Popular Posts
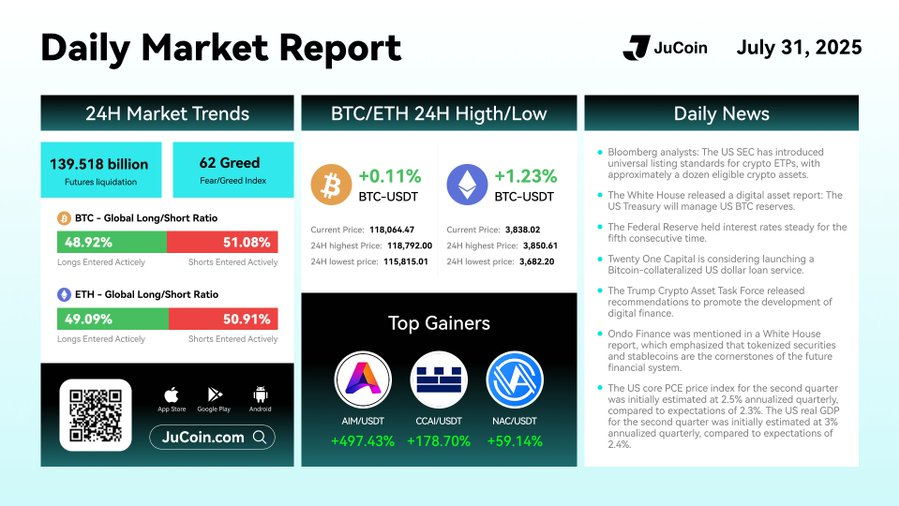
🚀 JuCoin Daily Market Report|July 31, 2025
📅 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
Sign up👉 http://bit.ly/3BVxlZ2
Blog👉 https://blog.jucoin.com/btc-eth-us-treasury-btc-reserves-july31-2025/
#JuCoin #CryptoNews


JuCoin Official
2025-07-31 09:10
🚀 JuCoin Daily Market Report|July 31, 2025
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Are There Specific Tools for Trading Credit Spreads?
Trading credit spreads requires a combination of analytical tools, market data, and trading platforms to effectively assess risk and identify profitable opportunities. These tools help traders interpret market signals, compare bond yields, and execute trades with confidence. Understanding the available resources is essential for both novice and experienced traders aiming to navigate the complexities of credit spread trading.
Key Market Indices and Benchmarks
One of the foundational tools in credit spreads trading is the use of indices that serve as benchmarks for assessing market performance. The Barclays Capital U.S. Corporate High Yield Index tracks the performance of high-yield bonds (junk bonds), while the Barclays Capital U.S. Credit Index measures investment-grade corporate bonds. These indices provide a broad view of how different segments are performing relative to each other, enabling traders to gauge whether credit spreads are widening or narrowing in response to economic conditions.
By comparing current bond yields against these benchmarks, traders can identify potential entry or exit points based on perceived over- or under-valued spreads. For example, an unusually wide spread might signal increased default risk or market stress, presenting a buying opportunity if fundamentals support it.
Bond Yield Curves as Analytical Tools
Yield curves are vital for visualizing how bond yields vary across different maturities within similar credit categories. They illustrate expectations about future interest rates and inflation trends—factors that influence credit spreads significantly.
A normal upward-sloping yield curve suggests healthy economic growth with manageable risk premiums; conversely, an inverted curve may indicate recession fears and wider spreads on risky assets like high-yield bonds. Traders analyze shifts in these curves over time to anticipate changes in credit risk sentiment before they fully materialize in spread movements.
Role of Credit Rating Agencies
Credit rating agencies such as Moody’s, S&P Global Ratings, and Fitch Ratings play a crucial role by providing independent assessments of issuer creditworthiness. Their ratings influence investor perceptions—and consequently—yield differences between various bonds.
When an agency downgrades a company's rating from investment grade to junk status—or vice versa—the associated bond's yield typically adjusts accordingly due to changing perceived risks. Traders monitor these ratings closely since sudden downgrades can cause rapid widening in credit spreads; thus making them key indicators when planning trades.
Financial News Platforms & Market Data Providers
Real-time information is indispensable when trading credit spreads because markets can shift quickly amid macroeconomic news or geopolitical events. Platforms like Bloomberg Terminal and Reuters Eikon offer comprehensive data feeds—including live bond prices, yield movements, news alerts—and analytical tools tailored specifically for fixed-income markets.
These platforms also provide access to historical data trends which help traders analyze patterns over time—crucial for developing effective strategies around spread movements during volatile periods or economic cycles.
Advanced Trading Software & Platforms
Modern trading software enhances decision-making by integrating multiple data sources into user-friendly interfaces that facilitate trade execution directly from analysis screens:
- Bloomberg Terminal: Offers extensive analytics on bond markets alongside customizable dashboards.
- Reuters Eikon: Provides real-time quotes combined with news updates relevant for fixed-income securities.
- Proprietary Trading Platforms: Many financial institutions develop their own systems optimized for specific strategies such as pair trades involving different segments within the debt market.
These platforms often include features like scenario analysis (stress testing), automated alerts based on preset criteria (e.g., spread thresholds), and order execution capabilities—all critical components when managing complex options around credit spread fluctuations efficiently.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Credit Spread Trading
Recent technological advancements have further empowered traders through machine learning algorithms capable of analyzing vast datasets faster than traditional methods—identifying subtle patterns indicating potential shifts in spread dynamics before they become apparent publicly.
Artificial intelligence-driven models now assist with predictive analytics regarding default probabilities or macroeconomic impacts influencing sector-specific risks—a significant advantage given how swiftly sentiment can change during periods of heightened volatility such as during global crises or regulatory shifts.
Summary: Essential Tools Every Trader Should Know
To succeed at trading credit spreads effectively:
- Use benchmark indices like Barclays High Yield Index & Investment Grade Index
- Analyze yield curves regularly
- Monitor updates from reputable rating agencies
- Leverage real-time financial news platforms
- Utilize advanced software solutions tailored for fixed-income analysis
- Keep abreast with emerging AI-driven analytics technologies
Combining these resources allows traders not only to interpret current market conditions but also anticipate future movements—an essential skill given how sensitive this segment is to macroeconomic factors ranging from central bank policies to geopolitical tensions.
Final Thoughts on Building Expertise in Credit Spread Trading Tools
Developing proficiency with these tools enhances your ability to make informed decisions rooted in sound analysis rather than speculation alone. As markets evolve—with increasing automation and sophisticated data modeling—the importance lies not just in having access but understanding how best leverage each resource within your overall strategy framework.
By integrating index benchmarks, yield curve insights, ratings assessments, real-time news feeds—and embracing innovative tech solutions—you position yourself better equipped against unpredictable swings inherent within fixed-income markets’ complex landscape.
Stay informed. Stay prepared. Trade smarter.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-06-09 22:35
Are there specific tools for trading credit spreads?
Are There Specific Tools for Trading Credit Spreads?
Trading credit spreads requires a combination of analytical tools, market data, and trading platforms to effectively assess risk and identify profitable opportunities. These tools help traders interpret market signals, compare bond yields, and execute trades with confidence. Understanding the available resources is essential for both novice and experienced traders aiming to navigate the complexities of credit spread trading.
Key Market Indices and Benchmarks
One of the foundational tools in credit spreads trading is the use of indices that serve as benchmarks for assessing market performance. The Barclays Capital U.S. Corporate High Yield Index tracks the performance of high-yield bonds (junk bonds), while the Barclays Capital U.S. Credit Index measures investment-grade corporate bonds. These indices provide a broad view of how different segments are performing relative to each other, enabling traders to gauge whether credit spreads are widening or narrowing in response to economic conditions.
By comparing current bond yields against these benchmarks, traders can identify potential entry or exit points based on perceived over- or under-valued spreads. For example, an unusually wide spread might signal increased default risk or market stress, presenting a buying opportunity if fundamentals support it.
Bond Yield Curves as Analytical Tools
Yield curves are vital for visualizing how bond yields vary across different maturities within similar credit categories. They illustrate expectations about future interest rates and inflation trends—factors that influence credit spreads significantly.
A normal upward-sloping yield curve suggests healthy economic growth with manageable risk premiums; conversely, an inverted curve may indicate recession fears and wider spreads on risky assets like high-yield bonds. Traders analyze shifts in these curves over time to anticipate changes in credit risk sentiment before they fully materialize in spread movements.
Role of Credit Rating Agencies
Credit rating agencies such as Moody’s, S&P Global Ratings, and Fitch Ratings play a crucial role by providing independent assessments of issuer creditworthiness. Their ratings influence investor perceptions—and consequently—yield differences between various bonds.
When an agency downgrades a company's rating from investment grade to junk status—or vice versa—the associated bond's yield typically adjusts accordingly due to changing perceived risks. Traders monitor these ratings closely since sudden downgrades can cause rapid widening in credit spreads; thus making them key indicators when planning trades.
Financial News Platforms & Market Data Providers
Real-time information is indispensable when trading credit spreads because markets can shift quickly amid macroeconomic news or geopolitical events. Platforms like Bloomberg Terminal and Reuters Eikon offer comprehensive data feeds—including live bond prices, yield movements, news alerts—and analytical tools tailored specifically for fixed-income markets.
These platforms also provide access to historical data trends which help traders analyze patterns over time—crucial for developing effective strategies around spread movements during volatile periods or economic cycles.
Advanced Trading Software & Platforms
Modern trading software enhances decision-making by integrating multiple data sources into user-friendly interfaces that facilitate trade execution directly from analysis screens:
- Bloomberg Terminal: Offers extensive analytics on bond markets alongside customizable dashboards.
- Reuters Eikon: Provides real-time quotes combined with news updates relevant for fixed-income securities.
- Proprietary Trading Platforms: Many financial institutions develop their own systems optimized for specific strategies such as pair trades involving different segments within the debt market.
These platforms often include features like scenario analysis (stress testing), automated alerts based on preset criteria (e.g., spread thresholds), and order execution capabilities—all critical components when managing complex options around credit spread fluctuations efficiently.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Credit Spread Trading
Recent technological advancements have further empowered traders through machine learning algorithms capable of analyzing vast datasets faster than traditional methods—identifying subtle patterns indicating potential shifts in spread dynamics before they become apparent publicly.
Artificial intelligence-driven models now assist with predictive analytics regarding default probabilities or macroeconomic impacts influencing sector-specific risks—a significant advantage given how swiftly sentiment can change during periods of heightened volatility such as during global crises or regulatory shifts.
Summary: Essential Tools Every Trader Should Know
To succeed at trading credit spreads effectively:
- Use benchmark indices like Barclays High Yield Index & Investment Grade Index
- Analyze yield curves regularly
- Monitor updates from reputable rating agencies
- Leverage real-time financial news platforms
- Utilize advanced software solutions tailored for fixed-income analysis
- Keep abreast with emerging AI-driven analytics technologies
Combining these resources allows traders not only to interpret current market conditions but also anticipate future movements—an essential skill given how sensitive this segment is to macroeconomic factors ranging from central bank policies to geopolitical tensions.
Final Thoughts on Building Expertise in Credit Spread Trading Tools
Developing proficiency with these tools enhances your ability to make informed decisions rooted in sound analysis rather than speculation alone. As markets evolve—with increasing automation and sophisticated data modeling—the importance lies not just in having access but understanding how best leverage each resource within your overall strategy framework.
By integrating index benchmarks, yield curve insights, ratings assessments, real-time news feeds—and embracing innovative tech solutions—you position yourself better equipped against unpredictable swings inherent within fixed-income markets’ complex landscape.
Stay informed. Stay prepared. Trade smarter.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are the Risks Associated with USDC?
Understanding the risks linked to USD Coin (USDC) is essential for investors, traders, and users of stablecoins. While USDC is designed to offer stability by pegging its value to the US dollar, it is not immune to various vulnerabilities that could impact its reliability and trustworthiness. This article explores these risks in detail, providing a comprehensive overview based on recent developments and industry insights.
Market Volatility and Depegging Risks
Although USDC aims to maintain a 1:1 peg with the US dollar, market volatility can still pose significant threats. Stablecoins rely heavily on their reserves and mechanisms for maintaining price stability. If confidence in the peg diminishes—due to economic shocks or systemic issues—USDC could experience a depegging event where its value drops below or rises above $1.
Such events can be triggered by liquidity crises, sudden market sell-offs, or loss of trust among users. A depegging not only affects individual investors but can also have ripple effects across the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem by undermining confidence in stablecoins as a whole.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Legal Risks
Regulatory environments around stablecoins like USDC are evolving rapidly. Governments worldwide are scrutinizing these digital assets more closely due to concerns over money laundering, fraud prevention, consumer protection, and financial stability. Increased regulation could lead to stricter compliance requirements such as enhanced KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures or reserve transparency mandates.
While regulation aims to improve legitimacy and reduce illicit activities associated with cryptocurrencies, it also introduces operational challenges for issuers like Circle and Coinbase—the entities behind USDC. Regulatory actions might restrict certain uses of stablecoins or impose limits that affect their liquidity pools or issuance processes.
Liquidity Challenges
The core strength of any stablecoin lies in its ability to quickly convert between fiat currency and digital tokens without significant price slippage. However, if there is a sudden surge in demand or an unexpected withdrawal from reserves—perhaps during market stress—it could strain liquidity pools backing USDC.
A lack of sufficient fiat reserves would threaten its peg stability; this risk underscores why transparent reserve management practices are critical for maintaining user trust. Any doubts about reserve adequacy can lead users to withdraw en masse—a classic bank run scenario—that may result in depegging.
Operational Failures
Technical glitches or operational failures represent another layer of risk for stablecoins like USDC. These issues might include smart contract bugs, security breaches targeting custodial wallets holding reserves, or infrastructure outages disrupting transaction processing.
Such failures can temporarily impair redemption processes or cause delays that erode user confidence. In worst-case scenarios involving security breaches leading to thefts from reserve accounts—or compromised smart contracts—the integrity of the entire system could be questioned.
Impact of External Events on Stability
External factors such as macroeconomic shifts—including inflation rates—and geopolitical tensions may indirectly influence stablecoin stability by affecting investor sentiment toward cryptocurrencies overall. For instance:
- Market downturns may prompt panic selling.
- Regulatory crackdowns might limit usage.
- Banking restrictions on crypto-related transactions could hinder access points for converting between fiat currencies and stablecoins like USDC.
These external pressures highlight how interconnected global financial systems are with cryptocurrency markets—and why vigilance remains crucial when dealing with assets pegged closely but not perfectly aligned with traditional currencies.
Recent Developments That Influence Risk Profile
Recent news highlights both opportunities and challenges facing USDC:
- Meta’s exploration into integrating stablecoins such as USDC into social media platforms signals potential growth avenues but also raises questions about regulatory oversight.
- Ongoing regulatory scrutiny emphasizes compliance risks; failure here could result in restrictions impacting usability.
- The possibility of depegging events remains an ever-present concern amid market volatility episodes—especially if confidence wanes due to unforeseen operational issues or regulatory interventions.
These developments underscore that while innovation drives adoption forward—for example through corporate integrations—they also introduce new layers of risk requiring careful monitoring by stakeholders involved with USDC holdings.
Managing Risks When Using Stablecoins Like USDC
Given these vulnerabilities—from market fluctuations through regulatory changes—it’s vital for users engaged with USD Coin (USDC) to adopt robust risk management strategies:
- Regularly monitor reserve disclosures issued by issuers such as Circle.
- Stay informed about evolving regulations affecting crypto assets within your jurisdiction.
- Use reputable exchanges offering secure redemption options during periods of high volatility.
- Diversify holdings across different asset classes beyond just cryptocurrencies.
By understanding potential pitfalls ahead—and actively managing exposure—users can better safeguard their investments against unforeseen disruptions related specifically—or indirectly—to stablecoin operations.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Stability Amid Uncertainty
While USD Coin offers numerous advantages—including ease of transferability within crypto markets—it carries inherent risks tied primarily to external shocks rather than intrinsic flaws alone. Its reliance on adequate reserves combined with ongoing regulatory oversight makes it susceptible at times despite being designed for stability purposes.
Staying informed about recent developments—from corporate initiatives like Meta’s exploration into blockchain payments—to emerging regulatory frameworks helps users anticipate possible impacts before they materialize fully online . As always when engaging with digital assets rooted partly in traditional finance structures , prudent risk assessment remains essential — especially given how swiftly this landscape continues evolving.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-29 09:17
What are the risks associated with USDC?
What Are the Risks Associated with USDC?
Understanding the risks linked to USD Coin (USDC) is essential for investors, traders, and users of stablecoins. While USDC is designed to offer stability by pegging its value to the US dollar, it is not immune to various vulnerabilities that could impact its reliability and trustworthiness. This article explores these risks in detail, providing a comprehensive overview based on recent developments and industry insights.
Market Volatility and Depegging Risks
Although USDC aims to maintain a 1:1 peg with the US dollar, market volatility can still pose significant threats. Stablecoins rely heavily on their reserves and mechanisms for maintaining price stability. If confidence in the peg diminishes—due to economic shocks or systemic issues—USDC could experience a depegging event where its value drops below or rises above $1.
Such events can be triggered by liquidity crises, sudden market sell-offs, or loss of trust among users. A depegging not only affects individual investors but can also have ripple effects across the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem by undermining confidence in stablecoins as a whole.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Legal Risks
Regulatory environments around stablecoins like USDC are evolving rapidly. Governments worldwide are scrutinizing these digital assets more closely due to concerns over money laundering, fraud prevention, consumer protection, and financial stability. Increased regulation could lead to stricter compliance requirements such as enhanced KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures or reserve transparency mandates.
While regulation aims to improve legitimacy and reduce illicit activities associated with cryptocurrencies, it also introduces operational challenges for issuers like Circle and Coinbase—the entities behind USDC. Regulatory actions might restrict certain uses of stablecoins or impose limits that affect their liquidity pools or issuance processes.
Liquidity Challenges
The core strength of any stablecoin lies in its ability to quickly convert between fiat currency and digital tokens without significant price slippage. However, if there is a sudden surge in demand or an unexpected withdrawal from reserves—perhaps during market stress—it could strain liquidity pools backing USDC.
A lack of sufficient fiat reserves would threaten its peg stability; this risk underscores why transparent reserve management practices are critical for maintaining user trust. Any doubts about reserve adequacy can lead users to withdraw en masse—a classic bank run scenario—that may result in depegging.
Operational Failures
Technical glitches or operational failures represent another layer of risk for stablecoins like USDC. These issues might include smart contract bugs, security breaches targeting custodial wallets holding reserves, or infrastructure outages disrupting transaction processing.
Such failures can temporarily impair redemption processes or cause delays that erode user confidence. In worst-case scenarios involving security breaches leading to thefts from reserve accounts—or compromised smart contracts—the integrity of the entire system could be questioned.
Impact of External Events on Stability
External factors such as macroeconomic shifts—including inflation rates—and geopolitical tensions may indirectly influence stablecoin stability by affecting investor sentiment toward cryptocurrencies overall. For instance:
- Market downturns may prompt panic selling.
- Regulatory crackdowns might limit usage.
- Banking restrictions on crypto-related transactions could hinder access points for converting between fiat currencies and stablecoins like USDC.
These external pressures highlight how interconnected global financial systems are with cryptocurrency markets—and why vigilance remains crucial when dealing with assets pegged closely but not perfectly aligned with traditional currencies.
Recent Developments That Influence Risk Profile
Recent news highlights both opportunities and challenges facing USDC:
- Meta’s exploration into integrating stablecoins such as USDC into social media platforms signals potential growth avenues but also raises questions about regulatory oversight.
- Ongoing regulatory scrutiny emphasizes compliance risks; failure here could result in restrictions impacting usability.
- The possibility of depegging events remains an ever-present concern amid market volatility episodes—especially if confidence wanes due to unforeseen operational issues or regulatory interventions.
These developments underscore that while innovation drives adoption forward—for example through corporate integrations—they also introduce new layers of risk requiring careful monitoring by stakeholders involved with USDC holdings.
Managing Risks When Using Stablecoins Like USDC
Given these vulnerabilities—from market fluctuations through regulatory changes—it’s vital for users engaged with USD Coin (USDC) to adopt robust risk management strategies:
- Regularly monitor reserve disclosures issued by issuers such as Circle.
- Stay informed about evolving regulations affecting crypto assets within your jurisdiction.
- Use reputable exchanges offering secure redemption options during periods of high volatility.
- Diversify holdings across different asset classes beyond just cryptocurrencies.
By understanding potential pitfalls ahead—and actively managing exposure—users can better safeguard their investments against unforeseen disruptions related specifically—or indirectly—to stablecoin operations.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Stability Amid Uncertainty
While USD Coin offers numerous advantages—including ease of transferability within crypto markets—it carries inherent risks tied primarily to external shocks rather than intrinsic flaws alone. Its reliance on adequate reserves combined with ongoing regulatory oversight makes it susceptible at times despite being designed for stability purposes.
Staying informed about recent developments—from corporate initiatives like Meta’s exploration into blockchain payments—to emerging regulatory frameworks helps users anticipate possible impacts before they materialize fully online . As always when engaging with digital assets rooted partly in traditional finance structures , prudent risk assessment remains essential — especially given how swiftly this landscape continues evolving.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Risks of Investing in Dogecoin
Investing in cryptocurrencies has become increasingly popular over recent years, with Dogecoin (DOGE) standing out as one of the most talked-about digital assets. Originally created as a joke, Dogecoin has gained substantial market value and a dedicated community. However, potential investors should be aware that investing in DOGE involves significant risks that can impact their financial outcomes.
What Is Dogecoin and How Did It Evolve?
Dogecoin was launched in 2013 by Jackson Palmer and Billy Markus as a parody of the cryptocurrency hype surrounding Bitcoin. Its mascot, the Shiba Inu dog from the "Doge" meme, quickly became iconic within internet culture. Despite its humorous origins, Dogecoin transitioned into a legitimate digital currency with active use cases such as tipping content creators online and charitable donations.
Over time, DOGE's popularity surged due to social media influence and endorsements from high-profile figures like Elon Musk. This rapid growth attracted many retail investors seeking quick profits but also introduced volatility that can pose risks for those unaware of market dynamics.
Cryptocurrency Market Volatility: A Major Concern
One of the primary risks associated with investing in Dogecoin is its extreme price volatility. Cryptocurrencies are inherently volatile assets; however, DOGE's price swings tend to be more pronounced compared to traditional investments or even other cryptocurrencies. Prices can skyrocket on positive news or social media hype but may plummet just as quickly during downturns or negative sentiment shifts.
This volatility makes it challenging for investors to predict future values accurately or develop stable investment strategies. For long-term wealth accumulation, such unpredictability requires careful risk management and an understanding that losses could occur rapidly.
Lack of Regulation Increases Exposure to Fraud
Unlike stocks traded on regulated exchanges governed by strict oversight bodies like the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), cryptocurrencies—including Dogecoin—operate largely outside formal regulatory frameworks. This lack of regulation creates opportunities for scams, pump-and-dump schemes, market manipulation tactics like wash trading, and fraudulent initial coin offerings (ICOs).
Investors must exercise caution when dealing with unregulated markets by verifying sources before purchasing DOGE tokens or engaging with new platforms claiming to offer trading services related to this cryptocurrency.
Security Risks: Hacks and Theft Threats
Security remains a critical concern when holding any digital asset. Cryptocurrency exchanges have historically been targets for hacking incidents resulting in significant financial losses for users who fail to implement proper security measures such as two-factor authentication (2FA) or cold storage wallets.
Dogecoin holdings stored on vulnerable exchanges are susceptible if those platforms experience breaches or operational failures. Investors should consider using reputable wallets designed specifically for secure storage rather than leaving funds on exchange accounts prone to cyberattacks.
Market Sentiment Drives Price Fluctuations
The value of DOGE is heavily influenced by market sentiment fueled through social media trends, celebrity endorsements, news coverage—and sometimes even memes! Positive developments like favorable regulatory news or institutional interest can cause sudden surges; conversely, negative reports about security issues or regulatory crackdowns often lead to sharp declines.
This emotional component adds another layer of unpredictability since investor psychology plays a significant role in short-term price movements rather than fundamental economic factors alone.
Regulatory Environment Changes Impacting Crypto Markets
Regulatory shifts at national levels significantly affect cryptocurrency prices globally—including Dogecoin’s valuation prospects. Recent restrictions imposed by authorities such as the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) have demonstrated how government policies can restrict certain activities related to digital currencies—potentially limiting access or increasing compliance costs for traders and holders alike.
Furthermore, ongoing debates around crypto taxation policies worldwide could influence investor confidence negatively if regulations become more restrictive over time.
Recent Developments That Could Influence Future Risks
In recent months leading up to 2025-05-27*, discussions about approving ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) focused on DOGE have gained traction among industry analysts who estimate there’s roughly a 63%–75% chance these financial products will receive approval[3]. While ETF approval could boost mainstream adoption—and potentially increase demand—the process also introduces new risks related to increased institutional involvement which might lead toward greater market manipulation concerns if not properly regulated*.
Additionally,* Hong Kong’s economy experienced growth driven partly by trade opportunities during specific periods[2], which might indirectly influence broader investment trends including cryptocurrencies like DOGE*. Such macroeconomic factors add complexity when assessing long-term risk profiles.
Potential Fallout Scenarios Investors Should Consider
Investors need awareness about possible adverse scenarios:
- Market Crash: A sudden downturn across global markets could drag down all cryptocurrencies including Dogecoin sharply.
- Regulatory Crackdowns: Governments tightening rules around crypto trading may restrict access further—reducing liquidity—and impacting prices adversely.
- Technological Failures: Security breaches at exchanges hosting DOGE could result in loss-of-funds incidents.
Being prepared involves understanding these potential pitfalls alongside ongoing developments affecting crypto markets overall.
Navigating Investment Decisions Safely
Given these inherent risks—volatility extremes , lack of regulation , security vulnerabilities , sentiment-driven pricing —investors should approach doge investments cautiously:
- Conduct thorough research before buying
- Use secure wallets
- Diversify holdings across different assets
- Stay updated on legal changes affecting crypto markets
- Avoid investing more than you’re willing—or able—to lose
By doing so within an informed framework rooted in transparency and due diligence—which aligns with principles underpinning credible financial advice—you enhance your ability not only to capitalize on potential gains but also mitigate downside exposure.
Understanding these key risk factors helps ensure smarter decision-making when considering whether adding Dogecoin into your investment portfolio makes sense given your individual risk tolerance.
Note: Dates mentioned refer primarily up-to-date events relevant until October 2023.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-29 05:42
What are the risks of investing in Dogecoin?
Understanding the Risks of Investing in Dogecoin
Investing in cryptocurrencies has become increasingly popular over recent years, with Dogecoin (DOGE) standing out as one of the most talked-about digital assets. Originally created as a joke, Dogecoin has gained substantial market value and a dedicated community. However, potential investors should be aware that investing in DOGE involves significant risks that can impact their financial outcomes.
What Is Dogecoin and How Did It Evolve?
Dogecoin was launched in 2013 by Jackson Palmer and Billy Markus as a parody of the cryptocurrency hype surrounding Bitcoin. Its mascot, the Shiba Inu dog from the "Doge" meme, quickly became iconic within internet culture. Despite its humorous origins, Dogecoin transitioned into a legitimate digital currency with active use cases such as tipping content creators online and charitable donations.
Over time, DOGE's popularity surged due to social media influence and endorsements from high-profile figures like Elon Musk. This rapid growth attracted many retail investors seeking quick profits but also introduced volatility that can pose risks for those unaware of market dynamics.
Cryptocurrency Market Volatility: A Major Concern
One of the primary risks associated with investing in Dogecoin is its extreme price volatility. Cryptocurrencies are inherently volatile assets; however, DOGE's price swings tend to be more pronounced compared to traditional investments or even other cryptocurrencies. Prices can skyrocket on positive news or social media hype but may plummet just as quickly during downturns or negative sentiment shifts.
This volatility makes it challenging for investors to predict future values accurately or develop stable investment strategies. For long-term wealth accumulation, such unpredictability requires careful risk management and an understanding that losses could occur rapidly.
Lack of Regulation Increases Exposure to Fraud
Unlike stocks traded on regulated exchanges governed by strict oversight bodies like the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), cryptocurrencies—including Dogecoin—operate largely outside formal regulatory frameworks. This lack of regulation creates opportunities for scams, pump-and-dump schemes, market manipulation tactics like wash trading, and fraudulent initial coin offerings (ICOs).
Investors must exercise caution when dealing with unregulated markets by verifying sources before purchasing DOGE tokens or engaging with new platforms claiming to offer trading services related to this cryptocurrency.
Security Risks: Hacks and Theft Threats
Security remains a critical concern when holding any digital asset. Cryptocurrency exchanges have historically been targets for hacking incidents resulting in significant financial losses for users who fail to implement proper security measures such as two-factor authentication (2FA) or cold storage wallets.
Dogecoin holdings stored on vulnerable exchanges are susceptible if those platforms experience breaches or operational failures. Investors should consider using reputable wallets designed specifically for secure storage rather than leaving funds on exchange accounts prone to cyberattacks.
Market Sentiment Drives Price Fluctuations
The value of DOGE is heavily influenced by market sentiment fueled through social media trends, celebrity endorsements, news coverage—and sometimes even memes! Positive developments like favorable regulatory news or institutional interest can cause sudden surges; conversely, negative reports about security issues or regulatory crackdowns often lead to sharp declines.
This emotional component adds another layer of unpredictability since investor psychology plays a significant role in short-term price movements rather than fundamental economic factors alone.
Regulatory Environment Changes Impacting Crypto Markets
Regulatory shifts at national levels significantly affect cryptocurrency prices globally—including Dogecoin’s valuation prospects. Recent restrictions imposed by authorities such as the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) have demonstrated how government policies can restrict certain activities related to digital currencies—potentially limiting access or increasing compliance costs for traders and holders alike.
Furthermore, ongoing debates around crypto taxation policies worldwide could influence investor confidence negatively if regulations become more restrictive over time.
Recent Developments That Could Influence Future Risks
In recent months leading up to 2025-05-27*, discussions about approving ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) focused on DOGE have gained traction among industry analysts who estimate there’s roughly a 63%–75% chance these financial products will receive approval[3]. While ETF approval could boost mainstream adoption—and potentially increase demand—the process also introduces new risks related to increased institutional involvement which might lead toward greater market manipulation concerns if not properly regulated*.
Additionally,* Hong Kong’s economy experienced growth driven partly by trade opportunities during specific periods[2], which might indirectly influence broader investment trends including cryptocurrencies like DOGE*. Such macroeconomic factors add complexity when assessing long-term risk profiles.
Potential Fallout Scenarios Investors Should Consider
Investors need awareness about possible adverse scenarios:
- Market Crash: A sudden downturn across global markets could drag down all cryptocurrencies including Dogecoin sharply.
- Regulatory Crackdowns: Governments tightening rules around crypto trading may restrict access further—reducing liquidity—and impacting prices adversely.
- Technological Failures: Security breaches at exchanges hosting DOGE could result in loss-of-funds incidents.
Being prepared involves understanding these potential pitfalls alongside ongoing developments affecting crypto markets overall.
Navigating Investment Decisions Safely
Given these inherent risks—volatility extremes , lack of regulation , security vulnerabilities , sentiment-driven pricing —investors should approach doge investments cautiously:
- Conduct thorough research before buying
- Use secure wallets
- Diversify holdings across different assets
- Stay updated on legal changes affecting crypto markets
- Avoid investing more than you’re willing—or able—to lose
By doing so within an informed framework rooted in transparency and due diligence—which aligns with principles underpinning credible financial advice—you enhance your ability not only to capitalize on potential gains but also mitigate downside exposure.
Understanding these key risk factors helps ensure smarter decision-making when considering whether adding Dogecoin into your investment portfolio makes sense given your individual risk tolerance.
Note: Dates mentioned refer primarily up-to-date events relevant until October 2023.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Trading Pairs on a Cryptocurrency Platform?
Trading pairs are fundamental to understanding how cryptocurrencies are bought and sold on digital platforms. Essentially, a trading pair consists of two different cryptocurrencies that can be exchanged against each other. For example, BTC/USDT is a common trading pair where Bitcoin (BTC) is traded against Tether (USDT). When you see this pair, it indicates that you can buy or sell Bitcoin using Tether as the quote currency. This setup allows traders to specify exactly what they want to exchange and at what rate.
The concept of trading pairs simplifies the process of cryptocurrency trading by providing clear pathways for asset conversion. Instead of needing to find someone willing to trade Bitcoin directly for Ethereum, traders can use an intermediary—such as USDT—to facilitate their transactions efficiently. This system not only streamlines trades but also enhances liquidity across markets.
Why Are Trading Pairs Important in Cryptocurrency Markets?
Trading pairs serve several critical functions in the crypto ecosystem. First and foremost, they provide liquidity—an essential component for healthy markets. Liquidity ensures that traders can buy or sell assets quickly without causing significant price changes. High liquidity in popular trading pairs like BTC/USDT or ETH/BTC means transactions happen smoothly and with minimal slippage.
Secondly, trading pairs play a vital role in price discovery—the process by which market prices are determined based on supply and demand dynamics within each pair. The value of one cryptocurrency relative to another helps establish fair market prices and provides transparency for investors making informed decisions.
Thirdly, these pairs enable diversification strategies within portfolios. By exchanging one digital asset for another through various trading pairs, investors can hedge risks or capitalize on emerging opportunities without needing multiple accounts across different exchanges.
Finally, managing market volatility often involves pairing volatile assets with stablecoins such as USDT or USDC—cryptocurrencies pegged 1:1 with fiat currencies like USD—to reduce exposure during turbulent periods.
Types of Trading Pairs Commonly Found on Crypto Platforms
There are several types of trading pairs available depending on the platform's offerings:
Crypto-to-Crypto Pairs: These involve two cryptocurrencies—for example, ETH/BTC or LTC/XRP—and allow direct exchange between digital assets.
Crypto-to-Fiat Pairs: These involve a cryptocurrency paired with traditional currencies like USD/EUR/JPY—for instance, BTC/USD or ETH/EUR—which facilitate buying/selling using fiat money.
Stablecoin-Based Pairs: Stablecoins such as USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), DAI are frequently used as base currencies because their value remains relatively stable compared to other cryptos.
Popular examples include BTC/USDT (Bitcoin vs Tether), ETH/USDC (Ethereum vs USD Coin), and DOGE/USDT (Dogecoin vs Tether). The choice depends largely on user preferences regarding stability versus potential growth opportunities.
How Do Trading Pairs Affect Price Discovery?
Price discovery is central to any financial market—and crypto markets are no exception—with trading pairs playing an integral role in this process. When traders buy or sell within specific pairs, their collective actions influence the current valuation of both assets involved.
For instance, if there’s increased demand for Bitcoin relative to Tether—say due to positive news—the price of BTC will rise against USDT within that pair until equilibrium is reached where supply matches demand again. Conversely, if selling pressure increases unexpectedly—perhaps due to regulatory concerns—the price may decline accordingly.
Because many cryptocurrencies have multiple pairing options across various exchanges worldwide—including decentralized exchanges (DEXs)—price discrepancies often emerge temporarily but tend toward convergence over time through arbitrage activities driven by these differing rates across platforms.
This dynamic highlights why understanding how different pairing options impact pricing is crucial for traders aiming at optimal entry and exit points while managing risk effectively.
How Stablecoins Influence Trading Pair Dynamics
Stablecoins have revolutionized crypto markets by offering low-volatility alternatives suitable as base currencies in many trading scenarios. Their primary advantage lies in maintaining near-pegged values—most commonly 1:1 with fiat currencies—which reduces exposure during high volatility periods typical in crypto markets.
As a result:
- They serve as reliable mediums for transferring value between trades.
- They enable more predictable pricing models.
- They attract institutional investors seeking safer avenues amid turbulent conditions.
Popular stablecoins like USDT dominate many exchange order books because they provide consistent liquidity pools facilitating rapid trades without worrying about sudden swings typical among more volatile coins like Dogecoin or Shiba Inu tokens.
Furthermore, stablecoin-based pairing has encouraged innovation around DeFi applications such as yield farming and staking protocols—all relying heavily on these reliable base tokens—to expand overall market depth further enhancing liquidity levels globally.
Recent Trends Impacting Crypto Trading Pairs
The landscape surrounding crypto trading pairs continues evolving rapidly due mainly to technological advancements and regulatory developments:
Increased Adoption Through DeFi
Decentralized finance platforms have introduced numerous new token swaps involving complex multi-layered pools beyond simple one-to-one swaps — increasing available options significantly while also improving efficiency via layer-2 solutions which reduce transaction costs and times substantially.
Rise Of Stablecoins
The proliferation of stablecoins has made them dominant players within most major exchanges’ order books; their stability attracts both retail users seeking safety during volatile periods—and institutional players looking into large-scale operations.
Regulatory Clarity
Countries such as Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA) along with U.S regulators have issued clearer guidelines concerning permissible activities around certain tokens; this clarity encourages more platforms worldwide to list diverse sets of tradable assets safely complying with local laws.
Market Trends & Meme Coins
The surge popularity seen recently around meme coins like Dogecoin has led exchanges worldwide adding dedicated DOGE/USD/Pairs alongside traditional ones — reflecting shifting investor interests toward community-driven projects.
Technological Innovations
Layer-two scaling solutions such as Lightning Network-like protocols improve transaction speeds dramatically while decentralized exchanges eliminate intermediaries altogether — creating new possibilities for innovative trade structures involving novel types of pairing mechanisms previously unavailable.
Risks Associated With Trading Pairs
While offering numerous benefits—including increased flexibility—they also come with inherent risks:
Regulatory Risks: Changes in legal frameworks could restrict access—or even ban certain types—from being traded altogether; this could lead some platforms withdrawing specific paired offerings impacting overall market depth.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies remain highly volatile; sudden swings especially affecting one asset within a pair might cause rapid shifts affecting trader positions adversely.
Security Concerns: Security breaches targeting centralized exchanges could compromise user funds stored alongside specific paired assets—a risk mitigated only through robust security measures.
Liquidity Shortages: Less popular/traded pairs may suffer from low volume leading difficulties when executing large orders without impacting prices negatively.
Economic FactorsGlobal economic conditions influence investor sentiment towards particular assets; during times when fiat inflation rises sharply—or geopolitical tensions escalate—traders might prefer safer holdings like stablecoins over risky altcoins.
Understanding what "trading pairs" mean provides valuable insight into how cryptocurrency markets operate efficiently yet dynamically respond under various influences—from technological innovations through regulatory changes—all shaping investment strategies today’s traders need knowledge about these foundational elements deeply embedded into every aspect of digital asset exchange systems


Lo
2025-05-22 16:36
What do "trading pairs" on a crypto platform mean?
What Are Trading Pairs on a Cryptocurrency Platform?
Trading pairs are fundamental to understanding how cryptocurrencies are bought and sold on digital platforms. Essentially, a trading pair consists of two different cryptocurrencies that can be exchanged against each other. For example, BTC/USDT is a common trading pair where Bitcoin (BTC) is traded against Tether (USDT). When you see this pair, it indicates that you can buy or sell Bitcoin using Tether as the quote currency. This setup allows traders to specify exactly what they want to exchange and at what rate.
The concept of trading pairs simplifies the process of cryptocurrency trading by providing clear pathways for asset conversion. Instead of needing to find someone willing to trade Bitcoin directly for Ethereum, traders can use an intermediary—such as USDT—to facilitate their transactions efficiently. This system not only streamlines trades but also enhances liquidity across markets.
Why Are Trading Pairs Important in Cryptocurrency Markets?
Trading pairs serve several critical functions in the crypto ecosystem. First and foremost, they provide liquidity—an essential component for healthy markets. Liquidity ensures that traders can buy or sell assets quickly without causing significant price changes. High liquidity in popular trading pairs like BTC/USDT or ETH/BTC means transactions happen smoothly and with minimal slippage.
Secondly, trading pairs play a vital role in price discovery—the process by which market prices are determined based on supply and demand dynamics within each pair. The value of one cryptocurrency relative to another helps establish fair market prices and provides transparency for investors making informed decisions.
Thirdly, these pairs enable diversification strategies within portfolios. By exchanging one digital asset for another through various trading pairs, investors can hedge risks or capitalize on emerging opportunities without needing multiple accounts across different exchanges.
Finally, managing market volatility often involves pairing volatile assets with stablecoins such as USDT or USDC—cryptocurrencies pegged 1:1 with fiat currencies like USD—to reduce exposure during turbulent periods.
Types of Trading Pairs Commonly Found on Crypto Platforms
There are several types of trading pairs available depending on the platform's offerings:
Crypto-to-Crypto Pairs: These involve two cryptocurrencies—for example, ETH/BTC or LTC/XRP—and allow direct exchange between digital assets.
Crypto-to-Fiat Pairs: These involve a cryptocurrency paired with traditional currencies like USD/EUR/JPY—for instance, BTC/USD or ETH/EUR—which facilitate buying/selling using fiat money.
Stablecoin-Based Pairs: Stablecoins such as USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), DAI are frequently used as base currencies because their value remains relatively stable compared to other cryptos.
Popular examples include BTC/USDT (Bitcoin vs Tether), ETH/USDC (Ethereum vs USD Coin), and DOGE/USDT (Dogecoin vs Tether). The choice depends largely on user preferences regarding stability versus potential growth opportunities.
How Do Trading Pairs Affect Price Discovery?
Price discovery is central to any financial market—and crypto markets are no exception—with trading pairs playing an integral role in this process. When traders buy or sell within specific pairs, their collective actions influence the current valuation of both assets involved.
For instance, if there’s increased demand for Bitcoin relative to Tether—say due to positive news—the price of BTC will rise against USDT within that pair until equilibrium is reached where supply matches demand again. Conversely, if selling pressure increases unexpectedly—perhaps due to regulatory concerns—the price may decline accordingly.
Because many cryptocurrencies have multiple pairing options across various exchanges worldwide—including decentralized exchanges (DEXs)—price discrepancies often emerge temporarily but tend toward convergence over time through arbitrage activities driven by these differing rates across platforms.
This dynamic highlights why understanding how different pairing options impact pricing is crucial for traders aiming at optimal entry and exit points while managing risk effectively.
How Stablecoins Influence Trading Pair Dynamics
Stablecoins have revolutionized crypto markets by offering low-volatility alternatives suitable as base currencies in many trading scenarios. Their primary advantage lies in maintaining near-pegged values—most commonly 1:1 with fiat currencies—which reduces exposure during high volatility periods typical in crypto markets.
As a result:
- They serve as reliable mediums for transferring value between trades.
- They enable more predictable pricing models.
- They attract institutional investors seeking safer avenues amid turbulent conditions.
Popular stablecoins like USDT dominate many exchange order books because they provide consistent liquidity pools facilitating rapid trades without worrying about sudden swings typical among more volatile coins like Dogecoin or Shiba Inu tokens.
Furthermore, stablecoin-based pairing has encouraged innovation around DeFi applications such as yield farming and staking protocols—all relying heavily on these reliable base tokens—to expand overall market depth further enhancing liquidity levels globally.
Recent Trends Impacting Crypto Trading Pairs
The landscape surrounding crypto trading pairs continues evolving rapidly due mainly to technological advancements and regulatory developments:
Increased Adoption Through DeFi
Decentralized finance platforms have introduced numerous new token swaps involving complex multi-layered pools beyond simple one-to-one swaps — increasing available options significantly while also improving efficiency via layer-2 solutions which reduce transaction costs and times substantially.
Rise Of Stablecoins
The proliferation of stablecoins has made them dominant players within most major exchanges’ order books; their stability attracts both retail users seeking safety during volatile periods—and institutional players looking into large-scale operations.
Regulatory Clarity
Countries such as Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA) along with U.S regulators have issued clearer guidelines concerning permissible activities around certain tokens; this clarity encourages more platforms worldwide to list diverse sets of tradable assets safely complying with local laws.
Market Trends & Meme Coins
The surge popularity seen recently around meme coins like Dogecoin has led exchanges worldwide adding dedicated DOGE/USD/Pairs alongside traditional ones — reflecting shifting investor interests toward community-driven projects.
Technological Innovations
Layer-two scaling solutions such as Lightning Network-like protocols improve transaction speeds dramatically while decentralized exchanges eliminate intermediaries altogether — creating new possibilities for innovative trade structures involving novel types of pairing mechanisms previously unavailable.
Risks Associated With Trading Pairs
While offering numerous benefits—including increased flexibility—they also come with inherent risks:
Regulatory Risks: Changes in legal frameworks could restrict access—or even ban certain types—from being traded altogether; this could lead some platforms withdrawing specific paired offerings impacting overall market depth.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies remain highly volatile; sudden swings especially affecting one asset within a pair might cause rapid shifts affecting trader positions adversely.
Security Concerns: Security breaches targeting centralized exchanges could compromise user funds stored alongside specific paired assets—a risk mitigated only through robust security measures.
Liquidity Shortages: Less popular/traded pairs may suffer from low volume leading difficulties when executing large orders without impacting prices negatively.
Economic FactorsGlobal economic conditions influence investor sentiment towards particular assets; during times when fiat inflation rises sharply—or geopolitical tensions escalate—traders might prefer safer holdings like stablecoins over risky altcoins.
Understanding what "trading pairs" mean provides valuable insight into how cryptocurrency markets operate efficiently yet dynamically respond under various influences—from technological innovations through regulatory changes—all shaping investment strategies today’s traders need knowledge about these foundational elements deeply embedded into every aspect of digital asset exchange systems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Benefits of Trading in the XT Carnival
Understanding the XT Carnival Platform
The XT Carnival is a decentralized trading platform that has gained attention within the cryptocurrency community for its innovative approach to digital asset trading. Built on blockchain technology, it aims to provide a secure, transparent, and user-friendly environment for both novice and experienced traders. Unlike traditional centralized exchanges, the XT Carnival emphasizes decentralization, which enhances security and reduces reliance on third-party intermediaries. Its infrastructure supports a wide array of cryptocurrencies and tokens, enabling users to diversify their investment portfolios efficiently.
Security and Transparency in Cryptocurrency Trading
One of the primary advantages of trading through the XT Carnival is its robust security framework rooted in blockchain technology. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger—an immutable record that ensures transparency and accountability. This transparency allows traders to verify transactions independently, fostering trust within the platform’s community. Additionally, decentralization minimizes risks associated with hacking or fraud common in centralized exchanges because there is no single point of failure.
Furthermore, recent security enhancements such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and advanced encryption algorithms have strengthened user account protection. Regular security audits further ensure that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed promptly—an essential feature given the increasing sophistication of cyber threats targeting crypto assets.
User Experience: Accessibility for All Levels
Ease of use is another significant benefit offered by the XT Carnival platform. Its intuitive interface caters to both beginners who are just starting their crypto journey and seasoned traders seeking efficient tools for complex strategies. The platform’s design simplifies navigation across various features like order placement, portfolio management, or accessing DeFi integrations.
For new users especially, having an accessible yet powerful trading environment reduces barriers often associated with cryptocurrency markets’ complexity. Clear menus, straightforward processes for deposits/withdrawals, real-time asset tracking—all contribute toward making trading less intimidating while maintaining professional-grade functionality.
Asset Diversity: Broadening Investment Opportunities
Supporting multiple cryptocurrencies—including popular tokens like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), along with numerous altcoins—the XT Carnival enables diversification across different digital assets easily within one platform. This flexibility helps mitigate risks tied to market volatility since investors can spread exposure rather than relying solely on one asset class.
Moreover, support for various tokens facilitates participation in emerging trends such as DeFi projects or yield farming opportunities directly through integrated protocols—expanding potential earning avenues beyond simple buy-and-sell trades.
Cost-Effective Trading: Lower Fees Compared to Traditional Platforms
Trading costs significantly influence profitability; hence lower transaction fees are highly valued by traders worldwide. The XT Carnival offers competitive fee structures compared to traditional financial markets or centralized exchanges—which often impose higher charges due to middlemen or legacy systems.
Reduced fees mean smaller spreads between buy/sell prices and less overhead during frequent trades—a crucial advantage especially for active day traders or those executing high-volume transactions regularly seeking maximum returns from their investments.
Community Engagement & Support Networks
A vibrant community can enhance user experience by providing support channels such as social media groups or forums where members share insights about market trends or platform updates. The XT Carnival actively fosters this sense of community engagement through regular updates about new features—like DeFi protocol integrations—and educational content aimed at empowering users with knowledge about secure trading practices.
This participatory approach not only builds trust but also encourages active involvement from users who feel part of an evolving ecosystem rather than just passive participants in a transactional process.
Recent Developments Enhancing Platform Capabilities
Since its launch early 2023, the XT Carnival has rapidly evolved by integrating additional functionalities aligned with industry trends:
DeFi Protocol Integration: Mid-2023 saw partnerships enabling access to decentralized finance services such as lending platforms or yield farming directly via the exchange interface.
Security Upgrades: Late 2023 brought multi-layered security measures including MFA options alongside regular audits ensuring ongoing safety against cyber threats.
Strategic Collaborations: Partnerships with other blockchain entities aim at expanding liquidity pools and offering more comprehensive financial products—further enriching user options.
These developments demonstrate how continuous innovation positions it favorably amidst growing competition.
Risks & Challenges Facing Traders on Xt Carnival
While benefits abound when engaging with this emerging platform — including low fees and diversified assets — potential risks should be acknowledged:
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more intensely worldwide—with some imposing bans—the regulatory landscape remains uncertain which could impact operations.
Security Concerns: Despite improvements; no system is entirely immune from cyber-attacks; thus vigilance remains essential when managing private keys or sensitive data.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices fluctuate wildly; sudden downturns may affect trader confidence leading possibly to decreased activity if not managed carefully.
Why Choose Trading Through Xt Carnival?
For individuals interested in exploring digital asset markets securely while benefiting from low-cost transactions coupled with broad asset support—the XT Carnival presents an attractive option rooted in transparency thanks to blockchain technology's inherent qualities. Its focus on community engagement combined with ongoing development efforts signals long-term potential despite existing challenges posed by regulation or market volatility.
By understanding these core benefits—from enhanced security measures over traditional platforms—to diversified investment options supported by an active ecosystem—users can make informed decisions suited toward their risk appetite and growth objectives within today’s dynamic crypto landscape.
Keywords: cryptocurrency trading benefits | decentralized exchange advantages | blockchain-based platforms | low transaction fees crypto | DeFi integration platforms | secure crypto trading environments


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-06-09 01:39
What are the benefits of trading in the XT Carnival?
Benefits of Trading in the XT Carnival
Understanding the XT Carnival Platform
The XT Carnival is a decentralized trading platform that has gained attention within the cryptocurrency community for its innovative approach to digital asset trading. Built on blockchain technology, it aims to provide a secure, transparent, and user-friendly environment for both novice and experienced traders. Unlike traditional centralized exchanges, the XT Carnival emphasizes decentralization, which enhances security and reduces reliance on third-party intermediaries. Its infrastructure supports a wide array of cryptocurrencies and tokens, enabling users to diversify their investment portfolios efficiently.
Security and Transparency in Cryptocurrency Trading
One of the primary advantages of trading through the XT Carnival is its robust security framework rooted in blockchain technology. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger—an immutable record that ensures transparency and accountability. This transparency allows traders to verify transactions independently, fostering trust within the platform’s community. Additionally, decentralization minimizes risks associated with hacking or fraud common in centralized exchanges because there is no single point of failure.
Furthermore, recent security enhancements such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and advanced encryption algorithms have strengthened user account protection. Regular security audits further ensure that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed promptly—an essential feature given the increasing sophistication of cyber threats targeting crypto assets.
User Experience: Accessibility for All Levels
Ease of use is another significant benefit offered by the XT Carnival platform. Its intuitive interface caters to both beginners who are just starting their crypto journey and seasoned traders seeking efficient tools for complex strategies. The platform’s design simplifies navigation across various features like order placement, portfolio management, or accessing DeFi integrations.
For new users especially, having an accessible yet powerful trading environment reduces barriers often associated with cryptocurrency markets’ complexity. Clear menus, straightforward processes for deposits/withdrawals, real-time asset tracking—all contribute toward making trading less intimidating while maintaining professional-grade functionality.
Asset Diversity: Broadening Investment Opportunities
Supporting multiple cryptocurrencies—including popular tokens like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), along with numerous altcoins—the XT Carnival enables diversification across different digital assets easily within one platform. This flexibility helps mitigate risks tied to market volatility since investors can spread exposure rather than relying solely on one asset class.
Moreover, support for various tokens facilitates participation in emerging trends such as DeFi projects or yield farming opportunities directly through integrated protocols—expanding potential earning avenues beyond simple buy-and-sell trades.
Cost-Effective Trading: Lower Fees Compared to Traditional Platforms
Trading costs significantly influence profitability; hence lower transaction fees are highly valued by traders worldwide. The XT Carnival offers competitive fee structures compared to traditional financial markets or centralized exchanges—which often impose higher charges due to middlemen or legacy systems.
Reduced fees mean smaller spreads between buy/sell prices and less overhead during frequent trades—a crucial advantage especially for active day traders or those executing high-volume transactions regularly seeking maximum returns from their investments.
Community Engagement & Support Networks
A vibrant community can enhance user experience by providing support channels such as social media groups or forums where members share insights about market trends or platform updates. The XT Carnival actively fosters this sense of community engagement through regular updates about new features—like DeFi protocol integrations—and educational content aimed at empowering users with knowledge about secure trading practices.
This participatory approach not only builds trust but also encourages active involvement from users who feel part of an evolving ecosystem rather than just passive participants in a transactional process.
Recent Developments Enhancing Platform Capabilities
Since its launch early 2023, the XT Carnival has rapidly evolved by integrating additional functionalities aligned with industry trends:
DeFi Protocol Integration: Mid-2023 saw partnerships enabling access to decentralized finance services such as lending platforms or yield farming directly via the exchange interface.
Security Upgrades: Late 2023 brought multi-layered security measures including MFA options alongside regular audits ensuring ongoing safety against cyber threats.
Strategic Collaborations: Partnerships with other blockchain entities aim at expanding liquidity pools and offering more comprehensive financial products—further enriching user options.
These developments demonstrate how continuous innovation positions it favorably amidst growing competition.
Risks & Challenges Facing Traders on Xt Carnival
While benefits abound when engaging with this emerging platform — including low fees and diversified assets — potential risks should be acknowledged:
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more intensely worldwide—with some imposing bans—the regulatory landscape remains uncertain which could impact operations.
Security Concerns: Despite improvements; no system is entirely immune from cyber-attacks; thus vigilance remains essential when managing private keys or sensitive data.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices fluctuate wildly; sudden downturns may affect trader confidence leading possibly to decreased activity if not managed carefully.
Why Choose Trading Through Xt Carnival?
For individuals interested in exploring digital asset markets securely while benefiting from low-cost transactions coupled with broad asset support—the XT Carnival presents an attractive option rooted in transparency thanks to blockchain technology's inherent qualities. Its focus on community engagement combined with ongoing development efforts signals long-term potential despite existing challenges posed by regulation or market volatility.
By understanding these core benefits—from enhanced security measures over traditional platforms—to diversified investment options supported by an active ecosystem—users can make informed decisions suited toward their risk appetite and growth objectives within today’s dynamic crypto landscape.
Keywords: cryptocurrency trading benefits | decentralized exchange advantages | blockchain-based platforms | low transaction fees crypto | DeFi integration platforms | secure crypto trading environments
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does Chainlink (LINK) Work?
Understanding how Chainlink operates is essential for grasping its role in the blockchain ecosystem. As a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink bridges the gap between smart contracts and real-world data, enabling a wide range of applications from finance to gaming. This article explores the core mechanisms behind Chainlink’s functionality, its key components, and how it maintains security and reliability.
What Is a Decentralized Oracle Network?
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. However, they inherently lack access to external data sources—such as market prices, weather conditions, or event outcomes—that are often necessary for their execution. Oracles serve as intermediaries that fetch and verify external data before relaying it to smart contracts.
Chainlink differentiates itself by creating a decentralized network of oracles rather than relying on single centralized sources. This decentralization reduces risks associated with data manipulation or failure from any one source, thereby enhancing trustworthiness.
The Core Components of Chainlink
Chainlink's architecture comprises several critical elements working together seamlessly:
Oracle Nodes: These are independent entities operated by various participants who provide external data to the network. Anyone can run an oracle node—this openness fosters decentralization but also requires incentivization mechanisms to ensure accuracy.
Data Feeds: These are curated streams of information sourced from reputable providers such as financial markets or weather services. Data feeds act as reliable inputs that oracle nodes fetch and deliver.
Smart Contracts: On-chain programs that automatically execute based on predefined conditions when they receive verified external data via Chainlink oracles.
This setup allows smart contracts to respond dynamically to real-world events without manual intervention.
How Does Chainlink Fetch External Data?
The process begins when a smart contract requests specific information—say, the current price of Bitcoin—to be used within its logic. The request is sent through an interface called an oracle request.
Once received, multiple oracle nodes independently fetch the requested data from their respective sources (data feeds). To prevent reliance on any single node—which could introduce bias—the network employs aggregation algorithms that compile responses into a consensus value before passing it back to the requesting smart contract.
This multi-node approach ensures higher accuracy and resistance against malicious actors attempting to manipulate results.
Incentivizing Accurate Data Provision
Chainlink uses its native token LINK as an incentive mechanism for node operators. Participants stake LINK tokens as collateral; if they provide false or inaccurate data intentionally—or fail in their duties—they risk losing their staked tokens through penalties known as slashing.
Rewards are distributed proportionally based on performance metrics such as response time and accuracy. This economic model encourages honest participation while maintaining high standards across the network.
Security Measures in Place
Security is paramount given that faulty or malicious data can have serious consequences—for example, incorrect financial transactions or contractual breaches. To mitigate these risks:
- Multiple independent nodes verify each piece of data.
- Aggregation algorithms filter out outliers.
- Stake-based incentives discourage dishonest behavior.
Additionally, recent updates have focused on improving security features like cryptographic proofs and enhanced consensus protocols which further safeguard against attacks such as Sybil attacks (where fake identities attempt to influence results).
Recent Innovations Enhancing Functionality
In recent years, Chainlink has expanded beyond simple price feeds into more complex use cases:
Automation with Keepers: Launched in 2023, Keepers automate off-chain actions triggered by specific on-chain events—reducing manual oversight needs.
Scalability Improvements: The 2024 update introduced enhancements aimed at increasing throughput capacity while maintaining security integrity—a crucial step toward supporting large-scale enterprise applications across industries like supply chain management and insurance.
Partnerships with major players including Google Cloud and IBM demonstrate confidence in its technology’s robustness for enterprise adoption.
Why Is Chainlink Important for Blockchain Ecosystems?
By providing secure access to real-world information without centralized points of failure—and doing so transparently—it enables developers worldwide to build more sophisticated decentralized applications (dApps). From DeFi protocols calculating interest rates based on live market prices—to gaming platforms reacting instantly during live events—Chainlink's infrastructure underpins many innovative solutions today.
Challenges Facing Chainlink
Despite its success story so far, several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Environment: As DeFi grows rapidly worldwide—and regulators scrutinize decentralized projects—compliance issues could impact operations.
Security Risks: While robust measures exist against common threats like node compromise or false reporting—as with all decentralized systems—the potential remains for sophisticated attacks targeting specific vulnerabilities.
Market Competition: Projects such as Band Protocol and Tellor offer alternative oracle solutions; thus maintaining technological leadership requires continuous innovation.
Final Thoughts: The Future Outlook
Chainlink’s ability to reliably connect blockchain-based smart contracts with real-world events positions it uniquely within both crypto markets and traditional industries seeking transparency & automation solutions. Its ongoing development efforts—including scalability upgrades & strategic partnerships—indicate strong growth potential despite regulatory uncertainties ahead.
By understanding how Chainlink functions—from fetching external data securely via incentivized nodes—to integrating seamlessly into diverse blockchain ecosystems—you gain insight into why this project remains pivotal in advancing decentralized technology globally.


kai
2025-05-29 02:28
How does Chainlink (LINK) work?
How Does Chainlink (LINK) Work?
Understanding how Chainlink operates is essential for grasping its role in the blockchain ecosystem. As a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink bridges the gap between smart contracts and real-world data, enabling a wide range of applications from finance to gaming. This article explores the core mechanisms behind Chainlink’s functionality, its key components, and how it maintains security and reliability.
What Is a Decentralized Oracle Network?
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. However, they inherently lack access to external data sources—such as market prices, weather conditions, or event outcomes—that are often necessary for their execution. Oracles serve as intermediaries that fetch and verify external data before relaying it to smart contracts.
Chainlink differentiates itself by creating a decentralized network of oracles rather than relying on single centralized sources. This decentralization reduces risks associated with data manipulation or failure from any one source, thereby enhancing trustworthiness.
The Core Components of Chainlink
Chainlink's architecture comprises several critical elements working together seamlessly:
Oracle Nodes: These are independent entities operated by various participants who provide external data to the network. Anyone can run an oracle node—this openness fosters decentralization but also requires incentivization mechanisms to ensure accuracy.
Data Feeds: These are curated streams of information sourced from reputable providers such as financial markets or weather services. Data feeds act as reliable inputs that oracle nodes fetch and deliver.
Smart Contracts: On-chain programs that automatically execute based on predefined conditions when they receive verified external data via Chainlink oracles.
This setup allows smart contracts to respond dynamically to real-world events without manual intervention.
How Does Chainlink Fetch External Data?
The process begins when a smart contract requests specific information—say, the current price of Bitcoin—to be used within its logic. The request is sent through an interface called an oracle request.
Once received, multiple oracle nodes independently fetch the requested data from their respective sources (data feeds). To prevent reliance on any single node—which could introduce bias—the network employs aggregation algorithms that compile responses into a consensus value before passing it back to the requesting smart contract.
This multi-node approach ensures higher accuracy and resistance against malicious actors attempting to manipulate results.
Incentivizing Accurate Data Provision
Chainlink uses its native token LINK as an incentive mechanism for node operators. Participants stake LINK tokens as collateral; if they provide false or inaccurate data intentionally—or fail in their duties—they risk losing their staked tokens through penalties known as slashing.
Rewards are distributed proportionally based on performance metrics such as response time and accuracy. This economic model encourages honest participation while maintaining high standards across the network.
Security Measures in Place
Security is paramount given that faulty or malicious data can have serious consequences—for example, incorrect financial transactions or contractual breaches. To mitigate these risks:
- Multiple independent nodes verify each piece of data.
- Aggregation algorithms filter out outliers.
- Stake-based incentives discourage dishonest behavior.
Additionally, recent updates have focused on improving security features like cryptographic proofs and enhanced consensus protocols which further safeguard against attacks such as Sybil attacks (where fake identities attempt to influence results).
Recent Innovations Enhancing Functionality
In recent years, Chainlink has expanded beyond simple price feeds into more complex use cases:
Automation with Keepers: Launched in 2023, Keepers automate off-chain actions triggered by specific on-chain events—reducing manual oversight needs.
Scalability Improvements: The 2024 update introduced enhancements aimed at increasing throughput capacity while maintaining security integrity—a crucial step toward supporting large-scale enterprise applications across industries like supply chain management and insurance.
Partnerships with major players including Google Cloud and IBM demonstrate confidence in its technology’s robustness for enterprise adoption.
Why Is Chainlink Important for Blockchain Ecosystems?
By providing secure access to real-world information without centralized points of failure—and doing so transparently—it enables developers worldwide to build more sophisticated decentralized applications (dApps). From DeFi protocols calculating interest rates based on live market prices—to gaming platforms reacting instantly during live events—Chainlink's infrastructure underpins many innovative solutions today.
Challenges Facing Chainlink
Despite its success story so far, several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Environment: As DeFi grows rapidly worldwide—and regulators scrutinize decentralized projects—compliance issues could impact operations.
Security Risks: While robust measures exist against common threats like node compromise or false reporting—as with all decentralized systems—the potential remains for sophisticated attacks targeting specific vulnerabilities.
Market Competition: Projects such as Band Protocol and Tellor offer alternative oracle solutions; thus maintaining technological leadership requires continuous innovation.
Final Thoughts: The Future Outlook
Chainlink’s ability to reliably connect blockchain-based smart contracts with real-world events positions it uniquely within both crypto markets and traditional industries seeking transparency & automation solutions. Its ongoing development efforts—including scalability upgrades & strategic partnerships—indicate strong growth potential despite regulatory uncertainties ahead.
By understanding how Chainlink functions—from fetching external data securely via incentivized nodes—to integrating seamlessly into diverse blockchain ecosystems—you gain insight into why this project remains pivotal in advancing decentralized technology globally.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Are There Any Disadvantages to Market Orders? An In-Depth Analysis
Understanding the potential drawbacks of market orders is essential for investors aiming to make informed trading decisions. While market orders are popular due to their simplicity and speed, they carry certain risks that can impact investment outcomes. This article explores the disadvantages associated with market orders, recent developments influencing their use, and how investors can navigate these challenges effectively.
What Is a Market Order and How Does It Work?
A market order is an instruction from an investor to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price. This type of order prioritizes execution speed over price certainty, making it ideal for traders who want quick entry or exit positions. When placed, a broker executes the order promptly in most cases, but the actual transaction price may differ from expectations due to fluctuating market conditions.
Market orders are widely used across various financial markets—including stock exchanges, cryptocurrency platforms, and forex—because of their straightforward nature. They eliminate the need for complex decision-making about specific prices but introduce certain risks that traders should be aware of.
Key Disadvantages of Using Market Orders
While convenience is a significant advantage of market orders, several disadvantages warrant careful consideration:
Price Uncertainty
One primary concern with market orders is that they do not guarantee a specific execution price. Instead, they execute at what’s available at that moment in time—often called the "best available" price—which can fluctuate rapidly during volatile periods. As a result, investors might pay more than anticipated when buying or receive less when selling assets unexpectedly.
Liquidity Risks and Slippage
In markets with low liquidity or during times of high volatility—such as economic news releases or geopolitical events—market orders may not fill instantly or may fill at unfavorable prices due to slippage. Slippage occurs when there’s a difference between expected transaction prices and actual execution prices; this risk increases significantly in illiquid assets like small-cap stocks or certain cryptocurrencies.
Execution Delays During Fast-Moving Markets
Although generally executed quickly under normal conditions, fast-moving markets can cause delays in executing large or rapid trades through market orders. These delays might lead traders to miss out on favorable pricing opportunities or incur higher costs if prices move unfavorably before completion.
Impact on Small Markets Due to Large Orders
Large volume trades placed via market orders have the potential to influence asset prices directly—a phenomenon known as "market impact." For example, executing sizable buy/sell transactions in thinly traded securities could push prices upward/downward temporarily until equilibrium restores itself.
Gapping Risks During Extreme Conditions
Gaps happen when asset prices jump sharply between trading sessions without any trades occurring within those ranges—for instance after major news announcements—or during trading halts caused by regulatory issues or technical failures.
Executing a market order amid such gaps often results in unfavorable fills because it does not account for sudden jumps beyond current quotes; this exposes traders further risk especially during unpredictable events like earnings surprises or geopolitical crises.
Recent Developments Affecting Market Order Risks
The landscape surrounding market order usage has evolved considerably over recent years owing primarily to technological advancements and regulatory changes:
Cryptocurrency Volatility: Digital assets such as Bitcoin have experienced unprecedented swings recently—with daily fluctuations sometimes exceeding 10%. Such volatility amplifies risks associated with using simple-market instructions because rapid price changes mean traders could end up paying significantly more than intended—or receiving less if selling quickly.
Regulatory Initiatives: Authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing trading practices aimed at protecting retail investors from adverse outcomes linked with aggressive order types like immediate-or-candomarket executions without sufficient transparency mechanisms.
Technological Innovations: High-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms now execute thousands of transactions per second based on complex strategies—including exploiting minute arbitrage opportunities—that traditional retail-market participants cannot match manually.
These systems contribute both positively by increasing liquidity but also negatively by creating unpredictable short-term volatility which impacts all types of trade executions including standard-market orders.
Investor Education Efforts: Recognizing these complexities has led many financial institutions and regulators toward emphasizing investor education about different order types’ advantages versus their inherent risks—helping individuals understand when alternative strategies such as limit orders might better serve their objectives.
Potential Impacts on Investors and Markets
The disadvantages tied specifically to market orders extend beyond individual trader losses—they also influence broader financial stability:
Investor Losses: Without control over exact pricing points—even if executed swiftly—increased exposure exists during volatile periods where unexpected slippage leads directly into losses.
Market Stability Concerns: Large aggregate use of aggressive ordering strategies can induce short-term instability by causing abrupt shifts in supply-demand dynamics; this raises systemic concerns especially within less liquid markets where single large trades disproportionately affect pricing trends.
Regulatory Responses: To mitigate these issues—and protect retail participants—regulators may impose restrictions such as minimum resting times for certain order types (e.g., limit vs.market), enhanced transparency requirements around trade execution quality—and even ban some high-risk practices altogether depending on evolving circumstances.
How Investors Can Manage Risks Associated With Market Orders
Given these disadvantages—and ongoing developments—it’s crucial for investors not only understand how marketplace dynamics work but also adopt prudent strategies:
Use limit Orders When Possible: Unlike simple-market instructions which accept prevailing quotes automatically—a limit order allows setting maximum purchase price (or minimum sale) thresholds ensuring better control over trade costs amidst volatile environments.
Stay Informed About Market Conditions: Monitoring real-time data feeds helps anticipate periods where rapid fluctuations could adversely affect your intended trade execution strategy.
Diversify Order Types: Combining different approaches based on specific goals—for example employing stop-loss limits alongside traditional entries—can help manage downside risk effectively while maintaining flexibility.
Educate Yourself Continually: Staying updated about technological innovations affecting markets—as well as regulatory changes—is vital for adapting your approach accordingly.
By understanding both the inherent limitations and recent advancements related to market orders—and applying strategic safeguards—you position yourself better against unforeseen adverse outcomes while participating actively across diverse financial landscapes.
This comprehensive overview underscores that while marketplace simplicity makes them attractive tools for quick transactions, awareness about their pitfalls remains essential — particularly amid evolving technology-driven environments shaping modern investing practices today.*


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-29 02:04
Are there any disadvantages to market orders?
Are There Any Disadvantages to Market Orders? An In-Depth Analysis
Understanding the potential drawbacks of market orders is essential for investors aiming to make informed trading decisions. While market orders are popular due to their simplicity and speed, they carry certain risks that can impact investment outcomes. This article explores the disadvantages associated with market orders, recent developments influencing their use, and how investors can navigate these challenges effectively.
What Is a Market Order and How Does It Work?
A market order is an instruction from an investor to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price. This type of order prioritizes execution speed over price certainty, making it ideal for traders who want quick entry or exit positions. When placed, a broker executes the order promptly in most cases, but the actual transaction price may differ from expectations due to fluctuating market conditions.
Market orders are widely used across various financial markets—including stock exchanges, cryptocurrency platforms, and forex—because of their straightforward nature. They eliminate the need for complex decision-making about specific prices but introduce certain risks that traders should be aware of.
Key Disadvantages of Using Market Orders
While convenience is a significant advantage of market orders, several disadvantages warrant careful consideration:
Price Uncertainty
One primary concern with market orders is that they do not guarantee a specific execution price. Instead, they execute at what’s available at that moment in time—often called the "best available" price—which can fluctuate rapidly during volatile periods. As a result, investors might pay more than anticipated when buying or receive less when selling assets unexpectedly.
Liquidity Risks and Slippage
In markets with low liquidity or during times of high volatility—such as economic news releases or geopolitical events—market orders may not fill instantly or may fill at unfavorable prices due to slippage. Slippage occurs when there’s a difference between expected transaction prices and actual execution prices; this risk increases significantly in illiquid assets like small-cap stocks or certain cryptocurrencies.
Execution Delays During Fast-Moving Markets
Although generally executed quickly under normal conditions, fast-moving markets can cause delays in executing large or rapid trades through market orders. These delays might lead traders to miss out on favorable pricing opportunities or incur higher costs if prices move unfavorably before completion.
Impact on Small Markets Due to Large Orders
Large volume trades placed via market orders have the potential to influence asset prices directly—a phenomenon known as "market impact." For example, executing sizable buy/sell transactions in thinly traded securities could push prices upward/downward temporarily until equilibrium restores itself.
Gapping Risks During Extreme Conditions
Gaps happen when asset prices jump sharply between trading sessions without any trades occurring within those ranges—for instance after major news announcements—or during trading halts caused by regulatory issues or technical failures.
Executing a market order amid such gaps often results in unfavorable fills because it does not account for sudden jumps beyond current quotes; this exposes traders further risk especially during unpredictable events like earnings surprises or geopolitical crises.
Recent Developments Affecting Market Order Risks
The landscape surrounding market order usage has evolved considerably over recent years owing primarily to technological advancements and regulatory changes:
Cryptocurrency Volatility: Digital assets such as Bitcoin have experienced unprecedented swings recently—with daily fluctuations sometimes exceeding 10%. Such volatility amplifies risks associated with using simple-market instructions because rapid price changes mean traders could end up paying significantly more than intended—or receiving less if selling quickly.
Regulatory Initiatives: Authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing trading practices aimed at protecting retail investors from adverse outcomes linked with aggressive order types like immediate-or-candomarket executions without sufficient transparency mechanisms.
Technological Innovations: High-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms now execute thousands of transactions per second based on complex strategies—including exploiting minute arbitrage opportunities—that traditional retail-market participants cannot match manually.
These systems contribute both positively by increasing liquidity but also negatively by creating unpredictable short-term volatility which impacts all types of trade executions including standard-market orders.
Investor Education Efforts: Recognizing these complexities has led many financial institutions and regulators toward emphasizing investor education about different order types’ advantages versus their inherent risks—helping individuals understand when alternative strategies such as limit orders might better serve their objectives.
Potential Impacts on Investors and Markets
The disadvantages tied specifically to market orders extend beyond individual trader losses—they also influence broader financial stability:
Investor Losses: Without control over exact pricing points—even if executed swiftly—increased exposure exists during volatile periods where unexpected slippage leads directly into losses.
Market Stability Concerns: Large aggregate use of aggressive ordering strategies can induce short-term instability by causing abrupt shifts in supply-demand dynamics; this raises systemic concerns especially within less liquid markets where single large trades disproportionately affect pricing trends.
Regulatory Responses: To mitigate these issues—and protect retail participants—regulators may impose restrictions such as minimum resting times for certain order types (e.g., limit vs.market), enhanced transparency requirements around trade execution quality—and even ban some high-risk practices altogether depending on evolving circumstances.
How Investors Can Manage Risks Associated With Market Orders
Given these disadvantages—and ongoing developments—it’s crucial for investors not only understand how marketplace dynamics work but also adopt prudent strategies:
Use limit Orders When Possible: Unlike simple-market instructions which accept prevailing quotes automatically—a limit order allows setting maximum purchase price (or minimum sale) thresholds ensuring better control over trade costs amidst volatile environments.
Stay Informed About Market Conditions: Monitoring real-time data feeds helps anticipate periods where rapid fluctuations could adversely affect your intended trade execution strategy.
Diversify Order Types: Combining different approaches based on specific goals—for example employing stop-loss limits alongside traditional entries—can help manage downside risk effectively while maintaining flexibility.
Educate Yourself Continually: Staying updated about technological innovations affecting markets—as well as regulatory changes—is vital for adapting your approach accordingly.
By understanding both the inherent limitations and recent advancements related to market orders—and applying strategic safeguards—you position yourself better against unforeseen adverse outcomes while participating actively across diverse financial landscapes.
This comprehensive overview underscores that while marketplace simplicity makes them attractive tools for quick transactions, awareness about their pitfalls remains essential — particularly amid evolving technology-driven environments shaping modern investing practices today.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
