrated services.
- Sharp declines during market corrections or adverse regulatory developments (e.g., dropping below $30K during late-2022).
Technological Innovations
Advancements continue at pace:
- Layer two solutions such as Lightning Network aim at scaling capabilities—enabling faster transactions with lower fees suitable for everyday use.
- Efforts toward integrating smart contract functionalities into existing protocols are ongoing through proposals like RSK (Rootstock), which seeks compatibility with Ethereum-based smart contracts while leveraging Bitcoin’s security model.
Potential Risks Facing Cryptocurrency
While innovation propels adoption forward, several risks threaten long-term stability:
Regulatory Risks: Uncertain legal frameworks could lead governments worldwide either embracing or restricting usage altogether—impacting investor confidence significantly.
Security Concerns: Despite robust cryptography securing most operations today—including high-profile hacks such as Mt Gox—the threat persists from potential attacks like “51% attacks,” where malicious actors gain majority control over mining power enabling double-spending frauds if unchecked.
Environmental Impact: The energy-intensive nature of proof-of-work mining has sparked debates about sustainability; some advocate transitioning toward greener alternatives without compromising decentralization principles fully yet remain cautious about environmental costs associated with current practices.
Market Volatility & Future Outlook
Price fluctuations remain characteristic features influencing both retail investors and institutional players alike—from rapid bull runs followed by sharp corrections—as seen during recent years including dips below $30K amid broader economic uncertainties in late 2022.
Despite these challenges—and ongoing discussions about regulation—the overall trajectory indicates growing acceptance across sectors worldwide coupled with technological innovations aimed at scalability and sustainability.
Understanding these elements provides crucial insights into what shapes bitcoin’s past evolution—and what might influence its future path amidst evolving global financial landscapes.
By examining who created bitcoin along with key milestones since inception—including technological advances and regulatory shifts—we gain comprehensive perspective essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency markets today.


Lo
2025-05-22 14:31
Who created Bitcoin (BTC)?
Who Created Bitcoin (BTC)?
Understanding the origins of Bitcoin is essential for grasping its significance in the digital currency landscape. Bitcoin was created by an individual or a group operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Despite extensive speculation and numerous claims, Nakamoto’s true identity remains unknown, adding an element of mystery that has fueled both intrigue and debate within the cryptocurrency community. This anonymity has contributed to Bitcoin’s decentralized ethos, emphasizing that no single entity controls it.
The creation of Bitcoin marked a revolutionary shift in how we perceive money and financial transactions. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments or central banks, Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network without intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. This decentralization aims to provide users with greater control over their assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
The story begins with Nakamoto publishing the whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" on October 31, 2008. This document laid out the technical blueprint for a new kind of digital currency that could facilitate secure, transparent transactions without third-party oversight. The whitepaper detailed innovative concepts like blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system—and proof-of-work consensus mechanisms that underpin Bitcoin's security.
When Was Bitcoin Launched?
Bitcoin officially came into existence on January 3, 2009, with the mining of its first block known as the Genesis Block. Embedded within this initial block was a message referencing contemporary economic concerns: "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks." This message not only timestamped its creation but also subtly critiqued traditional banking systems and monetary policies—highlighting one of Bitcoin’s core motivations: providing an alternative to fiat currencies susceptible to inflation and government control.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, Bitcoin relies heavily on blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger maintained collectively by thousands of computers worldwide called nodes. Each transaction is verified through cryptographic processes and added as a block linked sequentially to previous blocks—forming an immutable chain accessible publicly for transparency purposes.
This open-source nature ensures no single authority can alter transaction history unilaterally, fostering trust among participants despite lacking central oversight. Blockchain's resilience against tampering makes it highly secure but also requires significant computational power—especially during mining—to validate new transactions efficiently.
How Does Mining Work?
Mining is fundamental to how new Bitcoins are created and how transaction integrity is maintained within the network. Miners use powerful hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work—which validates transactions before they are recorded onto the blockchain.
Successful miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins; this process introduces new coins into circulation while incentivizing miners’ participation in maintaining network security. Initially set at 50 BTC per block when launched in 2009, this reward halves approximately every four years during scheduled “halving” events—reducing supply inflation over time.
Recent Developments in Bitcoin
Halving Events
Bitcoin's protocol includes programmed halving events designed to control supply growth systematically:
- The third halving occurred on May 11, 2020 — reducing rewards from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC per block.
- The upcoming fourth halving is expected around mid-2024 — further decreasing rewards to approximately 3.125 BTC per block.
These halvings tend to influence market dynamics significantly by constraining supply growth amid increasing demand.
Regulatory Environment
Globally, regulatory attitudes toward cryptocurrencies vary widely:
- El Salvador made headlines as it became the first country officially adopting Bitcoin as legal tender in September 2021.
- In contrast, countries like China have imposed strict bans on crypto trading and mining activities.
In jurisdictions like the United States, agencies such as SEC actively regulate aspects related to cryptocurrencies—including enforcement actions against entities involved in securities violations related to tokens like XRP issued by Ripple Labs.
Market Volatility & Institutional Adoption
Bitcoin remains highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically due primarily to regulatory news or macroeconomic factors affecting investor sentiment globally—for example:
- Price surges driven by institutional interest from firms like Fidelity or PayPal offering integrated services.
- Sharp declines during market corrections or adverse regulatory developments (e.g., dropping below $30K during late-2022).
Technological Innovations
Advancements continue at pace:
- Layer two solutions such as Lightning Network aim at scaling capabilities—enabling faster transactions with lower fees suitable for everyday use.
- Efforts toward integrating smart contract functionalities into existing protocols are ongoing through proposals like RSK (Rootstock), which seeks compatibility with Ethereum-based smart contracts while leveraging Bitcoin’s security model.
Potential Risks Facing Cryptocurrency
While innovation propels adoption forward, several risks threaten long-term stability:
Regulatory Risks: Uncertain legal frameworks could lead governments worldwide either embracing or restricting usage altogether—impacting investor confidence significantly.
Security Concerns: Despite robust cryptography securing most operations today—including high-profile hacks such as Mt Gox—the threat persists from potential attacks like “51% attacks,” where malicious actors gain majority control over mining power enabling double-spending frauds if unchecked.
Environmental Impact: The energy-intensive nature of proof-of-work mining has sparked debates about sustainability; some advocate transitioning toward greener alternatives without compromising decentralization principles fully yet remain cautious about environmental costs associated with current practices.
Market Volatility & Future Outlook
Price fluctuations remain characteristic features influencing both retail investors and institutional players alike—from rapid bull runs followed by sharp corrections—as seen during recent years including dips below $30K amid broader economic uncertainties in late 2022.
Despite these challenges—and ongoing discussions about regulation—the overall trajectory indicates growing acceptance across sectors worldwide coupled with technological innovations aimed at scalability and sustainability.
Understanding these elements provides crucial insights into what shapes bitcoin’s past evolution—and what might influence its future path amidst evolving global financial landscapes.
By examining who created bitcoin along with key milestones since inception—including technological advances and regulatory shifts—we gain comprehensive perspective essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency markets today.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Utility NFTs Differ from Purely Collectible NFTs?
Understanding the distinctions between different types of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is essential as the digital asset market continues to expand. While many are familiar with NFTs as digital collectibles, a newer category known as utility NFTs is gaining prominence. This article explores how utility NFTs differ from purely collectible ones, providing clarity on their functions, benefits, and recent trends.
What Are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain that verify ownership and authenticity of a specific item. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable and fungible, each NFT is one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness makes them ideal for representing digital art, music, virtual items in gaming environments, or other creative works.
The blockchain technology underpinning NFTs ensures transparency in ownership history and scarcity—key factors driving their value. As a result, they have become popular among artists, collectors, gamers, and investors seeking verifiable ownership of digital assets.
Characteristics of Purely Collectible NFTs
Purely collectible NFTs primarily serve aesthetic or sentimental purposes. They often take the form of digital art pieces or exclusive music tracks created by renowned artists or musicians. These tokens are bought for their rarity and potential future value rather than functional benefits.
Marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible facilitate trading these collectibles globally. The demand has surged significantly over recent years; some artworks have sold for millions of dollars at auction houses like Christie's or Sotheby's in NFT form.
Investors often purchase collectible NFTs with the hope that their value will appreciate over time so they can resell at a profit later on—a practice similar to traditional art collecting but within the digital realm.
What Are Utility NFTs?
In contrast to purely aesthetic-focused tokens, utility NFTs provide tangible benefits beyond mere ownership acknowledgment. They grant holders access to exclusive content such as early product releases or special events; offer voting rights within decentralized communities; or represent stakes in projects—effectively functioning as membership cards with added privileges.
These tokens foster deeper engagement by creating interactive experiences around an asset rather than just owning it visually. For example:
- Access Rights: Holding certain utility NFTs might unlock VIP access to concerts or virtual events.
- Participation: Some enable voting on project development decisions within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
- Ownership Stakes: Certain utility tokens symbolize partial ownership in startups or community-driven initiatives.
This functional aspect encourages ongoing participation from holders while adding real-world value aligned with technological innovation trends like blockchain-based governance systems.
Recent Trends Shaping Utility vs Collectibles
The evolving landscape highlights several key developments:
Gaming & Virtual Worlds
Platforms such as Decentraland and The Sandbox leverage utility NFT models extensively by allowing users to buy land parcels and assets that confer gameplay advantages—like building virtual spaces—or grant access rights within immersive environments.
Social Media & Community Engagement
Social platforms increasingly integrate utility features through NFT-based memberships—for instance: Discord servers offering exclusive channels accessible only via holding specific tokens—enhancing user loyalty through tangible perks rather than simple visual collectibles.
DeFi Integration & Financial Benefits
Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols now incorporate utility aspects into NFT offerings by enabling interest accruals on holdings or dividend distributions tied directly to token ownership—adding financial incentives alongside community participation elements.
Challenges Facing Utility vs Collectible NFT Markets
Despite rapid growth across both categories, several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks surrounding NFT classification vary across jurisdictions; questions about intellectual property rights management persist.
Market Volatility: Prices for both collectible and utility-based tokens can fluctuate wildly due to speculation rather than intrinsic value.
Scalability Concerns: Blockchain infrastructure still faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs—which could hinder mass adoption if not addressed effectively.
How To Identify Value in Different Types of NFTs
When evaluating whether an NFT is primarily collectible or offers genuine utility:
- Check if it grants access: Does owning this token unlock services?
- Review community involvement: Is there active participation enabled through this token?
- Consider project backing: Does it represent an investment stake?
- Analyze provenance: Is its origin linked directly with creators’ reputation?
Understanding these factors helps buyers make informed decisions aligned with personal goals—whether investing for appreciation potential via collectibles—or seeking ongoing benefits through utilities.
The Future Outlook for Utility vs Collectibles
As blockchain technology matures further—with improvements in scalability solutions like Layer 2 protocols—the scope for more sophisticated use cases expands significantly for both categories but especially so for utility-focused applications that blend social engagement with financial incentives.
Emerging sectors such as metaverse development suggest that utilities embedded into virtual environments will become increasingly integral—not just enhancing user experience but also creating sustainable economic models around these assets.
By recognizing the fundamental differences between purely collectible non-fungible tokens and those offering practical functionalities—and staying aware of current trends—you can better navigate this rapidly evolving space tailored toward your interests whether artistic appreciation versus active participation within communities driven by blockchain innovations.


Lo
2025-05-22 11:45
How do utility NFTs differ from purely collectible NFTs?
How Do Utility NFTs Differ from Purely Collectible NFTs?
Understanding the distinctions between different types of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is essential as the digital asset market continues to expand. While many are familiar with NFTs as digital collectibles, a newer category known as utility NFTs is gaining prominence. This article explores how utility NFTs differ from purely collectible ones, providing clarity on their functions, benefits, and recent trends.
What Are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain that verify ownership and authenticity of a specific item. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable and fungible, each NFT is one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness makes them ideal for representing digital art, music, virtual items in gaming environments, or other creative works.
The blockchain technology underpinning NFTs ensures transparency in ownership history and scarcity—key factors driving their value. As a result, they have become popular among artists, collectors, gamers, and investors seeking verifiable ownership of digital assets.
Characteristics of Purely Collectible NFTs
Purely collectible NFTs primarily serve aesthetic or sentimental purposes. They often take the form of digital art pieces or exclusive music tracks created by renowned artists or musicians. These tokens are bought for their rarity and potential future value rather than functional benefits.
Marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible facilitate trading these collectibles globally. The demand has surged significantly over recent years; some artworks have sold for millions of dollars at auction houses like Christie's or Sotheby's in NFT form.
Investors often purchase collectible NFTs with the hope that their value will appreciate over time so they can resell at a profit later on—a practice similar to traditional art collecting but within the digital realm.
What Are Utility NFTs?
In contrast to purely aesthetic-focused tokens, utility NFTs provide tangible benefits beyond mere ownership acknowledgment. They grant holders access to exclusive content such as early product releases or special events; offer voting rights within decentralized communities; or represent stakes in projects—effectively functioning as membership cards with added privileges.
These tokens foster deeper engagement by creating interactive experiences around an asset rather than just owning it visually. For example:
- Access Rights: Holding certain utility NFTs might unlock VIP access to concerts or virtual events.
- Participation: Some enable voting on project development decisions within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
- Ownership Stakes: Certain utility tokens symbolize partial ownership in startups or community-driven initiatives.
This functional aspect encourages ongoing participation from holders while adding real-world value aligned with technological innovation trends like blockchain-based governance systems.
Recent Trends Shaping Utility vs Collectibles
The evolving landscape highlights several key developments:
Gaming & Virtual Worlds
Platforms such as Decentraland and The Sandbox leverage utility NFT models extensively by allowing users to buy land parcels and assets that confer gameplay advantages—like building virtual spaces—or grant access rights within immersive environments.
Social Media & Community Engagement
Social platforms increasingly integrate utility features through NFT-based memberships—for instance: Discord servers offering exclusive channels accessible only via holding specific tokens—enhancing user loyalty through tangible perks rather than simple visual collectibles.
DeFi Integration & Financial Benefits
Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols now incorporate utility aspects into NFT offerings by enabling interest accruals on holdings or dividend distributions tied directly to token ownership—adding financial incentives alongside community participation elements.
Challenges Facing Utility vs Collectible NFT Markets
Despite rapid growth across both categories, several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks surrounding NFT classification vary across jurisdictions; questions about intellectual property rights management persist.
Market Volatility: Prices for both collectible and utility-based tokens can fluctuate wildly due to speculation rather than intrinsic value.
Scalability Concerns: Blockchain infrastructure still faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs—which could hinder mass adoption if not addressed effectively.
How To Identify Value in Different Types of NFTs
When evaluating whether an NFT is primarily collectible or offers genuine utility:
- Check if it grants access: Does owning this token unlock services?
- Review community involvement: Is there active participation enabled through this token?
- Consider project backing: Does it represent an investment stake?
- Analyze provenance: Is its origin linked directly with creators’ reputation?
Understanding these factors helps buyers make informed decisions aligned with personal goals—whether investing for appreciation potential via collectibles—or seeking ongoing benefits through utilities.
The Future Outlook for Utility vs Collectibles
As blockchain technology matures further—with improvements in scalability solutions like Layer 2 protocols—the scope for more sophisticated use cases expands significantly for both categories but especially so for utility-focused applications that blend social engagement with financial incentives.
Emerging sectors such as metaverse development suggest that utilities embedded into virtual environments will become increasingly integral—not just enhancing user experience but also creating sustainable economic models around these assets.
By recognizing the fundamental differences between purely collectible non-fungible tokens and those offering practical functionalities—and staying aware of current trends—you can better navigate this rapidly evolving space tailored toward your interests whether artistic appreciation versus active participation within communities driven by blockchain innovations.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Can I Convert My Cryptocurrency Back Into Traditional Fiat Currency?
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the way we think about money, offering decentralized and digital alternatives to traditional currencies. However, one of the most common questions among users and investors is whether they can convert their crypto holdings back into fiat currency—such as USD, EUR, or JPY—and how this process works. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversions, covering methods, challenges, recent developments, and best practices to ensure secure and efficient transactions.
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Fiat Currency
Before diving into conversion options, it’s essential to understand what cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies are. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets secured by cryptography that operate on decentralized blockchain networks. Bitcoin remains the most prominent example but is just one among over 5,000 different cryptocurrencies available today.
In contrast, fiat currencies are government-issued legal tender with no intrinsic value but backed by national authorities. Examples include the US dollar (USD), euro (EUR), yen (JPY), among others. These currencies are widely accepted for everyday transactions across borders.
Why Do People Convert Cryptocurrency to Fiat?
Converting crypto into fiat currency serves multiple purposes:
- Realizing Profits: Investors often buy cryptocurrencies at lower prices with plans to sell later when prices increase.
- Daily Spending: For routine expenses like groceries or bills that require traditional money.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many financial institutions mandate transactions in fiat for legal reasons.
- Liquidity Needs: Accessing cash quickly for emergencies or other financial commitments.
Understanding these motivations helps clarify why seamless conversion options are vital within the broader ecosystem of digital finance.
Methods for Converting Cryptocurrency to Fiat
There are several practical ways users can convert their cryptocurrencies into traditional money:
1. Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Exchanges such as Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Bitstamp provide user-friendly platforms where you can sell your crypto holdings directly for fiat currency. These platforms typically support various cryptocurrencies and offer real-time market rates.
Advantages:
- High liquidity
- Multiple supported coins
- Easy-to-use interfaces
Disadvantages:
- Transaction fees vary depending on platform
- Potential security risks if accounts aren’t properly secured
2. Digital Wallets with Conversion Features
Some digital wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet now incorporate features allowing users to swap tokens directly within their apps before transferring funds elsewhere or withdrawing as cash through linked services.
3. Crypto ATMs (Bitcoin ATMs)
Crypto ATMs enable in-person exchanges where you can insert cryptocurrency—either via a wallet QR code or card—and receive cash instantly in return.
Pros:
- Immediate access to physical cash
- No need for bank account linkage in some cases
Cons:
- Limited availability geographically
- Higher transaction fees compared to online exchanges
4. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Services
For large-volume conversions beyond typical exchange limits or when seeking privacy/security assurances—OTC desks facilitate direct trades between buyers and sellers outside public markets.
Fees Associated With Conversion Processes
Converting cryptocurrency isn’t free; various fees impact your net proceeds:
| Type of Fee | Description |
|---|---|
| Exchange Fees | Charged per transaction; varies by platform |
| Withdrawal Fees | Costs associated with transferring funds from exchange/wallet |
| Network Fees | Blockchain transaction costs paid by users during transfers |
Being aware of these charges helps optimize your conversion strategy — choosing platforms with competitive rates can significantly affect overall profitability.
Security Risks During Conversion
While converting crypto offers liquidity benefits, it also introduces certain risks:
Market Volatility: Prices fluctuate rapidly; timing your sale is crucial.Security Breaches: Hacks targeting exchanges have occurred historically; using reputable platforms enhances safety.Regulatory Changes: New laws may restrict certain conversions or impose additional compliance measures.Technical Failures: System outages or network issues could delay transactions leading to potential losses if market conditions change suddenly.
Implementing strong security practices—including two-factor authentication (2FA) and keeping software updated—is essential when managing conversions securely.
Recent Trends Impacting Crypto-to-Fiat Conversions
Recent years have seen notable developments influencing how easily users convert crypto assets:
Regulatory Clarity Enhances Confidence
In 2022 onwards, regulatory bodies like the U.S Securities & Exchange Commission began clarifying rules around cryptocurrencies’ legal status—affecting how exchanges operate across jurisdictions which impacts user access points for converting assets legally compliant manner[1].
Technological Innovations Improve Efficiency
Advancements such as AI integration in payment systems streamline transaction processes while reducing fraud risk[1]. For instance:
- Stripe’s new AI foundation model aims at bridging traditional banking systems with blockchain payments,
- Faster settlement times,
- Lower fees,
making conversions more accessible even during volatile market periods[1].
The Impact of Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile; sudden price swings mean timing your sale carefully is critical if you want favorable rates without incurring losses—a challenge especially relevant during rapid bull runs or downturns[1].
Future Outlook
By 2025+, innovations like integrated payment rails combining both traditional finance infrastructure and blockchain technology will likely make converting crypto into fiat more seamless than ever before[1]. Enhanced regulatory clarity combined with technological progress promises safer environments for retail investors seeking liquidity solutions efficiently.
Best Practices When Converting Crypto To Fiat
To maximize benefits while minimizing risks:
- Use reputable exchanges known for security standards,
- Monitor market conditions closely before executing large trades,
- Be aware of all applicable fees upfront,
- Enable strong account security measures,
- Stay informed about evolving regulations affecting your jurisdiction,
Adopting these practices ensures smoother experiences regardless of whether you're a casual user or an active trader seeking quick liquidity solutions.
Navigating the landscape of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversion involves understanding available methods alongside associated risks and recent technological trends that influence ease-of-use today. As adoption continues expanding globally amidst evolving regulations—and innovations making processes faster—the ability to convert digital assets into tangible cash remains a cornerstone feature supporting mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies worldwide.
References
[1] Based on data up until October 2023 regarding technological advancements like Stripe's AI models integrating payments systems alongside regulatory shifts impacting cryptocurrency markets globally.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 05:25
Can I convert my cryptocurrency back into traditional fiat currency?
Can I Convert My Cryptocurrency Back Into Traditional Fiat Currency?
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the way we think about money, offering decentralized and digital alternatives to traditional currencies. However, one of the most common questions among users and investors is whether they can convert their crypto holdings back into fiat currency—such as USD, EUR, or JPY—and how this process works. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversions, covering methods, challenges, recent developments, and best practices to ensure secure and efficient transactions.
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Fiat Currency
Before diving into conversion options, it’s essential to understand what cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies are. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets secured by cryptography that operate on decentralized blockchain networks. Bitcoin remains the most prominent example but is just one among over 5,000 different cryptocurrencies available today.
In contrast, fiat currencies are government-issued legal tender with no intrinsic value but backed by national authorities. Examples include the US dollar (USD), euro (EUR), yen (JPY), among others. These currencies are widely accepted for everyday transactions across borders.
Why Do People Convert Cryptocurrency to Fiat?
Converting crypto into fiat currency serves multiple purposes:
- Realizing Profits: Investors often buy cryptocurrencies at lower prices with plans to sell later when prices increase.
- Daily Spending: For routine expenses like groceries or bills that require traditional money.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many financial institutions mandate transactions in fiat for legal reasons.
- Liquidity Needs: Accessing cash quickly for emergencies or other financial commitments.
Understanding these motivations helps clarify why seamless conversion options are vital within the broader ecosystem of digital finance.
Methods for Converting Cryptocurrency to Fiat
There are several practical ways users can convert their cryptocurrencies into traditional money:
1. Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Exchanges such as Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Bitstamp provide user-friendly platforms where you can sell your crypto holdings directly for fiat currency. These platforms typically support various cryptocurrencies and offer real-time market rates.
Advantages:
- High liquidity
- Multiple supported coins
- Easy-to-use interfaces
Disadvantages:
- Transaction fees vary depending on platform
- Potential security risks if accounts aren’t properly secured
2. Digital Wallets with Conversion Features
Some digital wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet now incorporate features allowing users to swap tokens directly within their apps before transferring funds elsewhere or withdrawing as cash through linked services.
3. Crypto ATMs (Bitcoin ATMs)
Crypto ATMs enable in-person exchanges where you can insert cryptocurrency—either via a wallet QR code or card—and receive cash instantly in return.
Pros:
- Immediate access to physical cash
- No need for bank account linkage in some cases
Cons:
- Limited availability geographically
- Higher transaction fees compared to online exchanges
4. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Services
For large-volume conversions beyond typical exchange limits or when seeking privacy/security assurances—OTC desks facilitate direct trades between buyers and sellers outside public markets.
Fees Associated With Conversion Processes
Converting cryptocurrency isn’t free; various fees impact your net proceeds:
| Type of Fee | Description |
|---|---|
| Exchange Fees | Charged per transaction; varies by platform |
| Withdrawal Fees | Costs associated with transferring funds from exchange/wallet |
| Network Fees | Blockchain transaction costs paid by users during transfers |
Being aware of these charges helps optimize your conversion strategy — choosing platforms with competitive rates can significantly affect overall profitability.
Security Risks During Conversion
While converting crypto offers liquidity benefits, it also introduces certain risks:
Market Volatility: Prices fluctuate rapidly; timing your sale is crucial.Security Breaches: Hacks targeting exchanges have occurred historically; using reputable platforms enhances safety.Regulatory Changes: New laws may restrict certain conversions or impose additional compliance measures.Technical Failures: System outages or network issues could delay transactions leading to potential losses if market conditions change suddenly.
Implementing strong security practices—including two-factor authentication (2FA) and keeping software updated—is essential when managing conversions securely.
Recent Trends Impacting Crypto-to-Fiat Conversions
Recent years have seen notable developments influencing how easily users convert crypto assets:
Regulatory Clarity Enhances Confidence
In 2022 onwards, regulatory bodies like the U.S Securities & Exchange Commission began clarifying rules around cryptocurrencies’ legal status—affecting how exchanges operate across jurisdictions which impacts user access points for converting assets legally compliant manner[1].
Technological Innovations Improve Efficiency
Advancements such as AI integration in payment systems streamline transaction processes while reducing fraud risk[1]. For instance:
- Stripe’s new AI foundation model aims at bridging traditional banking systems with blockchain payments,
- Faster settlement times,
- Lower fees,
making conversions more accessible even during volatile market periods[1].
The Impact of Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile; sudden price swings mean timing your sale carefully is critical if you want favorable rates without incurring losses—a challenge especially relevant during rapid bull runs or downturns[1].
Future Outlook
By 2025+, innovations like integrated payment rails combining both traditional finance infrastructure and blockchain technology will likely make converting crypto into fiat more seamless than ever before[1]. Enhanced regulatory clarity combined with technological progress promises safer environments for retail investors seeking liquidity solutions efficiently.
Best Practices When Converting Crypto To Fiat
To maximize benefits while minimizing risks:
- Use reputable exchanges known for security standards,
- Monitor market conditions closely before executing large trades,
- Be aware of all applicable fees upfront,
- Enable strong account security measures,
- Stay informed about evolving regulations affecting your jurisdiction,
Adopting these practices ensures smoother experiences regardless of whether you're a casual user or an active trader seeking quick liquidity solutions.
Navigating the landscape of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversion involves understanding available methods alongside associated risks and recent technological trends that influence ease-of-use today. As adoption continues expanding globally amidst evolving regulations—and innovations making processes faster—the ability to convert digital assets into tangible cash remains a cornerstone feature supporting mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies worldwide.
References
[1] Based on data up until October 2023 regarding technological advancements like Stripe's AI models integrating payments systems alongside regulatory shifts impacting cryptocurrency markets globally.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Difference Between Public and Private Blockchains
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way data is stored, verified, and shared across various industries. As this technology matures, understanding the fundamental differences between public and private blockchains becomes essential for organizations, developers, investors, and enthusiasts alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of both types of blockchains, their characteristics, use cases, recent developments, and implications for the future.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source ledger that anyone can access without restrictions. It operates on a decentralized network where multiple participants (nodes) maintain the integrity of data through consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Because it is open to all users worldwide—whether they are individual developers or large institutions—public blockchains promote transparency and security.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of public blockchains. Bitcoin pioneered digital currency by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Ethereum expanded on this concept by supporting decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and token creation within its ecosystem.
The key advantages include decentralization—no single entity controls the network—and transparency since all transactions are publicly recorded on an immutable ledger accessible to anyone with internet access. These features make public blockchains ideal for applications requiring trustless environments where participants do not need to rely on centralized authorities.
However, challenges such as scalability issues due to high energy consumption in PoW systems or slower transaction speeds have prompted ongoing innovations like layer 2 solutions or transitioning towards more sustainable consensus algorithms.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to their public counterparts, private blockchains operate within closed networks with restricted access controls. They are often employed by organizations seeking secure internal record-keeping systems that benefit from blockchain's tamper-evident properties but do not require full decentralization.
Private blockchain networks typically have centralized control managed by one organization or a consortium—a group of trusted entities working together—for governance purposes. Access rights are granted selectively; only authorized users can participate in transaction validation or view sensitive data.
Industries such as finance—particularly banking—and healthcare utilize private blockchains for tasks like secure transaction processing or patient record management because they offer enhanced privacy while maintaining auditability. For example:
- Supply Chain Management: Companies track product provenance internally.
- Financial Services: Banks share confidential transaction data securely.
- Healthcare: Patient records remain protected yet accessible among authorized providers.
While private blockchains sacrifice some degree of transparency compared to public ones—they restrict who can see what—they gain in speed, efficiency, customization options tailored to organizational needs—and compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
Choosing Between Public and Private Blockchains
Deciding whether to implement a public or private blockchain depends heavily on specific project requirements:
Transparency & Decentralization Needs: If openness is critical—for instance in cryptocurrencies—public chains are preferable.
Control & Privacy Requirements: For internal operations needing confidentiality—with limited external exposure—a private chain offers better control over data sharing.
Regulatory Compliance: Industries facing strict regulations may favor private chains that facilitate compliance while leveraging blockchain benefits.
Scalability & Performance Goals: Private networks generally provide faster transactions due to fewer nodes involved in validation processes.
Understanding these factors helps organizations align their technological choices with strategic objectives effectively.
Recent Developments Impacting Blockchain Types
The landscape surrounding both types continues evolving rapidly:
Regulatory Environment
Recent investigations highlight regulatory challenges faced predominantly by public cryptocurrencies. For example:
- The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) launched an investigation into Coinbase Global Inc., scrutinizing whether it misrepresented user numbers[1]. Such oversight underscores how regulators view activities tied closely with public blockchain platforms operating at scale.
Adoption Trends
Private blockchain adoption accelerates across sectors seeking secure yet controlled environments:
- Financial institutions leverage permissioned ledgers for compliant transactions.
- Supply chain firms enhance traceability internally using customized solutions tailored specifically for their operational needs[2].
Technological Innovations
Hybrid models combining elements from both worlds emerge increasingly popular:
- Hybrid blockchains enable selective transparency—publicly visible components alongside restricted segments—which balances decentralization benefits with privacy demands[3].
Cryptocurrency Market Dynamics
Market volatility remains prominent; meme coins like $TRUMP exemplify how digital assets face delays due to regulatory hurdles:
- The delayed token unlocks reflect ongoing uncertainties around legal frameworks governing tokens issued via public platforms[4].
These developments demonstrate how legal considerations influence design choices between different types of chains while highlighting innovation pathways aimed at optimizing performance without sacrificing security or compliance standards.
Key Facts About Public vs Private Blockchains
To clarify core distinctions:
| Aspect | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Openly accessible worldwide | Restricted access; controlled environment |
| Control | Decentralized governance | Centralized control / Consortium-based |
| Transparency | Fully transparent; all transactions visible | Limited visibility based on permissions |
| Security Mechanisms | Cryptography + consensus protocols like PoW/PoS | Cryptography + permissioned validation |
| Use Cases | Digital currencies; decentralized apps; open ecosystems | Internal enterprise processes; regulated industries |
Understanding these facts helps stakeholders evaluate which type aligns best with their goals regarding security posture, operational flexibility,and user engagement levels.
Future Outlook: Trends Shaping Blockchain Development
Looking ahead through 2025+, several trends will influence how organizations choose between these two models:
Hybrid Solutions Gain Traction: Combining features from both worlds allows businesses flexibility—public components ensure trustlessness while private segments safeguard sensitive information [3].
Enhanced Regulatory Clarity: Governments worldwide work toward clearer frameworks governing digital assets which could impact adoption strategies [1].
Interoperability Protocols: Cross-chain communication enables seamless interaction among diverse networks regardless of being public/private — fostering integrated ecosystems [5].
Focus on Sustainability: Transitioning away from energy-intensive consensus mechanisms toward eco-friendly alternatives will be crucial especially for large-scale deployments [6].
Security Enhancements: Advances in cryptographic techniques aim at bolstering resistance against cyber threats across all blockchain types [7].
By staying informed about these developments—including technological innovations and regulatory shifts—stakeholders can make smarter decisions aligned with evolving industry standards.
References
1. SEC Investigation into Coinbase – May 16th 2025
2. Adoption Trends in Supply Chain & Finance – April 25th 2025
3. Hybrid Blockchains Overview – Industry Reports 2024
4. Meme Coins Market Volatility – March 2025
5. Cross-chain Interoperability Protocols – Tech Journals 2024
6. Sustainable Consensus Mechanisms – Environmental Tech Review 2024
7. Advances in Cryptography – Cybersecurity Publications 2023
This detailed exploration aims to equip readers with foundational knowledge about what differentiates pubic versus private blockchains—their strengths , limitations ,and strategic uses — empowering informed decision-making amid rapid technological change


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 04:27
What is the difference between a public blockchain and a private blockchain?
Understanding the Difference Between Public and Private Blockchains
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way data is stored, verified, and shared across various industries. As this technology matures, understanding the fundamental differences between public and private blockchains becomes essential for organizations, developers, investors, and enthusiasts alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of both types of blockchains, their characteristics, use cases, recent developments, and implications for the future.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source ledger that anyone can access without restrictions. It operates on a decentralized network where multiple participants (nodes) maintain the integrity of data through consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Because it is open to all users worldwide—whether they are individual developers or large institutions—public blockchains promote transparency and security.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of public blockchains. Bitcoin pioneered digital currency by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Ethereum expanded on this concept by supporting decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and token creation within its ecosystem.
The key advantages include decentralization—no single entity controls the network—and transparency since all transactions are publicly recorded on an immutable ledger accessible to anyone with internet access. These features make public blockchains ideal for applications requiring trustless environments where participants do not need to rely on centralized authorities.
However, challenges such as scalability issues due to high energy consumption in PoW systems or slower transaction speeds have prompted ongoing innovations like layer 2 solutions or transitioning towards more sustainable consensus algorithms.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to their public counterparts, private blockchains operate within closed networks with restricted access controls. They are often employed by organizations seeking secure internal record-keeping systems that benefit from blockchain's tamper-evident properties but do not require full decentralization.
Private blockchain networks typically have centralized control managed by one organization or a consortium—a group of trusted entities working together—for governance purposes. Access rights are granted selectively; only authorized users can participate in transaction validation or view sensitive data.
Industries such as finance—particularly banking—and healthcare utilize private blockchains for tasks like secure transaction processing or patient record management because they offer enhanced privacy while maintaining auditability. For example:
- Supply Chain Management: Companies track product provenance internally.
- Financial Services: Banks share confidential transaction data securely.
- Healthcare: Patient records remain protected yet accessible among authorized providers.
While private blockchains sacrifice some degree of transparency compared to public ones—they restrict who can see what—they gain in speed, efficiency, customization options tailored to organizational needs—and compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
Choosing Between Public and Private Blockchains
Deciding whether to implement a public or private blockchain depends heavily on specific project requirements:
Transparency & Decentralization Needs: If openness is critical—for instance in cryptocurrencies—public chains are preferable.
Control & Privacy Requirements: For internal operations needing confidentiality—with limited external exposure—a private chain offers better control over data sharing.
Regulatory Compliance: Industries facing strict regulations may favor private chains that facilitate compliance while leveraging blockchain benefits.
Scalability & Performance Goals: Private networks generally provide faster transactions due to fewer nodes involved in validation processes.
Understanding these factors helps organizations align their technological choices with strategic objectives effectively.
Recent Developments Impacting Blockchain Types
The landscape surrounding both types continues evolving rapidly:
Regulatory Environment
Recent investigations highlight regulatory challenges faced predominantly by public cryptocurrencies. For example:
- The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) launched an investigation into Coinbase Global Inc., scrutinizing whether it misrepresented user numbers[1]. Such oversight underscores how regulators view activities tied closely with public blockchain platforms operating at scale.
Adoption Trends
Private blockchain adoption accelerates across sectors seeking secure yet controlled environments:
- Financial institutions leverage permissioned ledgers for compliant transactions.
- Supply chain firms enhance traceability internally using customized solutions tailored specifically for their operational needs[2].
Technological Innovations
Hybrid models combining elements from both worlds emerge increasingly popular:
- Hybrid blockchains enable selective transparency—publicly visible components alongside restricted segments—which balances decentralization benefits with privacy demands[3].
Cryptocurrency Market Dynamics
Market volatility remains prominent; meme coins like $TRUMP exemplify how digital assets face delays due to regulatory hurdles:
- The delayed token unlocks reflect ongoing uncertainties around legal frameworks governing tokens issued via public platforms[4].
These developments demonstrate how legal considerations influence design choices between different types of chains while highlighting innovation pathways aimed at optimizing performance without sacrificing security or compliance standards.
Key Facts About Public vs Private Blockchains
To clarify core distinctions:
| Aspect | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Openly accessible worldwide | Restricted access; controlled environment |
| Control | Decentralized governance | Centralized control / Consortium-based |
| Transparency | Fully transparent; all transactions visible | Limited visibility based on permissions |
| Security Mechanisms | Cryptography + consensus protocols like PoW/PoS | Cryptography + permissioned validation |
| Use Cases | Digital currencies; decentralized apps; open ecosystems | Internal enterprise processes; regulated industries |
Understanding these facts helps stakeholders evaluate which type aligns best with their goals regarding security posture, operational flexibility,and user engagement levels.
Future Outlook: Trends Shaping Blockchain Development
Looking ahead through 2025+, several trends will influence how organizations choose between these two models:
Hybrid Solutions Gain Traction: Combining features from both worlds allows businesses flexibility—public components ensure trustlessness while private segments safeguard sensitive information [3].
Enhanced Regulatory Clarity: Governments worldwide work toward clearer frameworks governing digital assets which could impact adoption strategies [1].
Interoperability Protocols: Cross-chain communication enables seamless interaction among diverse networks regardless of being public/private — fostering integrated ecosystems [5].
Focus on Sustainability: Transitioning away from energy-intensive consensus mechanisms toward eco-friendly alternatives will be crucial especially for large-scale deployments [6].
Security Enhancements: Advances in cryptographic techniques aim at bolstering resistance against cyber threats across all blockchain types [7].
By staying informed about these developments—including technological innovations and regulatory shifts—stakeholders can make smarter decisions aligned with evolving industry standards.
References
1. SEC Investigation into Coinbase – May 16th 2025
2. Adoption Trends in Supply Chain & Finance – April 25th 2025
3. Hybrid Blockchains Overview – Industry Reports 2024
4. Meme Coins Market Volatility – March 2025
5. Cross-chain Interoperability Protocols – Tech Journals 2024
6. Sustainable Consensus Mechanisms – Environmental Tech Review 2024
7. Advances in Cryptography – Cybersecurity Publications 2023
This detailed exploration aims to equip readers with foundational knowledge about what differentiates pubic versus private blockchains—their strengths , limitations ,and strategic uses — empowering informed decision-making amid rapid technological change
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Buyback Spike Chart?
A buyback spike chart is a visual tool used by investors and analysts to track the volume of stock repurchases made by a company over specific periods. It graphically displays the number of shares bought back on particular days or during certain time frames, providing insight into corporate financial strategies and market sentiment. These charts help stakeholders understand whether a company is actively investing in its own stock, which can signal confidence in future growth or financial stability.
Typically, buyback spike charts are presented as bar graphs or line charts that highlight sudden increases—or "spikes"—in share repurchase activity. Such spikes often indicate strategic moves by management to support the stock price, return value to shareholders, or utilize excess cash reserves efficiently.
Why Do Companies Engage in Stock Buybacks?
Stock buybacks are an essential component of corporate finance strategies. When companies purchase their own shares from the open market or directly from shareholders, it reduces the total number of outstanding shares. This reduction can lead to several beneficial effects:
- Enhanced Earnings Per Share (EPS): With fewer shares outstanding, earnings are divided among fewer units, often resulting in higher EPS figures.
- Market Signal: A significant buyback activity suggests that management believes the company's stock is undervalued and has confidence in its future prospects.
- Shareholder Value: Buybacks can increase share prices and provide immediate value to shareholders who sell their stocks back at higher prices.
Buybacks also serve as an alternative way for companies to return capital when they have limited options for reinvestment opportunities within their operations.
How Does a Buyback Spike Chart Help Investors?
Investors use buyback spike charts as part of their broader analysis toolkit because these visuals offer quick insights into corporate behavior. A sudden increase in buyback activity might indicate that management perceives favorable valuation levels or has excess cash ready for distribution.
By analyzing these spikes over time alongside other financial metrics—such as revenue growth, profit margins, and debt levels—investors can gauge whether a company's strategic moves align with long-term value creation. Moreover, understanding when companies ramp up share repurchases helps investors anticipate potential upward movements in stock prices driven by reduced supply and increased earnings per share.
The Role of Market Sentiment and Regulatory Environment
Buyback activities are closely tied to overall market sentiment; positive perceptions about a company's health often lead to increased buybacks. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of uncertainty—like those seen during regulatory crackdowns—companies may slow down or halt such activities.
In recent years (notably 2023–2025), regulatory scrutiny around stock buybacks has intensified globally. Authorities aim to ensure transparency and prevent potential abuses like insider trading or manipulative practices that could distort markets. As regulations tighten—for example through stricter disclosure requirements—the nature and frequency of buyback spikes may change accordingly.
Understanding this evolving regulatory landscape helps investors interpret spike charts more accurately within current legal contexts while assessing risks associated with aggressive repurchase programs.
Recent Trends in Buyback Activity
The past few years have seen notable shifts regarding corporate repurchase behavior:
In 2023: Many large corporations increased their buyback programs significantly after accumulating substantial cash reserves during pandemic-related disruptions.
In 2024: Regulatory bodies began scrutinizing these activities more closely; some firms faced restrictions on how much they could spend on share repurchases.
As of mid-2025: Market sentiment remains largely positive toward buybacks due to perceived signals of strength; however, experts warn against overreliance on this strategy alone for long-term growth.
These trends reflect both strategic corporate decisions driven by available capital and external factors like regulation influencing how aggressively companies pursue share repurchases.
Risks Associated with Heavy Stock Repurchasing
While buying back shares generally boosts investor confidence temporarily—and can support higher stock prices—it carries inherent risks if mismanaged:
Debt Buildup: To fund large-scale buybacks without sufficient internal cash flow, some companies resorted to borrowing heavily—which increases leverage risk if revenues decline unexpectedly.
Market Volatility: Large-volume purchases concentrated over short periods might cause abrupt price swings if not executed carefully.
Regulatory Challenges: Stricter oversight could limit future flexibility for executing aggressive repurchase plans.
Opportunity Cost: Funds allocated toward buying back stocks might be better invested elsewhere—such as research & development—to foster sustainable growth rather than short-term price boosts.
Investors should consider these factors alongside spike chart data before making investment decisions based solely on recent buying activity patterns.
How Investors Can Use Buyback Spike Charts Effectively
To maximize insights from these charts:
Combine them with fundamental analysis: Look at revenue trends, profit margins, debt levels—all contextualize what high purchase volumes mean.
Watch for sustained versus one-off spikes: Consistent increases suggest ongoing confidence; isolated spikes might be opportunistic rather than strategic.
Monitor regulatory developments: Changes here could impact future activity levels—and thus influence interpretation accuracy.
By integrating technical visualizations like spike charts with comprehensive financial analysis—and staying aware of external influences—investors improve decision-making quality while aligning actions with sound investment principles rooted in transparency (E-A-T).
In summary, understanding what a buyback spike chart reveals about corporate behavior provides valuable context for evaluating company health and market dynamics today’s investors face complex environments where strategic insights matter more than ever before — especially amid evolving regulations and global economic shifts


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-20 05:42
What’s a buyback spike chart?
What Is a Buyback Spike Chart?
A buyback spike chart is a visual tool used by investors and analysts to track the volume of stock repurchases made by a company over specific periods. It graphically displays the number of shares bought back on particular days or during certain time frames, providing insight into corporate financial strategies and market sentiment. These charts help stakeholders understand whether a company is actively investing in its own stock, which can signal confidence in future growth or financial stability.
Typically, buyback spike charts are presented as bar graphs or line charts that highlight sudden increases—or "spikes"—in share repurchase activity. Such spikes often indicate strategic moves by management to support the stock price, return value to shareholders, or utilize excess cash reserves efficiently.
Why Do Companies Engage in Stock Buybacks?
Stock buybacks are an essential component of corporate finance strategies. When companies purchase their own shares from the open market or directly from shareholders, it reduces the total number of outstanding shares. This reduction can lead to several beneficial effects:
- Enhanced Earnings Per Share (EPS): With fewer shares outstanding, earnings are divided among fewer units, often resulting in higher EPS figures.
- Market Signal: A significant buyback activity suggests that management believes the company's stock is undervalued and has confidence in its future prospects.
- Shareholder Value: Buybacks can increase share prices and provide immediate value to shareholders who sell their stocks back at higher prices.
Buybacks also serve as an alternative way for companies to return capital when they have limited options for reinvestment opportunities within their operations.
How Does a Buyback Spike Chart Help Investors?
Investors use buyback spike charts as part of their broader analysis toolkit because these visuals offer quick insights into corporate behavior. A sudden increase in buyback activity might indicate that management perceives favorable valuation levels or has excess cash ready for distribution.
By analyzing these spikes over time alongside other financial metrics—such as revenue growth, profit margins, and debt levels—investors can gauge whether a company's strategic moves align with long-term value creation. Moreover, understanding when companies ramp up share repurchases helps investors anticipate potential upward movements in stock prices driven by reduced supply and increased earnings per share.
The Role of Market Sentiment and Regulatory Environment
Buyback activities are closely tied to overall market sentiment; positive perceptions about a company's health often lead to increased buybacks. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of uncertainty—like those seen during regulatory crackdowns—companies may slow down or halt such activities.
In recent years (notably 2023–2025), regulatory scrutiny around stock buybacks has intensified globally. Authorities aim to ensure transparency and prevent potential abuses like insider trading or manipulative practices that could distort markets. As regulations tighten—for example through stricter disclosure requirements—the nature and frequency of buyback spikes may change accordingly.
Understanding this evolving regulatory landscape helps investors interpret spike charts more accurately within current legal contexts while assessing risks associated with aggressive repurchase programs.
Recent Trends in Buyback Activity
The past few years have seen notable shifts regarding corporate repurchase behavior:
In 2023: Many large corporations increased their buyback programs significantly after accumulating substantial cash reserves during pandemic-related disruptions.
In 2024: Regulatory bodies began scrutinizing these activities more closely; some firms faced restrictions on how much they could spend on share repurchases.
As of mid-2025: Market sentiment remains largely positive toward buybacks due to perceived signals of strength; however, experts warn against overreliance on this strategy alone for long-term growth.
These trends reflect both strategic corporate decisions driven by available capital and external factors like regulation influencing how aggressively companies pursue share repurchases.
Risks Associated with Heavy Stock Repurchasing
While buying back shares generally boosts investor confidence temporarily—and can support higher stock prices—it carries inherent risks if mismanaged:
Debt Buildup: To fund large-scale buybacks without sufficient internal cash flow, some companies resorted to borrowing heavily—which increases leverage risk if revenues decline unexpectedly.
Market Volatility: Large-volume purchases concentrated over short periods might cause abrupt price swings if not executed carefully.
Regulatory Challenges: Stricter oversight could limit future flexibility for executing aggressive repurchase plans.
Opportunity Cost: Funds allocated toward buying back stocks might be better invested elsewhere—such as research & development—to foster sustainable growth rather than short-term price boosts.
Investors should consider these factors alongside spike chart data before making investment decisions based solely on recent buying activity patterns.
How Investors Can Use Buyback Spike Charts Effectively
To maximize insights from these charts:
Combine them with fundamental analysis: Look at revenue trends, profit margins, debt levels—all contextualize what high purchase volumes mean.
Watch for sustained versus one-off spikes: Consistent increases suggest ongoing confidence; isolated spikes might be opportunistic rather than strategic.
Monitor regulatory developments: Changes here could impact future activity levels—and thus influence interpretation accuracy.
By integrating technical visualizations like spike charts with comprehensive financial analysis—and staying aware of external influences—investors improve decision-making quality while aligning actions with sound investment principles rooted in transparency (E-A-T).
In summary, understanding what a buyback spike chart reveals about corporate behavior provides valuable context for evaluating company health and market dynamics today’s investors face complex environments where strategic insights matter more than ever before — especially amid evolving regulations and global economic shifts
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Implied Volatility Chart: A Complete Guide to Understanding Market Expectations
What Is Implied Volatility?
Implied volatility (IV) is a key metric used by traders and investors to gauge market sentiment and potential price fluctuations of a security. It reflects the market’s expectations for future volatility based on options prices, rather than historical data. Essentially, IV indicates how much the market anticipates the underlying asset's price will move over a specific period.
Options prices are influenced by various factors, including current stock prices, strike prices, time until expiration, interest rates, and dividends. By analyzing these options through models like Black-Scholes or other advanced algorithms, traders derive implied volatility figures that serve as forward-looking indicators. High implied volatility suggests that investors expect significant price swings—either upward or downward—while low implied volatility points to more stable markets with less anticipated movement.
Understanding this distinction is crucial because IV does not predict direction but rather the magnitude of potential moves. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical tension, implied volatility tends to rise as investors brace for unpredictable outcomes.
Context and Significance in Market Analysis
Implied volatility plays an essential role in options trading strategies and broader financial analysis. It helps traders assess risk levels associated with specific securities and decide on appropriate hedging or speculative positions. When IV spikes unexpectedly—say due to earnings reports or macroeconomic news—it often signals increased uncertainty among market participants.
Market analysts also use implied volatility charts to identify trends over time. For instance, sustained high levels may indicate prolonged periods of instability or investor fear (often called "fear gauges"), while declining IV can suggest growing confidence in an asset’s stability.
Moreover, understanding how implied volatility interacts with other indicators enhances decision-making processes:
- Volatility Skew: Variations in IV across different strike prices reveal investor sentiment about specific price levels.
- Volatility Smile: Patterns where at-the-money options have lower IV compared to out-of-the-money options.
- Historical vs Implied Volatility: Comparing past actual movements against expected future movements provides insights into whether markets are overly optimistic or pessimistic.
Recent Developments Highlighting Implied Volatility Trends
In recent months, notable shifts in implied volatility have been observed across various sectors and assets:
Chord Energy Corporation (WLLBW): The company has exhibited high implied volatilities recently—a sign that traders anticipate substantial upcoming price changes possibly driven by fluctuating oil prices or sector-specific news[1]. Such elevated levels often lead to increased premiums on options contracts but also signal heightened risk exposure for investors.
Iris Energy (IRAA): The renewable energy firm experienced a surge in bullish option activity alongside rising implied volatilities[2]. This pattern indicates growing optimism among investors regarding its growth prospects amid expanding renewable initiatives—a typical scenario where positive sentiment fuels higher option premiums due to expected favorable developments.
Broader Market Trends: In both traditional equity markets and cryptocurrencies alike—such as Bitcoin—the level of implied volatility serves as an important barometer for risk appetite among traders[1][2]. During volatile periods like economic downturns or geopolitical conflicts, these measures tend to spike sharply; conversely, they decline when markets stabilize.
Potential Risks & Strategies: Elevated IV can create lucrative opportunities through strategies such as straddles or strangles but also increases exposure if market moves do not materialize as anticipated[3]. Conversely, low-volatility environments might favor income-generating approaches like covered calls but could signal complacency among investors[4].
Tools for Tracking Implied Volatility
Modern financial platforms provide comprehensive tools enabling real-time monitoring of implied volatility charts:
- Historical Data Analysis: Platforms like Perplexity Finance allow users to examine past trends—identifying patterns before major events.
- Forecasting Models: Advanced algorithms project future changes based on current data points.
- Visual Charts & Graphs: Interactive visualizations help interpret complex data quickly.
These resources empower both professional traders and retail investors with actionable insights rooted in robust analytics.
How Implied Volatility Influences Trading Decisions
Investors leverage information from IV charts when designing their trading strategies:
High IV often correlates with increased premiums; thus buyers might prefer selling options (e.g., covered calls) while sellers look for favorable entry points.
Low IV suggests subdued expectations; this environment may favor buying protective puts if downside risk appears imminent—or engaging in spread strategies that capitalize on minimal premium decay.
Furthermore, understanding whether current conditions reflect genuine uncertainty versus complacency helps refine timing decisions around entries/exits within portfolios.
Key Factors Affecting Implied Volatility Levels
Several elements influence how much the market perceives future risks:
• Economic Indicators – GDP growth rates、inflation figures、employment data• Geopolitical Events – Elections、conflicts、policy changes• Earnings Reports – Company-specific performance announcements• Market Sentiment – Investor confidence indices、news flow
Additionally,macro factors such as monetary policy shifts by central banks significantly impact overall market stability perceptions—and consequently,implyed volatilities across assets。
Interpreting Implied Volatility Charts Effectively
To make meaningful use of these charts,investors should consider several best practices:
1.Compare current levels against historical averages:Identify whether present readings are unusually high/low relative to past cycles。2.Observe trend directions:Rising trends may indicate increasing uncertainty;declining ones suggest stabilization。3.Assess sector-specific patterns:Different industries exhibit unique behaviors based on cyclical nature。4.Combine with other technical indicators:Moving averages、RSI、MACD等工具提供更全面的市场视角。
By integrating these methods,traders can better anticipate potential breakout points或风险点,从而优化投资组合表现。
The Role of Tools Like Perplexity Finance
Platforms such as Perplexity Finance enhance analytical capabilities by offering detailed datasets和 predictive models。用户可以追踪历史波动率数据,分析未来趋势,并利用图表识别潜在的市场转折点。这些工具对于专业交易者和普通投资者都极具价值,因为它们帮助理解复杂的市场动态并做出更明智的决策。
Understanding How Implied Volatility Differs from Other Metrics
While historical realized volatility measures actual past price fluctuations,implied volatility反映的是市场对未来波动性的预期。两者之间的差异可以揭示市场情绪偏差。例如,当隐含波动率远高于历史波动率时,可能意味着投资者对未来的不确定性过度担忧(“恐慌”情绪);反之亦然。
Market Sentiment Indicators & Economic Conditions Impacting Implicit Expectations
Market sentiment指标如VIX指数常被用作衡量整体市场恐惧程度,而其变化与特定资产或行业的IV密切相关。此外,经 济环境如通胀水平和利率变动也会影响投资者对未来价格走势的不确定性预期,从而推动隐含波动率变化。
Why Investors Should Pay Attention To Implicit Trends
持续监控隐含波动率有助于捕捉潜在风险与机会。高企的隐含波动力度可能暗示即将到来的重大事件或转折点,而低迷则可能意味着市场缺乏动力或等待新信息。因此,将IV纳入日常分析框架,有助于实现更科学、更有根据的投资决策,提高整体盈利能力和风险管理水平。


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 07:14
What is Implied Volatility Chart?
Implied Volatility Chart: A Complete Guide to Understanding Market Expectations
What Is Implied Volatility?
Implied volatility (IV) is a key metric used by traders and investors to gauge market sentiment and potential price fluctuations of a security. It reflects the market’s expectations for future volatility based on options prices, rather than historical data. Essentially, IV indicates how much the market anticipates the underlying asset's price will move over a specific period.
Options prices are influenced by various factors, including current stock prices, strike prices, time until expiration, interest rates, and dividends. By analyzing these options through models like Black-Scholes or other advanced algorithms, traders derive implied volatility figures that serve as forward-looking indicators. High implied volatility suggests that investors expect significant price swings—either upward or downward—while low implied volatility points to more stable markets with less anticipated movement.
Understanding this distinction is crucial because IV does not predict direction but rather the magnitude of potential moves. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical tension, implied volatility tends to rise as investors brace for unpredictable outcomes.
Context and Significance in Market Analysis
Implied volatility plays an essential role in options trading strategies and broader financial analysis. It helps traders assess risk levels associated with specific securities and decide on appropriate hedging or speculative positions. When IV spikes unexpectedly—say due to earnings reports or macroeconomic news—it often signals increased uncertainty among market participants.
Market analysts also use implied volatility charts to identify trends over time. For instance, sustained high levels may indicate prolonged periods of instability or investor fear (often called "fear gauges"), while declining IV can suggest growing confidence in an asset’s stability.
Moreover, understanding how implied volatility interacts with other indicators enhances decision-making processes:
- Volatility Skew: Variations in IV across different strike prices reveal investor sentiment about specific price levels.
- Volatility Smile: Patterns where at-the-money options have lower IV compared to out-of-the-money options.
- Historical vs Implied Volatility: Comparing past actual movements against expected future movements provides insights into whether markets are overly optimistic or pessimistic.
Recent Developments Highlighting Implied Volatility Trends
In recent months, notable shifts in implied volatility have been observed across various sectors and assets:
Chord Energy Corporation (WLLBW): The company has exhibited high implied volatilities recently—a sign that traders anticipate substantial upcoming price changes possibly driven by fluctuating oil prices or sector-specific news[1]. Such elevated levels often lead to increased premiums on options contracts but also signal heightened risk exposure for investors.
Iris Energy (IRAA): The renewable energy firm experienced a surge in bullish option activity alongside rising implied volatilities[2]. This pattern indicates growing optimism among investors regarding its growth prospects amid expanding renewable initiatives—a typical scenario where positive sentiment fuels higher option premiums due to expected favorable developments.
Broader Market Trends: In both traditional equity markets and cryptocurrencies alike—such as Bitcoin—the level of implied volatility serves as an important barometer for risk appetite among traders[1][2]. During volatile periods like economic downturns or geopolitical conflicts, these measures tend to spike sharply; conversely, they decline when markets stabilize.
Potential Risks & Strategies: Elevated IV can create lucrative opportunities through strategies such as straddles or strangles but also increases exposure if market moves do not materialize as anticipated[3]. Conversely, low-volatility environments might favor income-generating approaches like covered calls but could signal complacency among investors[4].
Tools for Tracking Implied Volatility
Modern financial platforms provide comprehensive tools enabling real-time monitoring of implied volatility charts:
- Historical Data Analysis: Platforms like Perplexity Finance allow users to examine past trends—identifying patterns before major events.
- Forecasting Models: Advanced algorithms project future changes based on current data points.
- Visual Charts & Graphs: Interactive visualizations help interpret complex data quickly.
These resources empower both professional traders and retail investors with actionable insights rooted in robust analytics.
How Implied Volatility Influences Trading Decisions
Investors leverage information from IV charts when designing their trading strategies:
High IV often correlates with increased premiums; thus buyers might prefer selling options (e.g., covered calls) while sellers look for favorable entry points.
Low IV suggests subdued expectations; this environment may favor buying protective puts if downside risk appears imminent—or engaging in spread strategies that capitalize on minimal premium decay.
Furthermore, understanding whether current conditions reflect genuine uncertainty versus complacency helps refine timing decisions around entries/exits within portfolios.
Key Factors Affecting Implied Volatility Levels
Several elements influence how much the market perceives future risks:
• Economic Indicators – GDP growth rates、inflation figures、employment data• Geopolitical Events – Elections、conflicts、policy changes• Earnings Reports – Company-specific performance announcements• Market Sentiment – Investor confidence indices、news flow
Additionally,macro factors such as monetary policy shifts by central banks significantly impact overall market stability perceptions—and consequently,implyed volatilities across assets。
Interpreting Implied Volatility Charts Effectively
To make meaningful use of these charts,investors should consider several best practices:
1.Compare current levels against historical averages:Identify whether present readings are unusually high/low relative to past cycles。2.Observe trend directions:Rising trends may indicate increasing uncertainty;declining ones suggest stabilization。3.Assess sector-specific patterns:Different industries exhibit unique behaviors based on cyclical nature。4.Combine with other technical indicators:Moving averages、RSI、MACD等工具提供更全面的市场视角。
By integrating these methods,traders can better anticipate potential breakout points或风险点,从而优化投资组合表现。
The Role of Tools Like Perplexity Finance
Platforms such as Perplexity Finance enhance analytical capabilities by offering detailed datasets和 predictive models。用户可以追踪历史波动率数据,分析未来趋势,并利用图表识别潜在的市场转折点。这些工具对于专业交易者和普通投资者都极具价值,因为它们帮助理解复杂的市场动态并做出更明智的决策。
Understanding How Implied Volatility Differs from Other Metrics
While historical realized volatility measures actual past price fluctuations,implied volatility反映的是市场对未来波动性的预期。两者之间的差异可以揭示市场情绪偏差。例如,当隐含波动率远高于历史波动率时,可能意味着投资者对未来的不确定性过度担忧(“恐慌”情绪);反之亦然。
Market Sentiment Indicators & Economic Conditions Impacting Implicit Expectations
Market sentiment指标如VIX指数常被用作衡量整体市场恐惧程度,而其变化与特定资产或行业的IV密切相关。此外,经 济环境如通胀水平和利率变动也会影响投资者对未来价格走势的不确定性预期,从而推动隐含波动率变化。
Why Investors Should Pay Attention To Implicit Trends
持续监控隐含波动率有助于捕捉潜在风险与机会。高企的隐含波动力度可能暗示即将到来的重大事件或转折点,而低迷则可能意味着市场缺乏动力或等待新信息。因此,将IV纳入日常分析框架,有助于实现更科学、更有根据的投资决策,提高整体盈利能力和风险管理水平。
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Moving Average Ribbon?
The Moving Average Ribbon (MAR) is a technical analysis tool used by traders and investors to identify the strength, direction, and potential reversals of market trends. Unlike traditional moving averages that rely on one or two lines, the MAR employs multiple moving averages plotted simultaneously to create a ribbon-like visual. This layered approach provides a more detailed picture of market momentum and helps traders make more informed decisions.
At its core, the Moving Average Ribbon builds upon concepts from the classic MACD indicator but extends its utility by incorporating several moving averages with different periods—typically short-term, medium-term, and long-term. The interaction between these lines offers insights into trend shifts that might not be immediately apparent with standard indicators.
How Does Moving Average Ribbon Work?
The construction of a Moving Average Ribbon involves plotting three or more moving averages on the same chart:
- Short-term MA (e.g., 8-period): Reacts quickly to recent price changes.
- Medium-term MA (e.g., 12-period): Offers a balanced view of recent trends.
- Long-term MA (e.g., 26-period): Indicates overall trend direction over a longer horizon.
These multiple lines form what appears as a colorful ribbon across your trading chart. When shorter MAs cross above longer ones, it signals bullish momentum; when they cross below, it suggests bearish conditions. Traders often look for these crossover points as potential buy or sell signals.
In addition to crossovers, divergence between the MAs and price action can hint at upcoming reversals. For example, if prices are making new highs while the ribbon's shorter MAs fail to do so or start converging downward, it could indicate weakening momentum ahead of a reversal.
Why Use Moving Average Ribbon in Trading?
The primary advantage of using an MAR lies in its ability to provide nuanced insights into market dynamics that single or dual-moving average systems might miss. It allows traders to see not just whether an asset is trending but also how strong that trend is across different timeframes simultaneously.
This multi-layered perspective helps in several ways:
- Trend Confirmation: Multiple MAs aligned in one direction reinforce confidence in ongoing trends.
- Early Reversal Signals: Crossovers within the ribbon can serve as early warning signs before major price moves occur.
- Market Volatility Detection: Widening gaps between MAs suggest increasing volatility; narrowing gaps may indicate consolidation phases.
Furthermore, because it visually represents multiple data points at once—rather than relying solely on numerical indicators—the MAR simplifies complex information into an intuitive format suitable for both novice and experienced traders alike.
Practical Applications for Traders
Traders employ the Moving Average Ribbon across various markets—including stocks, forex, commodities—and increasingly within cryptocurrency trading due to its effectiveness in volatile environments. Here are some common uses:
- Identifying Trend Direction: When all short-, medium-, and long-term MAs align upwardly with minimal crossover activity—this indicates sustained bullishness.
- Spotting Entry Points: Bullish crossovers where shorter MAs move above longer ones can signal optimal entry points for long positions.
- Timing Exits: Conversely, when shorter MAs begin crossing below longer ones after an uptrend has been established—a sign that momentum may be waning—traders consider exiting positions.
- Confirming Breakouts: The ribbon’s structure helps validate breakouts from support/resistance levels by showing increased alignment among multiple moving averages during such events.
Additionally, combining MAR analysis with other indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or volume data enhances decision-making accuracy further—especially important given risks associated with false signals inherent in technical analysis tools.
Recent Trends: Adoption & Technological Integration
In recent years, interest around the Moving Average Ribbon has surged due to developments like increased adoption within cryptocurrency markets where rapid price swings demand sophisticated tools for trend detection. Crypto traders utilize MAR alongside other indicators such as RSI or Bollinger Bands for comprehensive analysis amid high volatility environments.
Moreover — advancements in AI and machine learning have integrated with traditional technical tools like MAR — enabling automated systems capable of analyzing vast datasets swiftly while providing real-time alerts based on complex pattern recognition algorithms rooted partly in moving average interactions.
Educational platforms have also expanded their content offerings around this technique; online courses now teach how best to interpret ribbons' signals amidst fluctuating markets effectively—making advanced technical strategies accessible even for less experienced traders seeking reliable methods beyond basic charts.
Limitations & Best Practices
While powerful when used correctly — it's essential not to rely solely on Moving Average Ribbons without considering fundamental factors influencing asset prices such as economic news releases or geopolitical events which can cause sudden shifts contrary to technical signals alone.
False positives are common during sideways consolidations where no clear trend exists yet multiple MAs may still produce misleading crossover signals temporarily suggesting reversals prematurely. To mitigate this risk:
- Always confirm signals through additional indicators
- Use proper stop-loss orders
- Consider broader market context before acting
Combining MAR insights with sound risk management practices ensures better outcomes over time rather than reacting impulsively based solely on indicator movements.
Summary
The Moving Average Ribbon offers traders an insightful way to visualize multi-timeframe trends through layered moving averages arranged visually like ribbons across charts. Its ability to detect early signs of trend changes makes it valuable across various financial instruments—from stocks and forex pairs up through cryptocurrencies—and adaptable via integration with AI-driven analytics enhances its predictive power further today’s dynamic markets require comprehensive analytical approaches combined with prudent risk management strategies for consistent success.


Lo
2025-05-19 04:21
What is Moving Average Ribbon?
What is Moving Average Ribbon?
The Moving Average Ribbon (MAR) is a technical analysis tool used by traders and investors to identify the strength, direction, and potential reversals of market trends. Unlike traditional moving averages that rely on one or two lines, the MAR employs multiple moving averages plotted simultaneously to create a ribbon-like visual. This layered approach provides a more detailed picture of market momentum and helps traders make more informed decisions.
At its core, the Moving Average Ribbon builds upon concepts from the classic MACD indicator but extends its utility by incorporating several moving averages with different periods—typically short-term, medium-term, and long-term. The interaction between these lines offers insights into trend shifts that might not be immediately apparent with standard indicators.
How Does Moving Average Ribbon Work?
The construction of a Moving Average Ribbon involves plotting three or more moving averages on the same chart:
- Short-term MA (e.g., 8-period): Reacts quickly to recent price changes.
- Medium-term MA (e.g., 12-period): Offers a balanced view of recent trends.
- Long-term MA (e.g., 26-period): Indicates overall trend direction over a longer horizon.
These multiple lines form what appears as a colorful ribbon across your trading chart. When shorter MAs cross above longer ones, it signals bullish momentum; when they cross below, it suggests bearish conditions. Traders often look for these crossover points as potential buy or sell signals.
In addition to crossovers, divergence between the MAs and price action can hint at upcoming reversals. For example, if prices are making new highs while the ribbon's shorter MAs fail to do so or start converging downward, it could indicate weakening momentum ahead of a reversal.
Why Use Moving Average Ribbon in Trading?
The primary advantage of using an MAR lies in its ability to provide nuanced insights into market dynamics that single or dual-moving average systems might miss. It allows traders to see not just whether an asset is trending but also how strong that trend is across different timeframes simultaneously.
This multi-layered perspective helps in several ways:
- Trend Confirmation: Multiple MAs aligned in one direction reinforce confidence in ongoing trends.
- Early Reversal Signals: Crossovers within the ribbon can serve as early warning signs before major price moves occur.
- Market Volatility Detection: Widening gaps between MAs suggest increasing volatility; narrowing gaps may indicate consolidation phases.
Furthermore, because it visually represents multiple data points at once—rather than relying solely on numerical indicators—the MAR simplifies complex information into an intuitive format suitable for both novice and experienced traders alike.
Practical Applications for Traders
Traders employ the Moving Average Ribbon across various markets—including stocks, forex, commodities—and increasingly within cryptocurrency trading due to its effectiveness in volatile environments. Here are some common uses:
- Identifying Trend Direction: When all short-, medium-, and long-term MAs align upwardly with minimal crossover activity—this indicates sustained bullishness.
- Spotting Entry Points: Bullish crossovers where shorter MAs move above longer ones can signal optimal entry points for long positions.
- Timing Exits: Conversely, when shorter MAs begin crossing below longer ones after an uptrend has been established—a sign that momentum may be waning—traders consider exiting positions.
- Confirming Breakouts: The ribbon’s structure helps validate breakouts from support/resistance levels by showing increased alignment among multiple moving averages during such events.
Additionally, combining MAR analysis with other indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or volume data enhances decision-making accuracy further—especially important given risks associated with false signals inherent in technical analysis tools.
Recent Trends: Adoption & Technological Integration
In recent years, interest around the Moving Average Ribbon has surged due to developments like increased adoption within cryptocurrency markets where rapid price swings demand sophisticated tools for trend detection. Crypto traders utilize MAR alongside other indicators such as RSI or Bollinger Bands for comprehensive analysis amid high volatility environments.
Moreover — advancements in AI and machine learning have integrated with traditional technical tools like MAR — enabling automated systems capable of analyzing vast datasets swiftly while providing real-time alerts based on complex pattern recognition algorithms rooted partly in moving average interactions.
Educational platforms have also expanded their content offerings around this technique; online courses now teach how best to interpret ribbons' signals amidst fluctuating markets effectively—making advanced technical strategies accessible even for less experienced traders seeking reliable methods beyond basic charts.
Limitations & Best Practices
While powerful when used correctly — it's essential not to rely solely on Moving Average Ribbons without considering fundamental factors influencing asset prices such as economic news releases or geopolitical events which can cause sudden shifts contrary to technical signals alone.
False positives are common during sideways consolidations where no clear trend exists yet multiple MAs may still produce misleading crossover signals temporarily suggesting reversals prematurely. To mitigate this risk:
- Always confirm signals through additional indicators
- Use proper stop-loss orders
- Consider broader market context before acting
Combining MAR insights with sound risk management practices ensures better outcomes over time rather than reacting impulsively based solely on indicator movements.
Summary
The Moving Average Ribbon offers traders an insightful way to visualize multi-timeframe trends through layered moving averages arranged visually like ribbons across charts. Its ability to detect early signs of trend changes makes it valuable across various financial instruments—from stocks and forex pairs up through cryptocurrencies—and adaptable via integration with AI-driven analytics enhances its predictive power further today’s dynamic markets require comprehensive analytical approaches combined with prudent risk management strategies for consistent success.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Time and Sales (T&S)?
Time and Sales (T&S) is a vital component of financial market data that provides a detailed, real-time record of every trade executed on a stock exchange or trading platform. This data feed captures essential information about each transaction, including the exact timestamp, the price at which the trade occurred, the number of shares traded, and whether it was a buy or sell order. For traders and investors seeking to understand market behavior at a granular level, T&S offers invaluable insights into current trading activity.
Understanding how T&S works is fundamental for grasping its significance in modern trading strategies. When trades happen rapidly during active market hours, T&S displays these transactions almost instantaneously. This allows market participants to see not just price movements but also the volume and direction behind those movements—whether buying pressure dominates or selling interest prevails.
Why Is Time and Sales Data Important?
The importance of T&S data stems from its ability to reveal real-time market dynamics that are often hidden in traditional price charts or aggregated summaries. By analyzing individual trades as they occur, traders can identify emerging trends before they become apparent through standard technical indicators. For example, an unusual surge in buy orders at specific price levels might signal strong institutional interest or impending breakout opportunities.
Investors also rely on T&S for assessing liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without impacting their prices—and volatility levels within specific stocks or markets. High liquidity typically indicates smoother trading conditions with less risk of sudden price gaps; conversely, low liquidity may suggest caution due to potential slippage.
Market analysts utilize historical T&S data to detect patterns over time that could forecast future movements. These patterns include clusters of large trades indicating institutional activity or irregular spikes signaling possible news events affecting supply and demand balance.
Key Components of Time and Sales Data
To fully appreciate what T&S provides, it’s helpful to understand its core components:
- Timestamp: The precise moment when each trade occurs—down to milliseconds—allowing for detailed chronological analysis.
- Trade Price: The actual execution price for each transaction; tracking these helps identify support/resistance levels.
- Trade Quantity: The number of shares exchanged during each trade; larger quantities often point toward institutional involvement.
- Trade Direction: Whether the transaction was initiated as a buy (aggressive buying) or sell (selling pressure), offering clues about prevailing market sentiment.
These components collectively enable traders to dissect complex market behaviors into actionable insights.
Applications Across Financial Markets
Time and Sales data serve multiple purposes across different types of traders:
- Real-Time Market Monitoring: Day traders use live T&S feeds during intraday sessions to make quick decisions based on immediate supply-demand shifts.
- Historical Trend Analysis: Longer-term investors analyze past T&S records to identify recurring patterns that could influence future investment choices.
- Risk Management: Both short-term traders and portfolio managers leverage this data for assessing risk exposure by understanding how volatile certain stocks are under current conditions.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated systems depend heavily on precise timing information from T&S feeds—they execute trades based on predefined criteria derived from live trade activity.
- Technical Analysis Support: Traders incorporate detailed trade-level data into charting tools like volume profile analysis or order flow indicators for more nuanced decision-making.
Recent Developments Enhancing Usefulness
The landscape surrounding Time and Sales has evolved significantly in recent years due to technological advances:
In cryptocurrency markets—which are characterized by high volatility—platforms such as Binance and Coinbase now provide specialized Trade & Sale feeds similar in function but tailored for digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Artificial Intelligence integration has transformed how traders interpret vast amounts of Trade & Sale data by enabling pattern recognition beyond human capacity—identifying subtle signals indicative of upcoming moves with greater accuracy.
Regulatory considerations have also come into focus recently; authorities aim to ensure transparency while preventing misuse such as market manipulation through overly detailed trade disclosures—a delicate balance requiring ongoing oversight.
Potential Risks Linked With Time & Sales Data
While invaluable, reliance on detailed Trade & Sale information introduces certain risks:
Cybersecurity threats pose significant dangers since breaches could expose sensitive trading activities leading upmarket manipulation attempts.
Excessive transparency might inadvertently facilitate manipulative practices if malicious actors exploit granular details—for instance, spoofing large orders followed by rapid cancellations—to deceive other participants about true supply/demand levels.
Therefore, robust security measures coupled with regulatory safeguards are essential components ensuring that this powerful tool remains beneficial rather than harmful.
The Future Role Of Time And Sales Data In Trading
Looking ahead, several trends indicate an increasing reliance on advanced technologies integrated with Trade & Sale feeds:
Enhanced AI algorithms will continue refining predictive capabilities based on real-time order flow analysis,
Cryptocurrency markets will expand their use cases as digital asset adoption grows,
Regulatory frameworks will evolve alongside technological innovations aiming at maintaining fair markets while safeguarding investor interests,
These developments underscore the critical role that accurate timely Trade & Sale information will play in shaping efficient financial ecosystems.
In summary,
Time And Sales (T& S) stands out as an indispensable resource within modern financial markets — providing granular insight into every executed trade across various asset classes—from equities to cryptocurrencies—and supporting diverse strategies ranging from day-trading tactics through long-term investing approaches.. Its components offer rich detail necessary for understanding immediate supply-demand dynamics while enabling sophisticated analytical techniques.. As technology advances continue pushing boundaries—with AI integration becoming commonplace—the importance placed upon secure handling practices grows ever more vital.. Recognizing both its power benefits along with associated risks ensures stakeholders can harness this tool effectively while maintaining trustworthiness within global financial systems


kai
2025-05-19 03:01
What is Time and Sales (T&S)?
What is Time and Sales (T&S)?
Time and Sales (T&S) is a vital component of financial market data that provides a detailed, real-time record of every trade executed on a stock exchange or trading platform. This data feed captures essential information about each transaction, including the exact timestamp, the price at which the trade occurred, the number of shares traded, and whether it was a buy or sell order. For traders and investors seeking to understand market behavior at a granular level, T&S offers invaluable insights into current trading activity.
Understanding how T&S works is fundamental for grasping its significance in modern trading strategies. When trades happen rapidly during active market hours, T&S displays these transactions almost instantaneously. This allows market participants to see not just price movements but also the volume and direction behind those movements—whether buying pressure dominates or selling interest prevails.
Why Is Time and Sales Data Important?
The importance of T&S data stems from its ability to reveal real-time market dynamics that are often hidden in traditional price charts or aggregated summaries. By analyzing individual trades as they occur, traders can identify emerging trends before they become apparent through standard technical indicators. For example, an unusual surge in buy orders at specific price levels might signal strong institutional interest or impending breakout opportunities.
Investors also rely on T&S for assessing liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without impacting their prices—and volatility levels within specific stocks or markets. High liquidity typically indicates smoother trading conditions with less risk of sudden price gaps; conversely, low liquidity may suggest caution due to potential slippage.
Market analysts utilize historical T&S data to detect patterns over time that could forecast future movements. These patterns include clusters of large trades indicating institutional activity or irregular spikes signaling possible news events affecting supply and demand balance.
Key Components of Time and Sales Data
To fully appreciate what T&S provides, it’s helpful to understand its core components:
- Timestamp: The precise moment when each trade occurs—down to milliseconds—allowing for detailed chronological analysis.
- Trade Price: The actual execution price for each transaction; tracking these helps identify support/resistance levels.
- Trade Quantity: The number of shares exchanged during each trade; larger quantities often point toward institutional involvement.
- Trade Direction: Whether the transaction was initiated as a buy (aggressive buying) or sell (selling pressure), offering clues about prevailing market sentiment.
These components collectively enable traders to dissect complex market behaviors into actionable insights.
Applications Across Financial Markets
Time and Sales data serve multiple purposes across different types of traders:
- Real-Time Market Monitoring: Day traders use live T&S feeds during intraday sessions to make quick decisions based on immediate supply-demand shifts.
- Historical Trend Analysis: Longer-term investors analyze past T&S records to identify recurring patterns that could influence future investment choices.
- Risk Management: Both short-term traders and portfolio managers leverage this data for assessing risk exposure by understanding how volatile certain stocks are under current conditions.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated systems depend heavily on precise timing information from T&S feeds—they execute trades based on predefined criteria derived from live trade activity.
- Technical Analysis Support: Traders incorporate detailed trade-level data into charting tools like volume profile analysis or order flow indicators for more nuanced decision-making.
Recent Developments Enhancing Usefulness
The landscape surrounding Time and Sales has evolved significantly in recent years due to technological advances:
In cryptocurrency markets—which are characterized by high volatility—platforms such as Binance and Coinbase now provide specialized Trade & Sale feeds similar in function but tailored for digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Artificial Intelligence integration has transformed how traders interpret vast amounts of Trade & Sale data by enabling pattern recognition beyond human capacity—identifying subtle signals indicative of upcoming moves with greater accuracy.
Regulatory considerations have also come into focus recently; authorities aim to ensure transparency while preventing misuse such as market manipulation through overly detailed trade disclosures—a delicate balance requiring ongoing oversight.
Potential Risks Linked With Time & Sales Data
While invaluable, reliance on detailed Trade & Sale information introduces certain risks:
Cybersecurity threats pose significant dangers since breaches could expose sensitive trading activities leading upmarket manipulation attempts.
Excessive transparency might inadvertently facilitate manipulative practices if malicious actors exploit granular details—for instance, spoofing large orders followed by rapid cancellations—to deceive other participants about true supply/demand levels.
Therefore, robust security measures coupled with regulatory safeguards are essential components ensuring that this powerful tool remains beneficial rather than harmful.
The Future Role Of Time And Sales Data In Trading
Looking ahead, several trends indicate an increasing reliance on advanced technologies integrated with Trade & Sale feeds:
Enhanced AI algorithms will continue refining predictive capabilities based on real-time order flow analysis,
Cryptocurrency markets will expand their use cases as digital asset adoption grows,
Regulatory frameworks will evolve alongside technological innovations aiming at maintaining fair markets while safeguarding investor interests,
These developments underscore the critical role that accurate timely Trade & Sale information will play in shaping efficient financial ecosystems.
In summary,
Time And Sales (T& S) stands out as an indispensable resource within modern financial markets — providing granular insight into every executed trade across various asset classes—from equities to cryptocurrencies—and supporting diverse strategies ranging from day-trading tactics through long-term investing approaches.. Its components offer rich detail necessary for understanding immediate supply-demand dynamics while enabling sophisticated analytical techniques.. As technology advances continue pushing boundaries—with AI integration becoming commonplace—the importance placed upon secure handling practices grows ever more vital.. Recognizing both its power benefits along with associated risks ensures stakeholders can harness this tool effectively while maintaining trustworthiness within global financial systems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Blockchain Oracle Network and How Is Decentralization Ensured?
Understanding Blockchain Oracle Networks
A blockchain oracle network is an essential component in the ecosystem of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It functions as a bridge that connects on-chain smart contracts with off-chain data sources, enabling these contracts to interact with real-world information. Unlike traditional systems that rely solely on internal blockchain data, oracle networks fetch external data such as market prices, weather conditions, or event outcomes. This external data is critical for executing complex logic within smart contracts—automated agreements that self-execute when predefined conditions are met.
Smart contracts are inherently limited because they cannot access information outside their blockchain environment. For example, a decentralized insurance contract might need to verify weather reports or flight delays before releasing funds. Without reliable external data feeds, such applications would be severely constrained. That’s where blockchain oracle networks come into play—they provide the necessary real-world inputs securely and efficiently.
The Role of External Data in Smart Contracts
Smart contracts operate based on code stored on blockchains like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. They execute automatically once certain criteria are fulfilled but depend heavily on accurate and timely data inputs to function correctly. Since blockchains do not have native access to off-chain information due to their closed nature, they require an intermediary—an oracle—to supply this data.
Oracle networks gather information from multiple sources such as APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), databases, sensors (for IoT devices), or even human input in some cases. Once collected, this data undergoes verification processes before being transmitted onto the blockchain for use by smart contracts. This process ensures that decisions made by these digital agreements reflect real-world conditions accurately.
Decentralization: Why It Matters for Oracles
Decentralization is fundamental when it comes to maintaining trustworthiness and security within oracle networks. A centralized oracle relies on a single source of truth; if this source becomes compromised or provides false information—either intentionally or accidentally—the entire system's integrity could be at risk.
To mitigate such vulnerabilities, decentralized oracle networks employ multiple independent nodes that verify and validate external data collectively before feeding it into the blockchain see more about decentralization here. This approach reduces reliance on any single point of failure and enhances resilience against manipulation attempts.
By distributing trust across numerous nodes operating under consensus mechanisms—such as voting schemes or cryptographic proofs—the network ensures higher security standards while preserving transparency learn about security measures here.
Types of Blockchain Oracles
There are several types of oracle architectures designed to suit different needs:
Centralized Oracles: These depend on one trusted entity providing all external data points; they tend to be faster but less secure due to single points of failure.
Decentralized Oracles: Utilize multiple independent nodes verifying the same piece of information; they offer enhanced security through redundancy.
Hybrid Oracles: Combine elements from both models—for instance, using centralized sources for speed but adding decentralization layers for validation—to balance efficiency with trustworthiness.
Each type has its advantages and trade-offs concerning speed, cost, complexity, and security considerations see detailed comparison here.
Recent Advances in Blockchain Oracle Technology
The rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has significantly increased demand for robust oracle solutions capable of delivering high-quality off-chain data securely explore DeFi's impact here. Prominent projects like Chainlink have pioneered decentralized oracle platforms offering extensive libraries of verified datasets—including asset prices—which DeFi protocols rely upon heavily.
Innovations also include cross-chain interoperability solutions where multiple blockchains share verified external datasets via interconnected oracles—a step toward more interconnected decentralized ecosystems more about Chainlink’s role here.
However, reliance on these systems introduces risks like potential manipulation if not properly secured—a concern addressed through cryptographic techniques such as multi-signature schemes and reputation-based node selection processes see how security is maintained.
Risks Associated with Oracle Networks
Despite their importance in expanding what smart contracts can achieve beyond simple transactions within a single chain context—and increasing automation capabilities—they pose unique challenges:
- Data Manipulation & Spoofing: Malicious actors may attempt to feed false info into the system.
- Single Point Failures: Centralized models risk collapse if their sole source becomes compromised.
- Oracle Failure & Latency: Delays in fetching accurate info can lead to incorrect contract execution.
- Economic Attacks: Exploiting economic incentives around certain datasets may influence node behavior unfairly.
Addressing these issues involves implementing rigorous verification methods—including cryptography-based proofs—and designing incentive structures aligned with honest participation more details available here.
Future Outlook for Blockchain Oracle Networks
As blockchain technology matures alongside growing adoption across industries—from finance and supply chain management to gaming—the importance of reliable decentralization will only increase[see industry trends]. Ongoing research aims at enhancing scalability without compromising security through innovations like threshold signatures or zero-knowledge proofs which enable secure validation without revealing sensitive info publicly[read more about emerging tech].
Furthermore, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) could improve anomaly detection within feeds—making them even more trustworthy—and facilitate dynamic updates based on changing circumstances globally[future prospects].
Ensuring robust decentralization remains central—not just from technical perspectives but also through governance frameworks—that empower community oversight over node operations helps sustain long-term trustworthiness across diverse applications.
By understanding how blockchain oracle networks work—and why decentralizing them matters—you gain insight into one key pillar supporting modern decentralized ecosystems’ growth while safeguarding against vulnerabilities inherent in relying solely on centralized sources.Learn more about securing your systems here. As innovation continues apace—with new protocols emerging—it’s clear that resiliently designed—oracular infrastructure will remain vital for realizing fully autonomous digital economies built upon trustworthy foundations.


Lo
2025-05-14 11:29
What is a blockchain oracle network and how is decentralization ensured?
What Is a Blockchain Oracle Network and How Is Decentralization Ensured?
Understanding Blockchain Oracle Networks
A blockchain oracle network is an essential component in the ecosystem of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It functions as a bridge that connects on-chain smart contracts with off-chain data sources, enabling these contracts to interact with real-world information. Unlike traditional systems that rely solely on internal blockchain data, oracle networks fetch external data such as market prices, weather conditions, or event outcomes. This external data is critical for executing complex logic within smart contracts—automated agreements that self-execute when predefined conditions are met.
Smart contracts are inherently limited because they cannot access information outside their blockchain environment. For example, a decentralized insurance contract might need to verify weather reports or flight delays before releasing funds. Without reliable external data feeds, such applications would be severely constrained. That’s where blockchain oracle networks come into play—they provide the necessary real-world inputs securely and efficiently.
The Role of External Data in Smart Contracts
Smart contracts operate based on code stored on blockchains like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. They execute automatically once certain criteria are fulfilled but depend heavily on accurate and timely data inputs to function correctly. Since blockchains do not have native access to off-chain information due to their closed nature, they require an intermediary—an oracle—to supply this data.
Oracle networks gather information from multiple sources such as APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), databases, sensors (for IoT devices), or even human input in some cases. Once collected, this data undergoes verification processes before being transmitted onto the blockchain for use by smart contracts. This process ensures that decisions made by these digital agreements reflect real-world conditions accurately.
Decentralization: Why It Matters for Oracles
Decentralization is fundamental when it comes to maintaining trustworthiness and security within oracle networks. A centralized oracle relies on a single source of truth; if this source becomes compromised or provides false information—either intentionally or accidentally—the entire system's integrity could be at risk.
To mitigate such vulnerabilities, decentralized oracle networks employ multiple independent nodes that verify and validate external data collectively before feeding it into the blockchain see more about decentralization here. This approach reduces reliance on any single point of failure and enhances resilience against manipulation attempts.
By distributing trust across numerous nodes operating under consensus mechanisms—such as voting schemes or cryptographic proofs—the network ensures higher security standards while preserving transparency learn about security measures here.
Types of Blockchain Oracles
There are several types of oracle architectures designed to suit different needs:
Centralized Oracles: These depend on one trusted entity providing all external data points; they tend to be faster but less secure due to single points of failure.
Decentralized Oracles: Utilize multiple independent nodes verifying the same piece of information; they offer enhanced security through redundancy.
Hybrid Oracles: Combine elements from both models—for instance, using centralized sources for speed but adding decentralization layers for validation—to balance efficiency with trustworthiness.
Each type has its advantages and trade-offs concerning speed, cost, complexity, and security considerations see detailed comparison here.
Recent Advances in Blockchain Oracle Technology
The rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has significantly increased demand for robust oracle solutions capable of delivering high-quality off-chain data securely explore DeFi's impact here. Prominent projects like Chainlink have pioneered decentralized oracle platforms offering extensive libraries of verified datasets—including asset prices—which DeFi protocols rely upon heavily.
Innovations also include cross-chain interoperability solutions where multiple blockchains share verified external datasets via interconnected oracles—a step toward more interconnected decentralized ecosystems more about Chainlink’s role here.
However, reliance on these systems introduces risks like potential manipulation if not properly secured—a concern addressed through cryptographic techniques such as multi-signature schemes and reputation-based node selection processes see how security is maintained.
Risks Associated with Oracle Networks
Despite their importance in expanding what smart contracts can achieve beyond simple transactions within a single chain context—and increasing automation capabilities—they pose unique challenges:
- Data Manipulation & Spoofing: Malicious actors may attempt to feed false info into the system.
- Single Point Failures: Centralized models risk collapse if their sole source becomes compromised.
- Oracle Failure & Latency: Delays in fetching accurate info can lead to incorrect contract execution.
- Economic Attacks: Exploiting economic incentives around certain datasets may influence node behavior unfairly.
Addressing these issues involves implementing rigorous verification methods—including cryptography-based proofs—and designing incentive structures aligned with honest participation more details available here.
Future Outlook for Blockchain Oracle Networks
As blockchain technology matures alongside growing adoption across industries—from finance and supply chain management to gaming—the importance of reliable decentralization will only increase[see industry trends]. Ongoing research aims at enhancing scalability without compromising security through innovations like threshold signatures or zero-knowledge proofs which enable secure validation without revealing sensitive info publicly[read more about emerging tech].
Furthermore, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) could improve anomaly detection within feeds—making them even more trustworthy—and facilitate dynamic updates based on changing circumstances globally[future prospects].
Ensuring robust decentralization remains central—not just from technical perspectives but also through governance frameworks—that empower community oversight over node operations helps sustain long-term trustworthiness across diverse applications.
By understanding how blockchain oracle networks work—and why decentralizing them matters—you gain insight into one key pillar supporting modern decentralized ecosystems’ growth while safeguarding against vulnerabilities inherent in relying solely on centralized sources.Learn more about securing your systems here. As innovation continues apace—with new protocols emerging—it’s clear that resiliently designed—oracular infrastructure will remain vital for realizing fully autonomous digital economies built upon trustworthy foundations.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Future of Solana in Blockchain and DeFi?
Solana has rapidly emerged as a leading blockchain platform, capturing attention with its high throughput, low latency, and innovative consensus mechanism. As the landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to evolve, many investors and developers are asking: what does the future hold for Solana? This article explores Solana’s current position, recent developments, challenges, and potential trajectory within the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Understanding Solana’s Technology and Ecosystem
Launched in 2017 by Anatoly Yakovenko along with Greg Fitzgerald and Stephen Akridge, Solana was designed to address common scalability issues faced by earlier blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Its core innovation is the Proof of History (PoH) consensus algorithm—a unique timestamping method that enables faster transaction processing without compromising security.
This architecture allows Solana to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), making it highly suitable for applications requiring high throughput such as DeFi protocols, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), gaming platforms, and enterprise solutions. Its ability to scale efficiently positions it as a formidable competitor in an increasingly crowded market dominated by Ethereum but challenged by newer entrants like Binance Smart Chain or Polkadot.
The platform's robust ecosystem includes a variety of decentralized applications—ranging from lending protocols to stablecoins—and has attracted significant institutional interest. Notably, major players have invested millions into projects built on or related to Solana—highlighting confidence in its long-term potential.
Recent Price Movements Indicate Growing Adoption
As of May 2025, Solana’s native token SOL experienced a notable surge past $150 amid heightened trading activity. This price rally reflects increased investor confidence driven by several factors:
- Institutional Investment: The launch of financial products such as the SOLZ ETF has garnered attention from institutional investors. Bloomberg predicts high approval rates for these ETFs amid favorable regulatory trends.
- Ecosystem Expansion: New projects launching on Solana—including DeFi platforms offering yield farming or lending services—have contributed to demand.
- Market Sentiment: Broader bullish trends across cryptocurrencies have also played a role in boosting SOL prices temporarily.
However, analysts warn that this rally could be susceptible to short-term volatility due to macroeconomic factors affecting global markets or shifts within crypto sentiment itself.
Regulatory Environment: Opportunities & Risks
The evolving regulatory landscape remains one of the most critical factors influencing Solana's future prospects. While clarity around cryptocurrency regulations can foster investor confidence—and potentially lead to mainstream adoption—any adverse policy changes could hinder growth prospects significantly.
In 2025 alone, regulators worldwide are scrutinizing digital assets more closely; some countries have introduced stricter compliance requirements while others explore central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). For platforms like Solana that host numerous dApps—including those involved with DeFi—the risk lies in potential restrictions on certain activities such as yield farming or token issuance.
Nevertheless, proactive engagement with regulators coupled with transparent compliance strategies can help mitigate these risks over time.
Institutional Interest Signaling Long-Term Confidence
One notable development is Neptune Digital Assets Corp.'s increased holdings in Bitcoin alongside investments in Solana-based projects. Such moves suggest growing institutional recognition that blockchain ecosystems like Solana may offer sustainable growth opportunities beyond retail speculation alone.
Institutional backing often translates into greater liquidity support and credibility for blockchain networks—factors crucial for long-term success especially when competing against well-established chains like Ethereum which benefits from extensive developer communities but faces scalability issues itself.
Furthermore, large-scale investments tend to attract more developers seeking reliable infrastructure for their decentralized applications—a positive feedback loop reinforcing network effects over time.
Challenges Facing Future Growth
Despite promising signs ahead; several hurdles could impact how farSolano can go:
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are inherently volatile; sharp corrections can affect investor sentiment regardless of underlying technology.
Competition: Platforms such as Ethereum 2.0 upgrade efforts aim at improving scalability but still face congestion issues; Binance Smart Chain offers lower fees but less decentralization; Polkadot emphasizes interoperability—all vying for market share.
Security Concerns: As more complex dApps emerge on solanA’s network—including meme coins like $TRUMP launched early 2025—the risk profile increases regarding smart contract vulnerabilities or malicious attacks.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing technological innovation combined with strategic community engagement and regulatory compliance efforts.
The Road Ahead: Will Solarna Maintain Its Momentum?
Looking forward into 2025+ , several key factors will influence whether solanA sustains its current momentum:
- Continued Ecosystem Development: Expanding partnerships with enterprises and onboarding new developers will be vital.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Navigating evolving legal frameworks effectively can prevent setbacks caused by policy shifts.
- Technological Innovation: Upgrades enhancing security features while maintaining speed will reinforce trust among users.
- Market Conditions: Broader economic stability may reduce volatility-driven sell-offs enabling steady growth trajectories.
While no project is immune from risks inherent within crypto markets; solanA's innovative architecture combined with increasing institutional interest suggests it could remain at the forefront among scalable Layer 1 blockchains if it manages these dynamics well.
Final Thoughts
Solano stands out today not just because of its impressive technical capabilities but also due to growing adoption across sectors—from DeFi protocols through NFTs—to enterprise use cases . Its ability to adapt amidst competition hinges on continuous innovation paired with strategic regulation navigation .
As we move further into this decade marked by rapid technological change , solanA's future appears promising—but cautious optimism remains prudent given inherent market uncertainties . Stakeholders should monitor ongoing developments closely while leveraging its strengths toward building resilient decentralized ecosystems.
Note: This overview aims at providing an informed perspective based on current data up until October 2023 plus recent developments noted through early 2025 — always consider ongoing updates when evaluating long-term prospects


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-09 03:47
what is the future of Solana ?
What Is the Future of Solana in Blockchain and DeFi?
Solana has rapidly emerged as a leading blockchain platform, capturing attention with its high throughput, low latency, and innovative consensus mechanism. As the landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to evolve, many investors and developers are asking: what does the future hold for Solana? This article explores Solana’s current position, recent developments, challenges, and potential trajectory within the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Understanding Solana’s Technology and Ecosystem
Launched in 2017 by Anatoly Yakovenko along with Greg Fitzgerald and Stephen Akridge, Solana was designed to address common scalability issues faced by earlier blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Its core innovation is the Proof of History (PoH) consensus algorithm—a unique timestamping method that enables faster transaction processing without compromising security.
This architecture allows Solana to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), making it highly suitable for applications requiring high throughput such as DeFi protocols, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), gaming platforms, and enterprise solutions. Its ability to scale efficiently positions it as a formidable competitor in an increasingly crowded market dominated by Ethereum but challenged by newer entrants like Binance Smart Chain or Polkadot.
The platform's robust ecosystem includes a variety of decentralized applications—ranging from lending protocols to stablecoins—and has attracted significant institutional interest. Notably, major players have invested millions into projects built on or related to Solana—highlighting confidence in its long-term potential.
Recent Price Movements Indicate Growing Adoption
As of May 2025, Solana’s native token SOL experienced a notable surge past $150 amid heightened trading activity. This price rally reflects increased investor confidence driven by several factors:
- Institutional Investment: The launch of financial products such as the SOLZ ETF has garnered attention from institutional investors. Bloomberg predicts high approval rates for these ETFs amid favorable regulatory trends.
- Ecosystem Expansion: New projects launching on Solana—including DeFi platforms offering yield farming or lending services—have contributed to demand.
- Market Sentiment: Broader bullish trends across cryptocurrencies have also played a role in boosting SOL prices temporarily.
However, analysts warn that this rally could be susceptible to short-term volatility due to macroeconomic factors affecting global markets or shifts within crypto sentiment itself.
Regulatory Environment: Opportunities & Risks
The evolving regulatory landscape remains one of the most critical factors influencing Solana's future prospects. While clarity around cryptocurrency regulations can foster investor confidence—and potentially lead to mainstream adoption—any adverse policy changes could hinder growth prospects significantly.
In 2025 alone, regulators worldwide are scrutinizing digital assets more closely; some countries have introduced stricter compliance requirements while others explore central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). For platforms like Solana that host numerous dApps—including those involved with DeFi—the risk lies in potential restrictions on certain activities such as yield farming or token issuance.
Nevertheless, proactive engagement with regulators coupled with transparent compliance strategies can help mitigate these risks over time.
Institutional Interest Signaling Long-Term Confidence
One notable development is Neptune Digital Assets Corp.'s increased holdings in Bitcoin alongside investments in Solana-based projects. Such moves suggest growing institutional recognition that blockchain ecosystems like Solana may offer sustainable growth opportunities beyond retail speculation alone.
Institutional backing often translates into greater liquidity support and credibility for blockchain networks—factors crucial for long-term success especially when competing against well-established chains like Ethereum which benefits from extensive developer communities but faces scalability issues itself.
Furthermore, large-scale investments tend to attract more developers seeking reliable infrastructure for their decentralized applications—a positive feedback loop reinforcing network effects over time.
Challenges Facing Future Growth
Despite promising signs ahead; several hurdles could impact how farSolano can go:
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are inherently volatile; sharp corrections can affect investor sentiment regardless of underlying technology.
Competition: Platforms such as Ethereum 2.0 upgrade efforts aim at improving scalability but still face congestion issues; Binance Smart Chain offers lower fees but less decentralization; Polkadot emphasizes interoperability—all vying for market share.
Security Concerns: As more complex dApps emerge on solanA’s network—including meme coins like $TRUMP launched early 2025—the risk profile increases regarding smart contract vulnerabilities or malicious attacks.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing technological innovation combined with strategic community engagement and regulatory compliance efforts.
The Road Ahead: Will Solarna Maintain Its Momentum?
Looking forward into 2025+ , several key factors will influence whether solanA sustains its current momentum:
- Continued Ecosystem Development: Expanding partnerships with enterprises and onboarding new developers will be vital.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Navigating evolving legal frameworks effectively can prevent setbacks caused by policy shifts.
- Technological Innovation: Upgrades enhancing security features while maintaining speed will reinforce trust among users.
- Market Conditions: Broader economic stability may reduce volatility-driven sell-offs enabling steady growth trajectories.
While no project is immune from risks inherent within crypto markets; solanA's innovative architecture combined with increasing institutional interest suggests it could remain at the forefront among scalable Layer 1 blockchains if it manages these dynamics well.
Final Thoughts
Solano stands out today not just because of its impressive technical capabilities but also due to growing adoption across sectors—from DeFi protocols through NFTs—to enterprise use cases . Its ability to adapt amidst competition hinges on continuous innovation paired with strategic regulation navigation .
As we move further into this decade marked by rapid technological change , solanA's future appears promising—but cautious optimism remains prudent given inherent market uncertainties . Stakeholders should monitor ongoing developments closely while leveraging its strengths toward building resilient decentralized ecosystems.
Note: This overview aims at providing an informed perspective based on current data up until October 2023 plus recent developments noted through early 2025 — always consider ongoing updates when evaluating long-term prospects
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 August 5 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
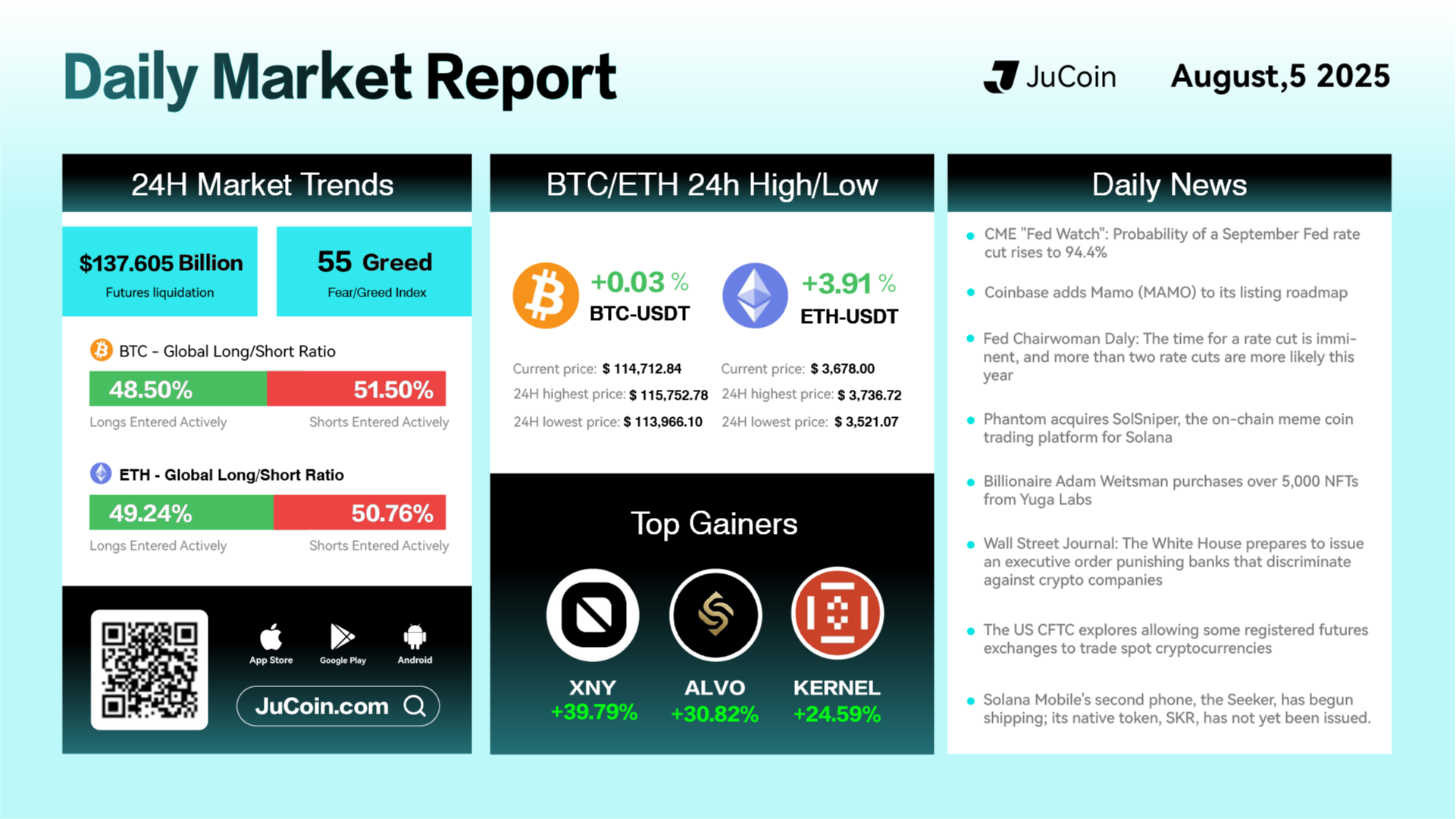


JuCoin Community
2025-08-05 04:32
🚀 #JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
BTC with his tank, ETH guy chilling, and gold-suit investor pretending all’s fine 😬 Same train, same goal — protect the bag 💼 Different look, same fear
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BitcoinVsGold #AssetProtection #CryptoContrast


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:30
Spot the difference: Bitcoin vs Gold holders 🛤️
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bridgewater Associates founder Ray Dalio has dramatically increased his Bitcoin allocation recommendation from 2% to 15%, citing escalating US debt risks that could trigger currency devaluation similar to historical collapses in the 1930s and 1970s.
💰 The Debt Crisis Reality:
-
US government spends $7 trillion annually vs. $5 trillion revenue = $2 trillion deficit
Federal debt now 6x annual revenue with $1 trillion yearly interest payments
Faces "debt doom loop": can only service debt by printing money or issuing more debt
Risk of currency collapse similar to British pound's mid-20th century decline
🎯 Why Bitcoin + Gold at 15%: 1️⃣ Bitcoin's 21 million coin cap provides protection against monetary debasement 2️⃣ Optimal risk-return strategy for portfolios "neutral on everything" 3️⃣ Diversified hedge against fiat currency devaluation risks 4️⃣ Combined allocation offers complementary protection strategies
⚡ Bitcoin's Strategic Advantages:
-
Limited supply creates scarcity premium
Efficient transactions and decentralized network
Lower correlation with traditional fiat currencies
Digital store of value with growing institutional adoption
⚠️ Dalio's Key Concerns:
-
Government surveillance capabilities due to blockchain transparency
Potential regulatory controls and technology vulnerabilities
Central banks unlikely to adopt Bitcoin as reserve currency
"Bitcoin's biggest risk is being successful" - regulatory backlash
🏆 Implementation Strategy:
-
Use dollar-cost averaging instead of lump-sum purchases
Conservative investors: favor gold over Bitcoin
Risk-tolerant investors: emphasize Bitcoin allocation
Adjust ratios based on individual risk tolerance and outlook
📈 Market Impact:
-
Bitcoin trading around $119,000 with institutional interest growing
Major exchanges report increased institutional activity
Strategy reflects broader institutional shift toward alternative assets
Focus on macroeconomic hedging rather than crypto speculation
💡 Key Insight: This represents Dalio's evolution from crypto skeptic to strategic advocate, driven by unprecedented US fiscal risks. The 15% allocation framework acknowledges growing need for alternatives to traditional fiat-based investments.
Read the complete analysis with detailed implementation strategies and risk assessment: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/ray-dalio-bitcoin-portfolio-allocation/?utm_source=blog
#RayDalio #Bitcoin #PortfolioAllocation #DebtCrisis #Bridgewater #Cryptocurrency #InvestmentStrategy #RiskHedge #CurrencyDevaluation #WealthPreservation #JuCoin #Blockchain #DigitalAssets #InstitutionalInvestment #MacroEconomics



JU Blog
2025-08-01 08:51
🚀 Ray Dalio Dramatically Boosts Bitcoin Allocation to 15% Amid US Debt Crisis!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
